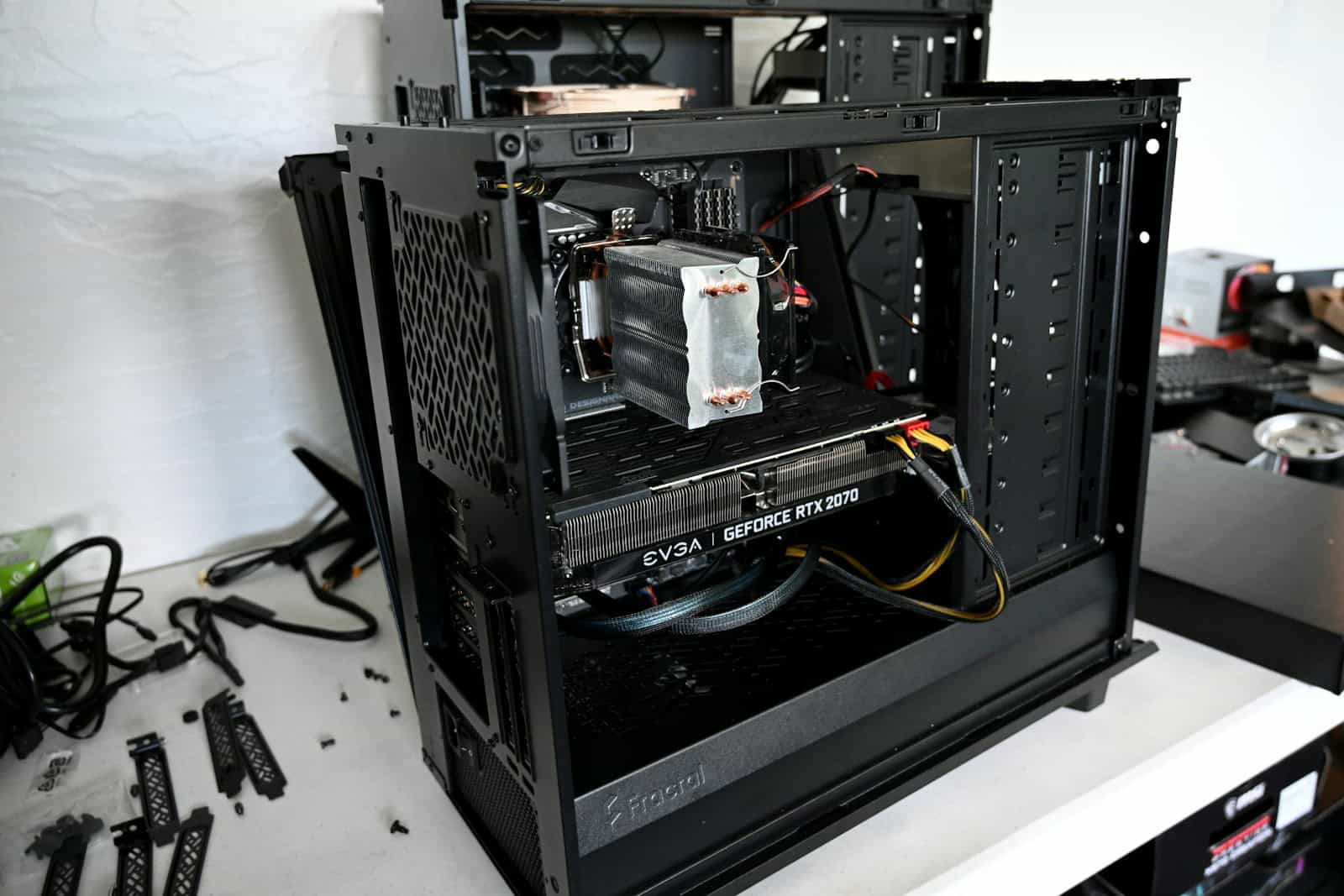
When a computer starts crashing, freezing, or refusing to power on, the cause often comes down to hardware. Components like the CPU, RAM, hard drive, SSD, motherboard, or power supply can fail over time or from stress. Knowing the signs of common computer hardware problems and how to fix them saves time, money, and frustration.
Simple checks often solve the issue. Loose RAM can cause random crashes, overheating can shut down a system, and a failing hard drive may slow everything down. Replacing faulty parts or upgrading to more reliable options like SSDs often restores performance quickly.
By learning how to spot symptoms and apply practical fixes, anyone can handle many hardware failures without guesswork. This guide explains the most frequent problems and gives clear steps to get a computer running again.
1. Computer Won’t Power On
Symptoms: No lights, no fan noise, no display.
Causes: Faulty power supply, loose cables, dead battery (laptops).
Fixes:
- Check if the power cable and outlet are working.
- For desktops: reseat or replace the power supply unit (PSU).
- For laptops: try a different charger or remove and reinsert the battery.
- Test with another wall socket or surge protector.
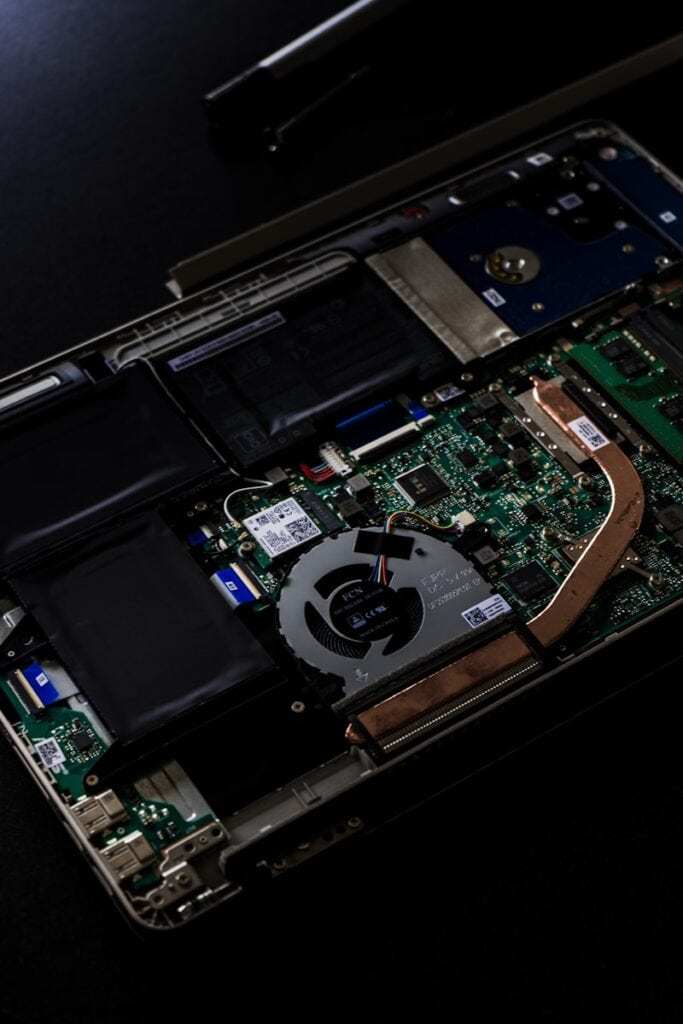

2. Overheating
Symptoms: Fans running loudly, system shutting down unexpectedly, hot case.
Causes: Dust buildup, poor ventilation, failing cooling system.
Fixes:
- Clean dust from fans, vents, and heatsinks using compressed air.
- Ensure the computer is placed on a hard surface with good airflow.
- Reapply thermal paste to the CPU if overheating persists.
- Replace faulty fans.
3. Slow Performance
Symptoms: Lagging applications, long boot times, unresponsive system.
Causes: Insufficient RAM, failing hard drive, overheating, or too many background processes.
Fixes:
- Upgrade RAM or switch to SSD storage.
- Run disk cleanup and defragmentation (HDD only).
- Check for overheating and clean the system.
- Disable unnecessary startup programs.
4. Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
Symptoms: Windows crashes with a blue error screen.
Causes: Faulty RAM, driver conflicts, overheating, or hardware failure.
Fixes:
- Note the error code on the BSOD.
- Update or roll back drivers.
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic to check RAM.
- Ensure cooling is adequate.
- Replace failing hardware if errors persist.
5. No Display / Monitor Issues
Symptoms: Computer powers on but screen is blank.
Causes: Loose cables, faulty graphics card, bad RAM.
Fixes:
- Check monitor power and cable connections.
- Test with another monitor or cable.
- Reseat or replace the graphics card.
- Reseat RAM sticks.
6. Beeping Sounds on Startup
Symptoms: PC beeps but doesn’t boot.
Causes: BIOS error codes for hardware failure (RAM, GPU, motherboard).
Fixes:
- Count the beeps and check the motherboard manual for error codes.
- Reseat RAM and GPU.
- Replace faulty components as indicated by the beep code.
7. Hard Drive Failure
Symptoms: Clicking noises, frequent crashes, slow file access, missing files.
Causes: Mechanical wear, corrupted sectors.
Fixes:
- Back up data immediately.
- Run disk check tools (CHKDSK on Windows, Disk Utility on Mac).
- Replace the drive with a new HDD or SSD.
8. Keyboard or Mouse Not Working
Symptoms: Input devices unresponsive.
Causes: Loose connections, driver issues, faulty peripherals.
Fixes:
- Try different USB ports.
- Test the device on another computer.
- Update or reinstall drivers.
- Replace the device if it’s defective.
9. Strange Noises
Symptoms: Grinding, clicking, or whirring sounds.
Causes: Failing hard drive, broken fans, or loose components.
Fixes:
- Identify the source of the noise.
- Replace failing fans or hard drives.
- Tighten loose screws inside the case.
10. USB Devices Not Recognized
Symptoms: USB devices not detected or malfunctioning.
Causes: Faulty ports, driver issues, or device failure.
Fixes:
- Plug into another USB port.
- Restart the computer.
- Update USB drivers.
- Test the device on another system.
Final Tips for Troubleshooting Hardware
- Start simple: check cables, connections, and power sources first.
- Listen and watch: noises, lights, and error codes often reveal the issue.
- Keep it clean: dust and heat are silent killers of hardware.
- Back up often: hardware can fail unexpectedly, so protect your data.
✅ By learning to identify and fix these common issues, you can extend the life of your computer, save money, and avoid downtime.
Key Takeaways
- Common hardware problems often have clear symptoms
- Simple fixes or part replacements solve most issues
- Knowing what to check first prevents wasted effort
Hardware problems are among the most frustrating computer issues, but many can be diagnosed and resolved without professional help. Below is a guide to the most common hardware problems, their symptoms, and step-by-step solutions.
Computer Hardware Troubleshooting Checklist
Before You Start
- Unplug and discharge: Always power down and unplug before opening the case.
- Ground yourself: Use an anti-static wrist strap or touch metal to avoid static damage.
- Check warranty: Opening your device may void it—verify first.
Step 1: Initial Checks
- Confirm power LED indicators (on motherboard, PSU, or laptop charging light).
- Test with a different power strip or adapter to rule out faulty surge protectors.
- Listen for POST sounds (beeps) or check diagnostic LEDs on modern motherboards.
Step 2: Quick Fixes
- Swap out RAM sticks one at a time to identify faulty modules.
- Boot into BIOS/UEFI to confirm hardware is detected (CPU, RAM, drives).
- Try Safe Mode (Windows) or Recovery Mode (Mac/Linux) to rule out software conflicts.
Step 3: Isolate the Problem
- Disconnect all non-essential peripherals (USB drives, printers, external HDDs).
- Use a bootable USB drive (with Linux or diagnostic tools) to test hardware independently of your OS.
- Run SMART tests for hard drives/SSDs to check health status.
Step 4: Prevent Recurrence
- Keep firmware (BIOS/UEFI) and drivers updated.
- Replace CMOS battery if your PC forgets time/date or BIOS settings.
- Use a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to protect against power surges.
- Schedule regular dust cleaning every 3–6 months.
✅ Pro tip: Keep a small kit with spare cables, thermal paste, and a known-good PSU or RAM stick—these are lifesavers for quick diagnostics.
Frequently Asked Questions
Computer hardware problems often show up as startup failures, overheating, sudden crashes, poor connections, or storage errors. Knowing the signs and applying simple checks can help identify faulty parts and keep a system running.
What steps can I take to diagnose and fix a computer that won’t start?
Check the power source first. Confirm the outlet, power cable, and switch are working.
If the system still does not start, inspect the power supply unit and motherboard connections. Remove non-essential devices like USB drives or external hardware to rule out conflicts.
If fans spin but no display appears, reseat the RAM and graphics card. A failed power supply or motherboard may require replacement.
How can I resolve overheating issues in my desktop or laptop?
Clean dust from fans, vents, and heatsinks with compressed air. Blocked airflow is the most common cause of overheating.
Place the computer in a well-ventilated area. Avoid soft surfaces that block vents.
Reapply thermal paste if the CPU or GPU runs hot. Consider adding case fans or using a cooling pad for laptops.
What should I do if I’m experiencing random computer crashes or blue screens?
Run built-in diagnostic tools like Windows Memory Diagnostic to test RAM. Faulty memory often causes crashes and blue screens.
Update drivers, especially for graphics and chipset hardware. Outdated or corrupted drivers can trigger instability.
If crashes continue, test components one at a time. Remove or replace RAM sticks, check the hard drive with disk utilities, and ensure the power supply is stable.
How can I troubleshoot and fix hardware connectivity issues?
Check all cables for secure connections. Loose or damaged cables often cause devices to fail.
Test ports with different devices. If one port fails but others work, the port may be damaged.
For network issues, restart the router and modem. Update firmware and drivers for network adapters.
What are the common signs of a failing hard drive and how can I address them?
Warning signs include slow file access, frequent system errors, and clicking or grinding noises.
Use built-in tools like Check Disk on Windows or Disk Utility on macOS to scan for bad sectors. Back up important data immediately.
If the drive shows physical failure, replace it. Use data recovery services only if the data is critical.
How do I identify and replace faulty RAM in my computer?
Frequent crashes, freezing, or blue screens often point to bad RAM. Run memory tests to confirm errors.
To locate the faulty stick, test each module one at a time. Remove all but one and boot the system, repeating until the bad module is found.
Replace the defective RAM with compatible modules. Check the motherboard’s specifications for supported type and capacity.