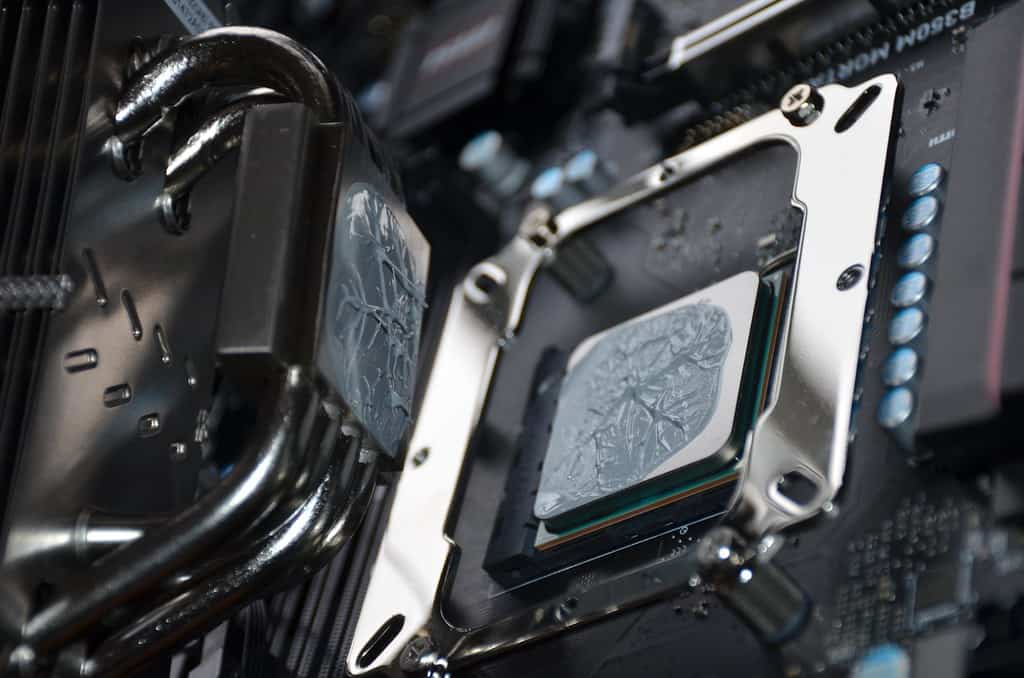
A hot CPU can slow down your computer and damage expensive parts. When processors get too warm, they throttle performance to protect themselves. This creates lag during games and crashes during important work.
The best way to reduce CPU temperature is through better cooling, cleaning dust buildup, and managing system loads effectively. Most temperature problems come from blocked airflow, old thermal paste, or too many programs running at once. Simple fixes often work better than expensive upgrades.
High CPU temperature affects everyone from casual users to hardcore gamers. The good news is that most cooling problems have straightforward solutions. This guide covers proven methods that work for both desktop computers and laptops.
Tips to Reduce CPU Temperature
High CPU temperature can cause performance throttling, system instability, or even hardware damage. Keeping your CPU cool ensures optimal performance and longevity. This step-by-step guide will help you reduce your CPU temperature effectively.
Step 1: Monitor Your CPU Temperature
Before making changes, check your current CPU temperature using tools like:
- HWMonitor
- Core Temp
- Speccy
- Built-in system tools or BIOS/UEFI monitoring
Aim to keep your CPU temperature below 80°C under load for most processors.
Step 2: Improve Airflow Inside Your PC Case
- Clean Dust: Dust buildup blocks airflow and insulates heat. Use compressed air to clean fans, vents, and heatsinks.
- Organize Cables: Tidy cables to avoid obstructing airflow.
- Add/Upgrade Fans: Install additional case fans or replace old ones with high-quality, quiet fans.
- Check Fan Direction: Ensure fans are positioned correctly for optimal airflow (intake at front/bottom, exhaust at rear/top).
Step 3: Reapply or Upgrade Thermal Paste
Thermal paste transfers heat from the CPU to the cooler. Over time, it can dry out:
- Remove the old thermal paste carefully.
- Apply a fresh, high-quality thermal paste in a pea-sized amount.
- Reattach the CPU cooler securely.
Step 4: Upgrade or Clean Your CPU Cooler
- Stock Cooler: Consider upgrading to a better air cooler or liquid cooling system.
- Liquid Cooling: AIO (All-in-One) liquid coolers can significantly reduce temperatures.
- Check Cooler Installation: Ensure the cooler is properly seated and making full contact with the CPU.
Step 5: Adjust System Settings
- Change Power Plan: Use Windows Power Plan settings to reduce maximum processor state, which lowers heat generation.
- Enable System Cooling Policy: Set to “Active” in Windows power options to increase fan speed proactively.
- Update BIOS/Firmware: Sometimes updates improve thermal management.
Step 6: Manage Background Processes
- Close unnecessary applications and background processes that cause high CPU usage.
- Use Task Manager or performance monitoring tools to identify CPU-heavy processes.
Step 7: Consider Undervolting or Underclocking (Advanced)
- Use software like Intel XTU or AMD Ryzen Master to reduce CPU voltage or clock speeds.
- This lowers heat output without significant performance loss but requires caution.
Step 8: Maintain a Cool Environment
- Keep your PC in a well-ventilated area.
- Avoid placing the PC near heat sources or inside enclosed spaces.
- Use external cooling solutions like laptop cooling pads if applicable.
Summary
By monitoring temperatures, improving airflow, maintaining your cooling system, and optimizing settings, you can effectively reduce your CPU temperature and keep your PC running smoothly.
Key Takeaways
- Clean dust from fans and components to restore proper airflow and cooling performance
- Replace old thermal paste between the CPU and cooler to improve heat transfer
- Monitor CPU usage and close unnecessary programs to reduce processor workload
Frequently Asked Questions
These common questions address proper thermal paste application, airflow optimization, temperature control during demanding tasks, undervolting benefits, BIOS adjustments, and laptop cooling strategies.
What are the steps to properly apply thermal paste to lower CPU temperatures?
Clean the old thermal paste from both the CPU and heatsink using alcohol pads. Let both surfaces dry completely before applying new paste.
Apply a small rice-grain sized amount of thermal paste to the center of the CPU. The paste will spread naturally when the heatsink is installed.
Mount the heatsink with even pressure to distribute the paste. Avoid removing and reseating the heatsink as this creates air bubbles.
Replace thermal paste every 2-4 years as it dries out over time. Old paste loses its heat transfer ability and causes higher temperatures.
How can I optimize my cooling system’s airflow to reduce my CPU’s heat?
Position intake fans at the front or bottom of the case to bring cool air inside. Place exhaust fans at the rear and top to remove hot air.
Keep wires away from fans to prevent airflow blockage. Secure cables with ties to maintain clear air paths throughout the case.
Clean dust from fans and components regularly using compressed air. Dust buildup reduces airflow and traps heat inside components.
Place the computer case in an open area with good ventilation. Avoid cramped spaces that restrict air movement around the case.
What techniques can I use to regulate my CPU’s temperature during high-performance tasks like gaming?
Take breaks during long gaming sessions to let the CPU cool down. Rest the system for 30 minutes after 2-3 hours of heavy use.
Close unnecessary programs before gaming to reduce CPU workload. Disable startup apps that consume processing power in the background.
Monitor CPU temperature during gaming using software tools. Stop gaming if temperatures exceed 80°C to prevent damage.
Consider liquid cooling systems for consistent heavy gaming. Water coolers handle high heat loads better than basic air coolers.
In what ways can undervolting the CPU contribute to temperature management?
Undervolting reduces the voltage supplied to the CPU while maintaining performance. Lower voltage means less heat generation during operation.
Use Intel Extreme Tuning Utility for Intel CPUs or Ryzen Master for AMD processors. Start with small voltage reductions like -0.020V.
Test stability after each voltage adjustment using stress tests. Find the lowest stable voltage through gradual decreases.
Save the settings once you find the optimal undervolt level. Most CPUs can handle -125mV to -140mV safely.
Can adjusting settings in BIOS effectively decrease CPU temperature, and how is it done?
Access BIOS by pressing Delete or F2 during startup. Look for fan speed control settings in the hardware or power sections.
Increase fan speeds to improve cooling performance. Higher fan speeds move more air but create more noise.
Disable hyperthreading if temperatures remain high during gaming. This limits each CPU core to one task at a time.
Set processor maximum frequency limits to reduce heat generation. Lower clock speeds produce less heat but may affect performance.
What are the best practices for maintaining a cool CPU temperature when using a laptop?
Use a laptop cooling pad to improve airflow underneath the device. External fans help remove heat from the laptop’s base.
Clean laptop vents regularly to prevent dust accumulation. Blocked vents cause rapid overheating in compact laptop designs.
Avoid placing laptops on soft surfaces like beds or couches. These surfaces block air vents and trap heat around the device.
Consider external cooling solutions for gaming laptops. High-performance laptops generate more heat than standard cooling can handle.