Your computer’s brain, the CPU, handles every task from opening files to running games. When it starts acting up, your entire system suffers from crashes, slowdowns, and frustrating freezes. Most CPU problems stem from overheating, outdated drivers, or software conflicts that users can fix with simple troubleshooting steps.
The CPU rarely fails completely, but small issues can make your computer feel broken. High temperatures from dust buildup cause sudden shutdowns. Background programs eat up processing power. Old drivers create conflicts that crash your system.
Quick fixes solve most CPU troubles without expensive repairs. Cleaning fans removes heat problems. Updating software stops conflicts. Checking task manager shows which programs slow things down. These simple steps get most computers running smoothly again.

Troubleshooting Common CPU Issues
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the heart of your computer, managing all instructions and operations. When CPU issues arise, they can severely impact your system’s performance or cause crashes. This expert guide walks you through common CPU problems and quick fixes to get your computer back on track.
Common CPU Issues and Their Symptoms
- Overheating: System shuts down unexpectedly or runs very hot.
- High CPU Usage: Slow performance, fan running loudly, or system lagging.
- CPU Not Detected: BIOS or system fails to recognize the CPU.
- System Crashes/BSOD: Blue screen errors or random restarts.
- CPU Throttling: Reduced performance due to thermal or power limitations.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting and Fixes
1. Check for Overheating
- Symptoms: Sudden shutdowns, loud fan noise, thermal warnings.
- Fixes:
- Clean dust from CPU heatsink and fans.
- Reapply thermal paste between CPU and cooler.
- Ensure proper airflow inside the case.
- Use monitoring tools like HWMonitor or Core Temp to check temperatures.
- Upgrade cooling solution if necessary.
2. Monitor and Manage High CPU Usage
- Symptoms: Slow system, unresponsive applications.
- Fixes:
- Open Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac) to identify processes with high CPU usage.
- Close or uninstall unnecessary programs.
- Scan for malware or viruses using trusted antivirus software.
- Update drivers, especially chipset and CPU drivers.
- Adjust power settings to balanced or high performance.
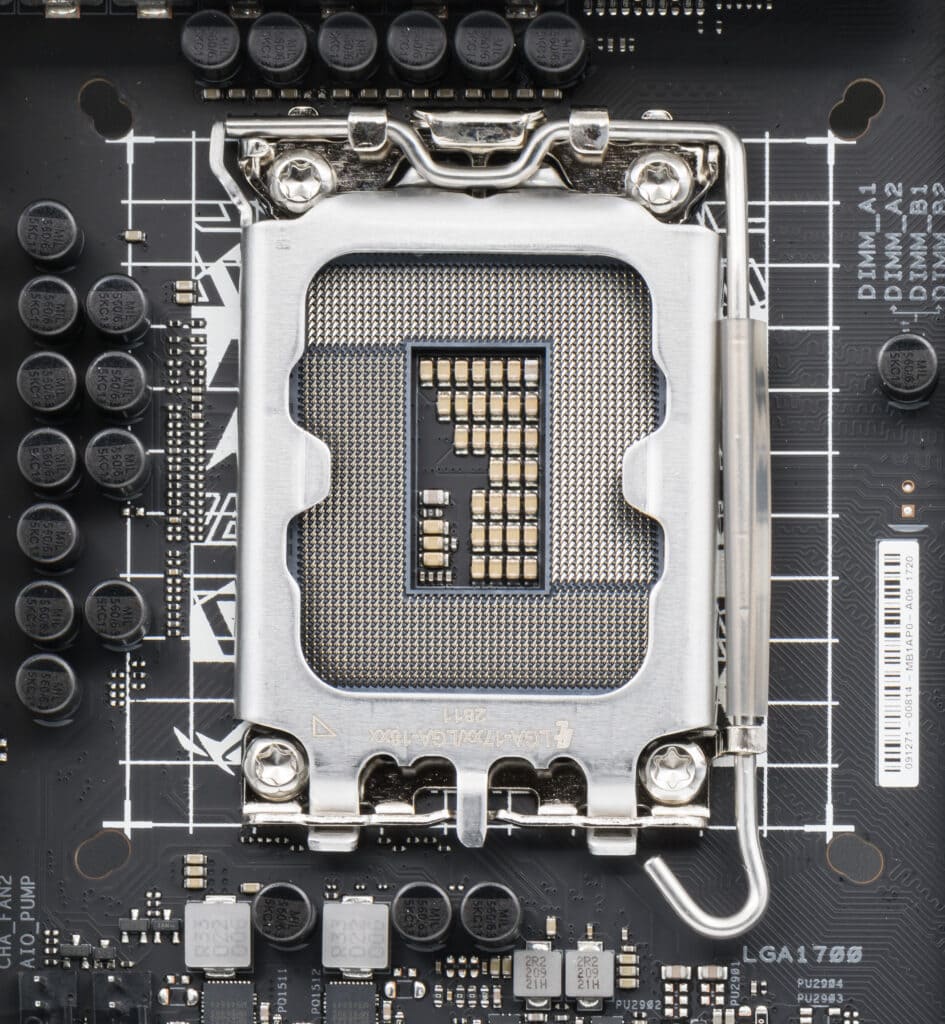
3. Verify CPU Detection in BIOS
- Symptoms: System won’t boot or doesn’t recognize CPU.
- Fixes:
- Enter BIOS/UEFI setup during boot (usually by pressing Del, F2, or F10).
- Check CPU information section to confirm detection.
- Reset BIOS to default settings.
- Update BIOS firmware to the latest version.
- Reseat the CPU carefully if comfortable doing so.
4. Resolve System Crashes and Blue Screens
- Symptoms: Blue screen errors, random restarts.
- Fixes:
- Note error codes on BSOD to identify issues.
- Run system diagnostics or memory tests.
- Update all drivers and Windows/macOS.
- Check for overheating.
- Test CPU stability with stress-testing tools like Prime95.
5. Address CPU Throttling Issues
- Symptoms: CPU clock speed drops under load, poor performance.
- Fixes:
- Check thermal status; overheating often causes throttling.
- Adjust power management settings.
- Disable CPU power-saving features temporarily to test.
- Ensure proper cooling.
Tools for CPU Troubleshooting
- HWMonitor: Monitors temperatures and voltages.
- Intel Processor Diagnostic Tool: Tests Intel CPUs for hardware faults.
- Prime95: Stress-tests CPU stability.
- Task Manager / Activity Monitor: Identify resource-heavy processes.
- Malwarebytes: Scans and removes malware.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve tried the above steps and CPU issues persist, or if you’re uncomfortable opening your PC, seek expert support. Hardware faults may require professional diagnosis or CPU replacement.
Key Takeaways
- Overheating from dust buildup causes most CPU problems like crashes and slowdowns
- Task manager helps identify programs using too much CPU power
- Simple maintenance like cleaning fans and updating drivers fixes most issues
Frequently Asked Questions
CPU problems can cause system crashes, slow performance, and boot failures. These common issues often stem from overheating, hardware conflicts, or compatibility problems that need specific troubleshooting steps.
What are the typical symptoms of CPU-related problems?
System crashes and unexpected shutdowns are the most common signs of CPU trouble. The computer may freeze during normal use or shut down without warning.
Blue screen errors appear when the CPU cannot process instructions properly. These screens show error codes that help identify the problem.
Slow performance happens when the CPU struggles to handle basic tasks. Programs take longer to open and respond slowly to commands.
Overheating causes the system to run loud fans constantly. The computer feels hot to touch and may throttle performance to cool down.
Boot problems occur when the CPU fails to start the system. The computer powers on but shows no display or gets stuck on startup screens.
How can one diagnose the cause of a CPU failure?
Check the Task Manager to see CPU usage levels. High usage with no programs running suggests a problem with background processes or malware.
Monitor CPU temperature using software tools. Temperatures above 80°C during normal use indicate overheating issues that need attention.
Listen for beep codes during startup. Different beep patterns tell you about specific hardware problems with the CPU or motherboard.
Look for error messages on startup screens. These messages often point to CPU detection problems or compatibility issues.
Test the CPU in another compatible system if possible. This helps confirm whether the CPU itself has failed or if other components cause the problem.
What steps can be taken to resolve overheating in a CPU?
Clean dust from the CPU fan and heatsink using compressed air. Dust blocks airflow and traps heat around the processor.
Remove old thermal paste and apply fresh paste between the CPU and heatsink. Old paste dries out and loses its ability to transfer heat.
Check that the CPU fan spins freely and connects properly to the motherboard. Replace the fan if it makes noise or spins slowly.
Improve case airflow by adding more fans or repositioning existing ones. Hot air needs to flow out while cool air flows in.
Lower CPU usage by closing unnecessary programs. High workloads generate more heat than the cooling system can handle.
Which tools are recommended for CPU troubleshooting and monitoring?
HWMonitor shows real-time CPU temperature and voltage readings. This free tool helps track overheating problems during different tasks.
Task Manager displays CPU usage and identifies programs that consume too much processing power. Access it by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
CPU-Z provides detailed information about the processor model, speed, and specifications. Use it to verify CPU compatibility with the motherboard.
Intel Processor Diagnostic Tool tests Intel CPUs for hardware failures. AMD has similar diagnostic software for their processors.
Performance Monitor tracks system resources over time. This Windows tool creates detailed reports about CPU performance patterns.
How can you identify and solve CPU compatibility issues with your motherboard?
Check the motherboard manual for supported CPU models and socket types. The CPU must match the exact socket on the motherboard.
Update the BIOS to the latest version before installing a new CPU. Newer processors often need updated BIOS files to work properly.
Verify power requirements for the new CPU. Some processors need more power than the motherboard or power supply can provide.
Compare CPU specifications with motherboard limits. Check maximum supported speed, core count, and thermal design power ratings.
Use manufacturer websites to confirm compatibility between specific CPU and motherboard models. They maintain updated compatibility lists.
What should be done if a CPU is not detected or fails to start during boot-up?
Reseat the CPU by removing it and placing it back in the socket carefully. Make sure all pins align properly and the retention mechanism locks.
Check for bent or damaged pins on the CPU or socket. Even small damage can prevent proper electrical contact.
Clear the CMOS by removing the motherboard battery for 10 minutes. This resets BIOS settings that might prevent CPU detection.
Test with minimal components by removing all unnecessary hardware. Keep only the CPU, one RAM stick, and power connections.
Update or reset BIOS settings to default values. Incorrect settings can prevent the system from recognizing the CPU properly.