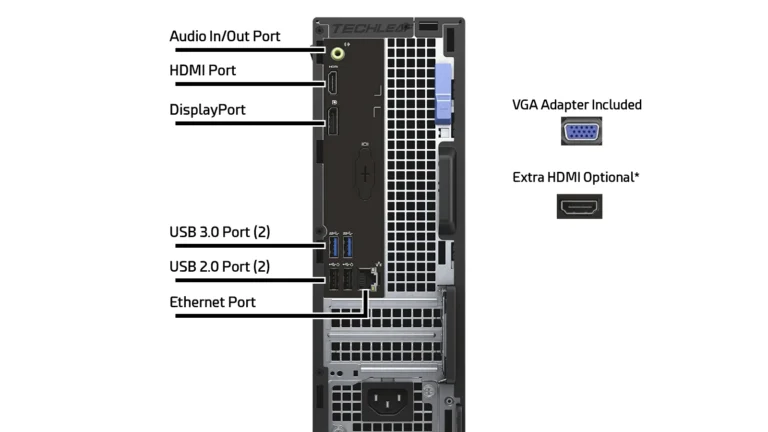
If your computer won’t turn on, it can disrupt your entire day. This issue can be caused by various things, from simple power problems to complex hardware failures. First, check if the power cable is connected and if the outlet is working. These simple solutions can often solve the problem. If not, you’ll need to do further troubleshooting. Check the computer’s hardware components like the motherboard, power supply, and connected devices to pinpoint the cause of the failure. By being careful and methodical, you can often find and fix the issue.
Troubleshooting Power Issues
If your computer steadfastly refuses to turn on, don’t despair yet. Before resorting to professional tech support, there are a few easy troubleshooting steps you can take at home.
Check the Basics
- Is it plugged in? Ensure both ends of the power cord are securely plugged into both the computer’s power supply and the wall outlet.
- Test the Outlet: Check if the outlet has power by plugging in another device (like a lamp or phone charger).
- Power Strip Woes: If using a power strip or surge protector, ensure it’s turned on and functioning. Test your computer by plugging it directly into the wall.
Digging Deeper
If the basics check out, here’s what to examine next:
| Component | What to Look For | Possible Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply Unit (PSU) | Listen for any abnormal sounds (clicking, buzzing) coming from the PSU. Unusual smells (burning) may also point to a faulty power supply | If the PSU appears faulty, it may need replacement. Important: Do not attempt to open or repair a PSU yourself |
| Monitor Connection | Verify the monitor is plugged in, turned on, and connected to the right port on your computer | Try a different monitor or cable |
| Internal Connections | If you recently worked inside your computer, double-check that all cables and components are properly connected and seated | Consult your computer’s manual for guidance on internal connections |
Advanced Troubleshooting
Should the above steps fail, consider these slightly more advanced approaches:
Remove Peripherals
Unplug any non-essential devices (USB drives, printers, etc.) and try rebooting. Occasionally a faulty external device can prevent your computer from powering on.
Restart in Safe Mode
Safe Mode starts your computer with minimal drivers. If your computer turns on in Safe Mode, it may point to a software or driver issue. Instructions for entering Safe Mode vary depending on your operating system.
Let me know if you’d like more details on the advanced troubleshooting options!
Key Takeaways
- Initial checks include verifying power connections and outlet functionality.
- Further troubleshooting requires inspecting internal hardware components.
- A methodical approach is essential for identifying and resolving startup issues.
Preliminary Checks
Before attempting to resolve any computer issues, it is essential to conduct basic but critical preliminary checks. These checks can often solve the most common reasons a computer won’t start.
Inspecting Physical Connections
First, ensure all cables connected to your computer are firmly in place. This includes the power cord, data cables, and any peripherals. For desktops, check the connection at the back of the case where the power cord meets the power supply. For laptops, verify that the battery is inserted correctly and that the power adapter is connected securely at both the outlet and the laptop.
Power Supply and Outlet Testing
Test the outlet where your computer is plugged in to make sure it’s providing power. You can use a different device to test the outlet. If you’re using a power strip or surge protector, test it with another device or try a different power source. For laptops, check if the battery has a charge and if it doesn’t, try charging with a different power adapter if possible.
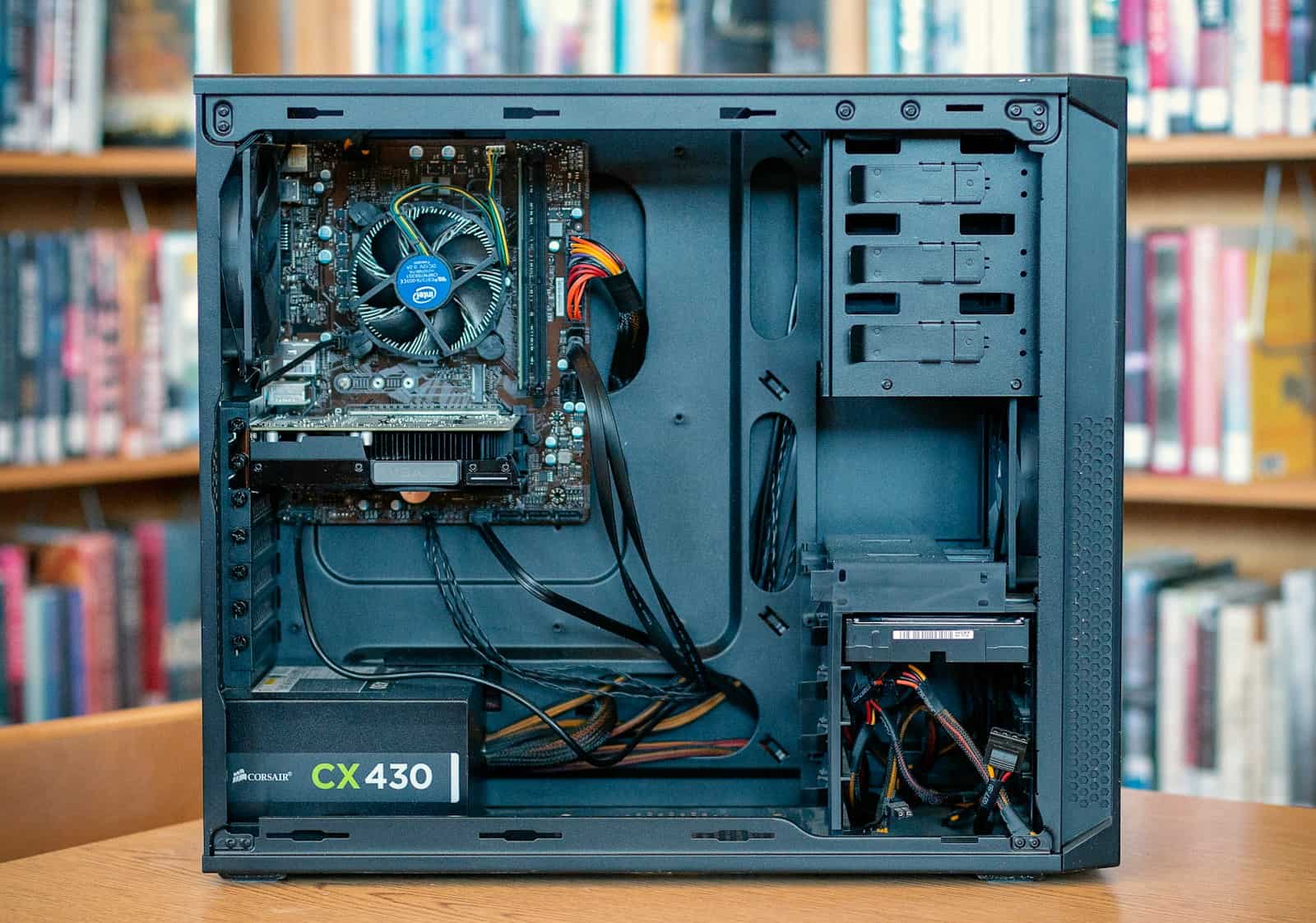
Hardware Component Verification
Open the case of your desktop to check the internal hardware. The RAM sticks should be securely slotted in. Loose RAM can prevent a computer from starting. If you hear any beep codes when you turn on the PC, they can indicate specific hardware issues. Beep codes vary by motherboard manufacturer, so consult your manual or support site for decoding them. If you’re using a UPS, confirm that it’s working and passing power to your computer efficiently.
Advanced Troubleshooting
When a computer won’t start, advanced troubleshooting is a vital step to diagnose the underlying issues. This section focuses on analyzing the boot process, exploring operating system recovery options, and performing hardware diagnostics and replacement.
System Boot Process Analysis
The boot process involves several checks and procedures your computer goes through before starting up. First, listen for beeps from the motherboard at startup. Beep codes can signal specific problems that need fixing. For example, a series of short beeps typically points to a memory issue. Check your computer’s manual or the motherboard manufacturer’s website for what these codes mean. If there are no beeps and the system still won’t turn on, the power supply could be faulty.
Operating System Recovery Options
Windows PCs have built-in recovery options that can help fix startup issues. To access these, press the special boot options key repeatedly after turning on your PC. This key is often F8 or F11. Once in the recovery menu, you can select “Windows Startup Repair” to automatically fix boot problems. If your computer faces ransomware or other malware issues, you might need to run anti-malware software from a safe environment, which you can also access through these options.
Hardware Diagnostics and Replacement
A non-starting computer can be a sign of overheating, which is often caused by dust or a failed fan. Open the computer case, disconnect the power supply, and visually inspect for dust or damage. Clean out dust using a can of compressed air. If you find a damaged component, such as a video or sound card, it might need replacing. For more serious hardware issues, like a bad processor or motherboard, you may need to consult with a professional or consider whether it’s time to replace the entire system.
Frequently Asked Questions
When facing issues with a computer that won’t turn on, it’s essential to perform some basic checks. This section answers common queries related to various start-up issues.
What steps should be taken if the power button is pressed but the computer shows no signs of starting?
First, ensure the power cord and battery are properly connected. Check that the outlet and power strip work by using a different device.
How to troubleshoot a computer that won’t boot despite the power light being on?
Try a hard reboot by holding down the power button for about 10 seconds. If this doesn’t work, it could be an issue with the display, so verify that the monitor is on and the brightness is adjusted properly.
What to do when a computer doesn’t start after an extended period of being powered off?
Examine the power supply and press the power button for about 30 seconds to drain any residual power. Plug it back in and try to turn it on. If it doesn’t start, it may require professional inspection.
What can be done if a computer is plugged in but remains unresponsive?
Confirm that all cables are secure and that the power source is working. If the system is still unresponsive, consider checking for faulty cables or a defective power supply.
How do you diagnose a PC that won’t turn on with no signs of power?
Inspect the outlet and power cord for any issues. Test other devices in the same outlet to rule out a power problem. If the outlet works but the PC doesn’t, the power supply unit may be the issue.
What are common solutions when a computer won’t boot up, although the fans and lights appear to be working?
Disconnect non-essential peripherals, such as USB devices, and try to boot the computer. If it starts, connect devices one at a time to identify the problem component. If this solution doesn’t apply, the issue may lie within the internal hardware which would require a professional’s help.