Subscription-based services have revolutionized the way people consume products and experiences, fueling what is now known as the subscription economy. Instead of making one-off purchases, customers pay a recurring fee—monthly, quarterly, or annually—for ongoing access to goods and services. This approach appeals to modern consumers who value convenience, personalization, and flexibility, while also relieving them of the need to make repeated buying decisions.
For businesses, the model delivers predictable revenue streams, deeper customer relationships, and opportunities to scale through loyalty-driven growth. Today, subscription services span nearly every industry—from streaming platforms and software to meal kits, fitness programs, and curated subscription boxes—reshaping not only consumer behavior but also entire markets. Successfully running a subscription business requires more than just recurring billing; it demands insight into customer preferences, consistent delivery of value, and a seamless user experience that keeps subscribers engaged over time.
1. Definition
A subscription-based service is a business model where customers pay a recurring fee—weekly, monthly, or annually—to access a product or service. Instead of making a one-time purchase, users “subscribe” and continue to receive value for as long as they keep paying.
This model has become common across industries like software, entertainment, fitness, food delivery, and even physical goods (e.g., subscription boxes).
2. How Subscription Services Work
- Sign-up – Customers register and choose a plan.
- Recurring payment – Payments are automatically billed at regular intervals.
- Access/Delivery – Customers gain ongoing access to the service or receive regular product deliveries.
- Renewal or cancellation – Subscriptions continue until the customer cancels.
3. Examples of Subscription-Based Services
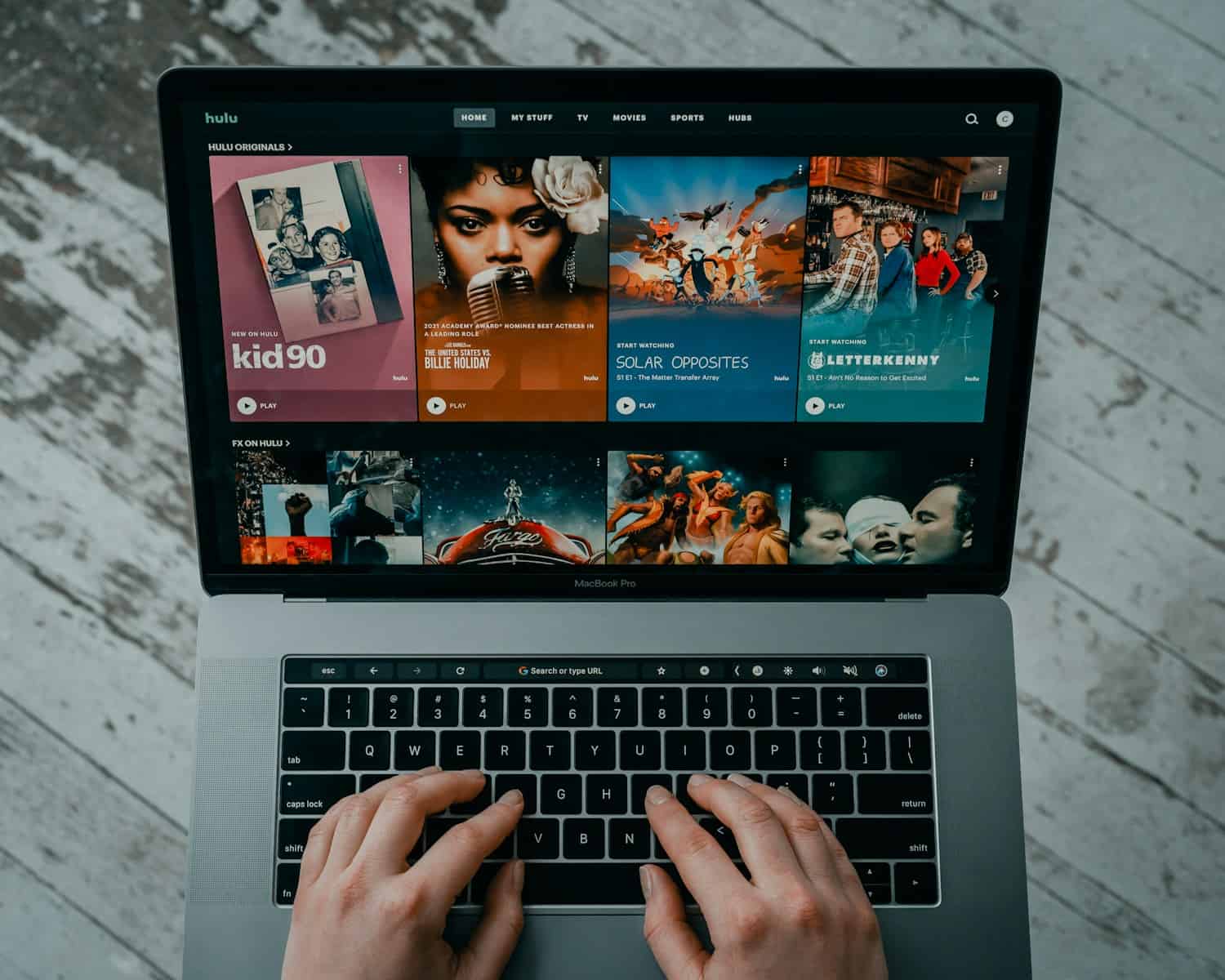
- Streaming platforms (Netflix, Spotify, Disney+)
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) tools (Microsoft 365, Adobe Creative Cloud)
- Subscription boxes (Birchbox, HelloFresh, Dollar Shave Club)
- Fitness & wellness apps (Peloton, Calm)
- News & digital content (The New York Times, Substack newsletters)
4. Advantages
For businesses:
- Predictable recurring revenue
- Stronger customer relationships
- Easier to upsell or cross-sell
- Scalable growth
For customers:
- Convenience (automatic renewals, no need to repurchase)
- Lower upfront cost compared to buying outright
- Continuous updates or fresh content/products
- Flexibility to cancel or change plans
5. Disadvantages
For businesses:
- High churn risk (customers canceling)
- Ongoing pressure to deliver consistent value
- Complex billing and customer support needs
For customers:
- Subscription fatigue (too many ongoing charges)
- Long-term cost may exceed one-time purchase
- Auto-renewals can feel restrictive if not transparent
6. Why They’re Popular Today
The rise of the subscription economy is driven by digital transformation and consumer preference for access over ownership. Customers want flexibility, personalization, and convenience—while businesses benefit from steady cash flow and deeper engagement (source: Startup Mindset, Profolus).
✅ In short: Subscription-based services are a win-win model when managed well—customers enjoy ongoing value, while businesses gain predictable revenue and loyalty.
Everything You Need to Know About Subscription Services
Subscription-based services replace the traditional point-of-sale model with recurring payments for access to a product or service. This model is popping up across a multitude of industries and can offer a wealth of benefits!
How Subscription Services Work
At their core, subscription services rely on a few core elements:
- Recurring Billing: You pay a set fee regularly (i.e., monthly, annually).
- Customer Contract: Subscriptions involve an agreement. The customer gets the product/service, and the business gets consistent revenue.
- Option to Renew or Cancel: Most subscriptions offer flexibility for the customer to decide if they want to continue.
Common Subscription Types
Subscription models differ across industries, but here are some widespread examples:
| Service Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Streaming | Netflix, Hulu, Disney+, Spotify |
| Box Services | Dollar Shave Club, HelloFresh, BarkBox |
| Software | Adobe Creative Cloud, Microsoft 365, Grammarly |
| Memberships | Costco, Amazon Prime, Gym Memberships |
Benefits of Subscriptions
For businesses, subscription models offer:
- Predictable Revenue Streams: Easier forecasting and financial stability.
- Stronger Customer Relationships: Ongoing engagement fosters loyalty.
For customers, benefits include:
- Convenience: Auto-delivery and streamlined access.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Subscriptions may be cheaper than one-time purchases.
- Flexibility: Many subscriptions offer plans and cancellation options.
Key Takeaways
- Subscription services offer ongoing access to products or services for a recurring fee.
- Convenience and simplicity are central to the subscription model’s appeal to consumers.
- Effective management of subscription businesses hinges on understanding and meeting customer needs.
Fundamentals of Subscription-Based Services
Subscription-based services hinge on repeat business. Clients pay regularly to access a product or service.
Defining the Subscription Model
A subscription model is a business strategy. Customers pay a set fee at regular times. They get ongoing access to a product or service. This approach helps with steady income for companies.
History and Evolution
Subscription services began with books and magazines. Now, they include streaming and software as a service (SaaS). Over time, they’ve become more diverse. Subscription boxes and digital media are recent additions.
Types of Subscription Services
Subscriptions fall into various groups. Streaming services, like movies and music, are well-known. Magazine subscriptions have been around for longer. SaaS provides software over the internet. Subscription boxes offer assortments of products. Each of these models has a role in modern business.
Managing Subscription Businesses
In subscription businesses, the focus lies on establishing solid customer relationships and ensuring a smooth customer experience. This is essential for maintaining steady revenue growth and keeping churn rates low.
Building Customer Relationships
Subscription business success depends on strong customer relationships. Clear communication is vital. It creates a foundation of trust. Businesses must listen to their customers and act on feedback promptly.
Strategies for Retention and Growth
To retain customers and grow revenue, companies employ various strategies. Offering flexible pricing tiers and customizing services to meet customer needs are common practices. Regular updates and added value through new features also play a vital role in retaining customers.
Key Metrics and Revenue Streams
The main metrics for subscription businesses include customer retention rates and recurring revenue. Analyzing these figures helps businesses understand their financial health. Subscription revenue models provide predictable revenue which aids in planning and stability.
Challenges and Risks
Managing a subscription business presents challenges such as customer churn and increased competition. Companies must ensure their offerings remain relevant and valuable to prevent loss of subscribers. Regular market analysis helps identify risks early on.
Frequently Asked Questions
This part of the article covers common queries about subscription-based services.
What differentiates subscription-based businesses from traditional business models?
Subscription-based businesses rely on regular payments for ongoing service access. Traditional models often focus on a one-time sale.
What are the primary types of subscriptions available in the market?
There are service subscriptions like streaming media, product subscriptions for regular deliveries, and access-based subscriptions for software.
Can you provide examples of successful subscription-based companies?
Companies like Netflix for streaming, Blue Apron for meal kits, and Adobe for software have all thrived with this model.
What are some innovative subscription-based business ideas?
Fresh meal subscriptions for pets or plant subscription services for home gardeners are fresh takes on the subscription model.
What are the potential disadvantages of operating a subscription business model?
Challenges include maintaining value to prevent cancellations and managing cash flow due to the recurring revenue nature.
What are the advantages and challenges associated with subscription business models?
Advantages include predictable income and customer loyalty. Challenges involve keeping the offerings fresh and limiting customer turnover.