Enabling hardware acceleration in Chrome is generally recommended for users with modern hardware and up-to-date drivers. The potential benefits in performance and responsiveness often outweigh the risks. However, if you experience instability issues or have an older system, disabling hardware acceleration may be preferable.
What Is Hardware Acceleration in Chrome?
In Google Chrome, hardware acceleration is a feature that delegates certain tasks to the device’s hardware components, notably the graphics hardware, to speed up processes and enhance the overall user experience. This technology has become increasingly significant as web applications and browsers, like Chrome, demand more than just RAM to function effectively. By allowing hardware acceleration, apps like Chrome can utilize more of your device’s hardware capabilities to boost performance.
Table: Benefits & Drawbacks Of Hardware Acceleration
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| What is it? | Uses your computer’s graphics processing unit (GPU) to handle graphics-intensive tasks, freeing up the CPU for other things. | – Smoother video playback, gaming, and web browsing – Improved performance for demanding tasks – Reduced CPU usage | – May not be compatible with all hardware or drivers – Can cause stability issues or crashes in some cases – May not always offer significant performance gains for all users |
| How it works | Chrome offloads certain tasks like video decoding and WebGL rendering to the GPU, freeing up the CPU for other tasks like web page rendering and JavaScript execution. | – Less strain on the CPU, leading to better overall system responsiveness – Faster loading times for graphics-heavy content | – Requires compatible and up-to-date graphics drivers – Can be affected by other software using the GPU |
| Enable/Disable | – Go to Chrome Settings > System – Toggle “Use hardware acceleration when available” on or off | – Allows you to control whether hardware acceleration is used – Can be helpful for troubleshooting issues | – Disabling hardware acceleration may impact performance |
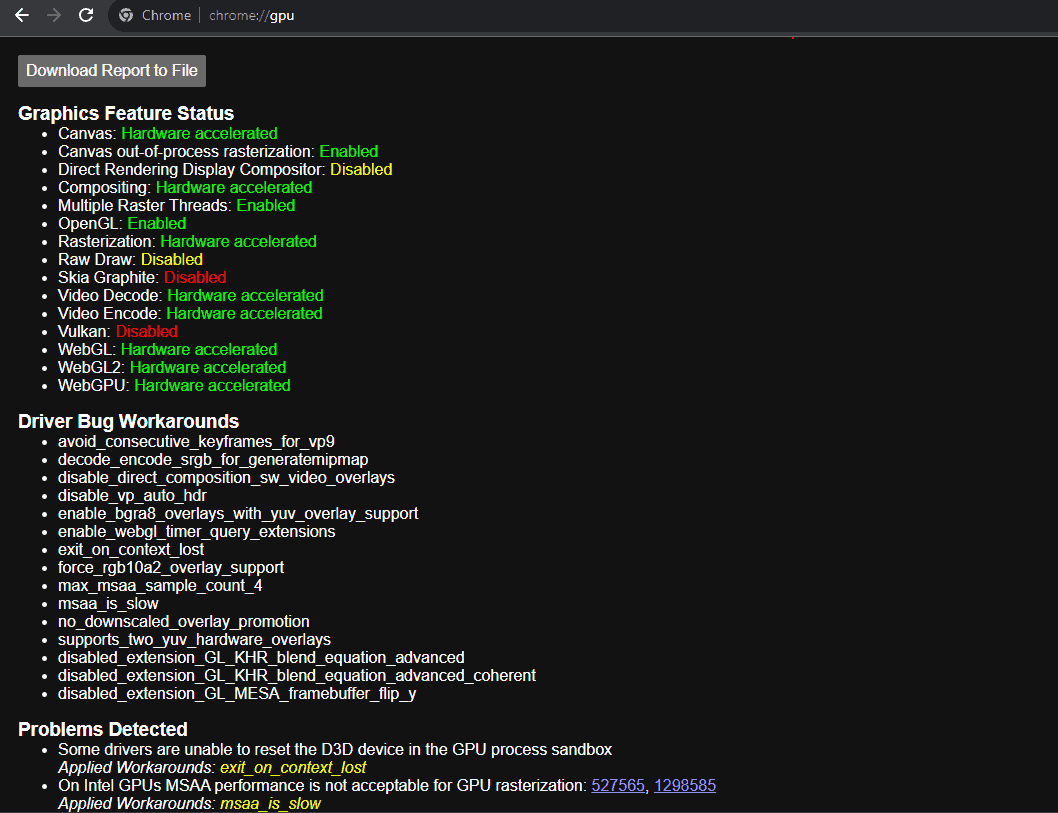
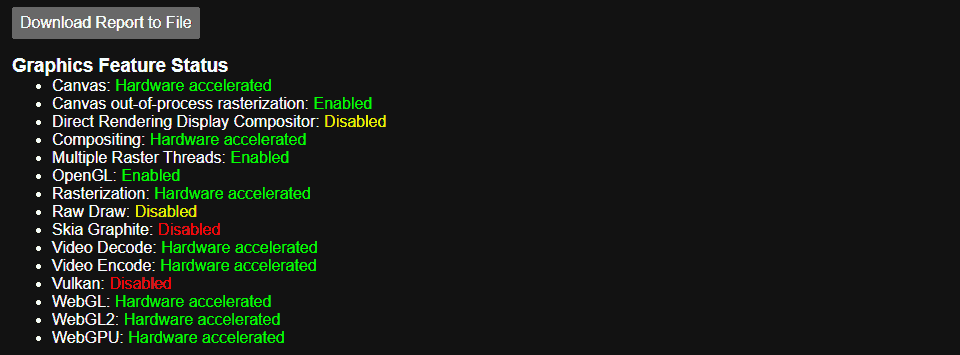
| Check status | – Type chrome://gpu in the address bar – Provides information about your GPU and whether hardware acceleration is enabled | – Helps diagnose potential problems with hardware acceleration | – Requires some technical understanding to interpret the information |
| Troubleshooting | – Update your graphics drivers – Disable hardware acceleration and see if the issue persists – Check for browser extensions that might interfere with hardware acceleration | – Can help identify and resolve issues related to hardware acceleration | – May require advanced troubleshooting skills |
Additional notes:
- The benefits of hardware acceleration vary depending on your computer’s hardware and the type of tasks you’re doing.
- Some users may experience stability issues when using hardware acceleration, especially with outdated or incompatible drivers.
- If you’re unsure whether to enable hardware acceleration, it’s generally safe to experiment and see what works best for your system.
Pros of Enabling Hardware Acceleration in Chrome:
- Improved performance: Hardware acceleration offloads graphics-intensive tasks like video playback, gaming, and WebGL rendering to your GPU, freeing up the CPU for essential tasks like web page rendering and JavaScript execution. This can lead to smoother, faster browsing experiences, especially on resource-demanding websites.
- Reduced CPU usage: By offloading tasks to the GPU, hardware acceleration reduces the workload on your CPU, allowing it to run more efficiently. This can result in better overall system responsiveness and potentially lower power consumption.
- Enhanced multimedia experience: Hardware acceleration can significantly improve video playback smoothness, particularly for high-resolution videos. It can also enhance the performance of web-based games and other graphics-intensive applications.
- Improved responsiveness for demanding tasks: For tasks like video editing, 3D modeling, and advanced data visualization, hardware acceleration can make a noticeable difference in performance and responsiveness.
Cons of Enabling Hardware Acceleration in Chrome:
- Potential for instability: Hardware acceleration can sometimes introduce instability issues, causing crashes or freezing in Chrome or other applications. This is more likely with outdated or incompatible graphics drivers.
- Compatibility issues: Not all hardware and drivers are fully compatible with hardware acceleration. Some older or integrated GPUs may not support it, or it may not work reliably with certain driver versions.
- Increased power consumption: While hardware acceleration can reduce overall power consumption by offloading tasks to the GPU, the GPU itself can draw more power than the CPU for certain workloads. This may be noticeable on laptops or other battery-powered devices.
- Troubleshooting complexity: Diagnosing and resolving issues related to hardware acceleration can be more complex than troubleshooting regular browser problems. It may require some technical knowledge to interpret error messages and troubleshoot driver compatibility issues.
Checking Hardware Acceleration Status in Chrome
Before deciding to turn hardware acceleration on or off, you should first check its current status in Chrome:
- Open Chrome and type
chrome://gpuin the address bar, then press Enter. - Focus on the ‘Graphics Feature Status’ section to determine if hardware acceleration is enabled (indicated by ‘Hardware accelerated’ in green next to most parameters).
How to Enable Hardware Acceleration in Chrome
If hardware acceleration is disabled, or you wish to ensure it’s activated, follow these steps:
- Click the More button (three vertical dots) in Chrome’s top-right corner and select Settings.
- Click on Advanced and then System.
- Toggle on ‘Use hardware acceleration when available’ under System.
- Relaunch Chrome if prompted.
Forcing Hardware Acceleration in Chrome
If standard methods don’t activate hardware acceleration, you can try overriding system flags:
- Enter
chrome://flagsin the address bar. - Enable the option ‘Override software rendering list’.
- Relaunch Chrome and check the status again at
chrome://gpu.
Turning Off Hardware Acceleration
There might be instances where hardware acceleration could cause issues, such as improper rendering of visual elements. In such cases, disabling it can be beneficial:
- Open Chrome, click the horizontal ellipsis menu button, and go to Settings.
- Select System.
- Turn off ‘Use hardware acceleration when available’.
- Click the Relaunch button.
Troubleshooting and Considerations
If hardware acceleration doesn’t work even after trying the above steps, the issue might not lie with Chrome’s settings but could be related to outdated video drivers or hardware issues with the graphics card.
Conclusion
Hardware acceleration in Chrome can significantly improve your browsing experience, especially for graphics-intensive tasks. However, it’s important to understand when to use it and how to troubleshoot issues related to it. Regularly checking the status and understanding how to toggle this feature can help optimize your Chrome experience.
This overview combines insights and step-by-step instructions from sources like Alphr, Pureinfotech, and Technipages, offering a comprehensive guide on managing hardware acceleration in Chrome.