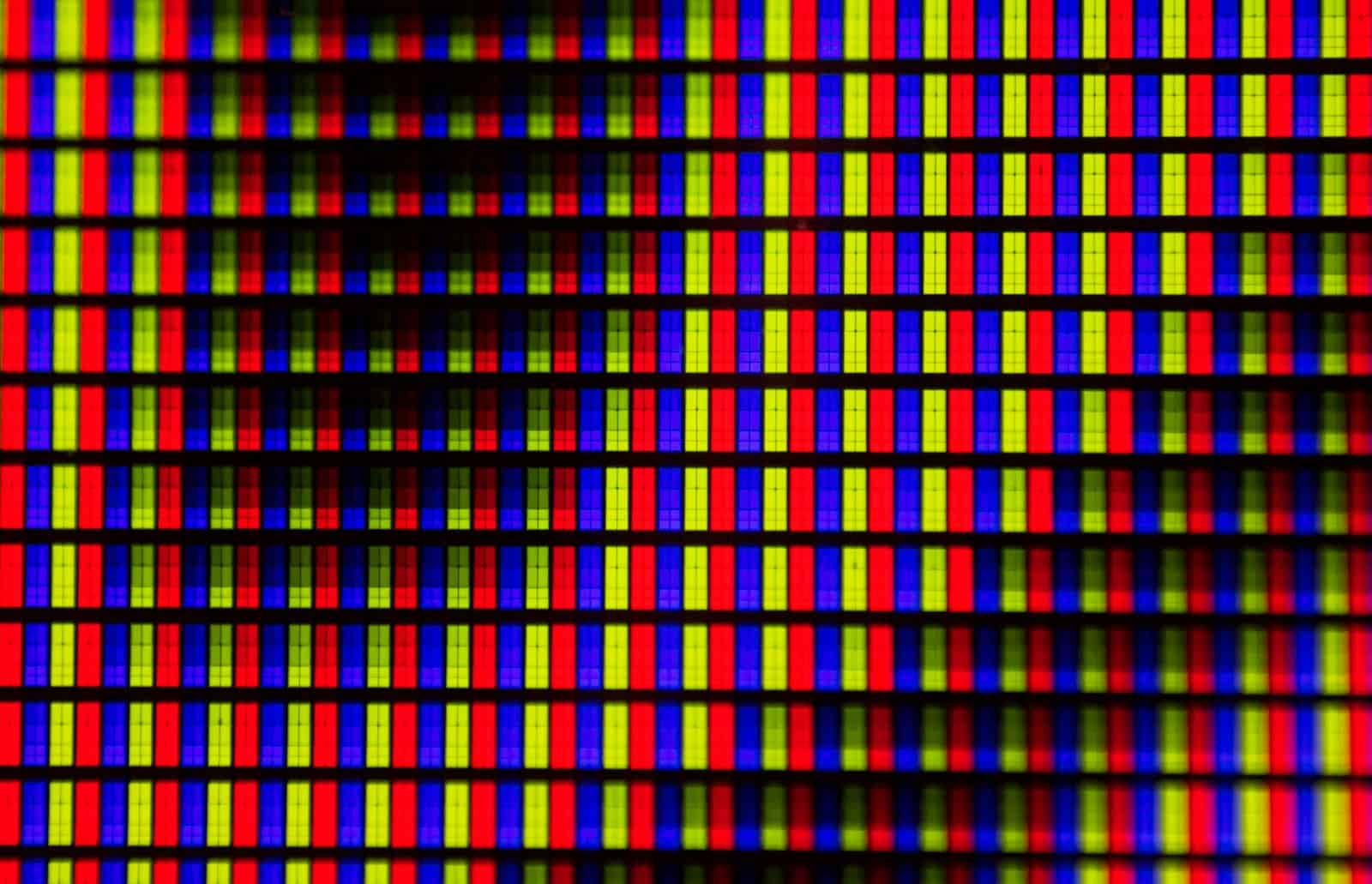
Choosing between LED and OLED screens can be tricky. Both offer stunning visuals, but questions about longevity linger. Let’s delve into the nitty-gritty of these display technologies to determine the champion of lifespan.
LED vs. OLED
When shopping for a new TV, monitor, or smartphone, you will inevitably face the choice between LED (specifically LED-backlit LCD) and OLED. While they may look similar on a shelf, the underlying technologies are fundamentally different, affecting everything from how much you pay to how long the screen lasts.
Here is a comprehensive guide to understanding the differences between LED and OLED.
1. The Fundamental Difference: How They Light Up
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): These are actually LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens that use a backlight. A panel of white LEDs sits behind a layer of liquid crystals. The crystals act like shutters, opening and closing to let light through or block it out to create an image.
- OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode): These are self-emissive. This means every single pixel is its own light source. When a pixel needs to be black, it turns off completely. There is no backlight.
2. Contrast and Black Levels
- LED: Because there is always a light on in the background, it is difficult for LED screens to achieve true black. Some light usually “leaks” through, resulting in a dark grey appearance. High-end LEDs use “Local Dimming” to help, but you often see a “halo” or “blooming” effect around bright objects on dark backgrounds.
- OLED: Since pixels can turn off entirely, OLED offers infinite contrast and “perfect blacks.” This creates a much more immersive, “poppy” image, especially in dark scenes.
- Winner: OLED
3. Brightness
- LED: Because they have a dedicated backlight, LED screens can get incredibly bright. This makes them the superior choice for well-lit living rooms with lots of windows or for outdoor use.
- OLED: While OLED technology has improved (especially with QD-OLED and MLA panels), they generally cannot reach the searing brightness levels of top-tier LED (Mini-LED) displays. They are best suited for controlled lighting or dark rooms.
- Winner: LED
4. Response Time and Gaming
- LED: The liquid crystals take a few milliseconds to physically shift positions, which can cause “ghosting” or motion blur in fast-paced games.
- OLED: OLED pixels change state almost instantaneously (usually <0.1ms). This results in incredibly fluid motion and is why OLED is currently the “gold standard” for competitive gaming.
- Winner: OLED
5. Lifespan and “Burn-In”
- LED: These are the workhorses of the display world. They can last for a decade or more of heavy use without the image degrading.
- OLED: Because the “O” in OLED stands for Organic, the compounds eventually break down. If you leave a static image (like a news ticker or a taskbar) on the screen for thousands of hours, it can leave a permanent ghost image, known as burn-in. While modern OLEDs have many safeguards to prevent this, the risk still exists.
- Winner: LED
6. Viewing Angles
- LED: On many LED panels (especially VA panels), the colors and contrast start to shift or fade if you aren’t sitting directly in front of the screen.
- OLED: You can watch an OLED from almost any angle without losing color accuracy or brightness.
- Winner: OLED
Summary Table
| Feature | LED (LCD) | OLED |
|---|---|---|
| Black Levels | Dark Grey / Good | Perfect Black |
| Brightness | Very High | Moderate to High |
| Contrast | Moderate | Infinite |
| Response Time | Fast | Instantaneous |
| Lifespan | Excellent | Risk of Burn-in |
| Price | Affordable to Premium | Premium |
The “Middle Ground”: Mini-LED
If you want the brightness of an LED but the contrast of an OLED, look for Mini-LED. This technology uses thousands of tiny LEDs as a backlight with hundreds or thousands of “dimming zones.” It gets much closer to OLED black levels while remaining much brighter and immune to burn-in.
Which Should You Choose?
Choose LED if:
- You are on a budget.
- The screen will be in a very bright room with lots of sunlight.
- You use the screen for work (static Excel sheets, taskbars) for 8+ hours a day.
- You want a screen that will last 10+ years without worry.
Choose OLED if:
- You are a movie buff who wants the best possible cinematic experience.
- You do most of your viewing/gaming in a dark or dimly lit room.
- You are a competitive gamer who needs the fastest response times.
- You want the thinnest possible display (OLEDs don’t need a backlight “sandwich,” so they can be paper-thin).
Understanding the Illumination Game
Before diving in, let’s establish the basics:
- LED (Light-Emitting Diode): These utilize a backlight to illuminate pixels, commonly found in LCD screens.
- OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode): Each pixel in an OLED screen acts as its own light source, resulting in superior black levels and vibrant colors.
OLED vs LED Lifespan
| Feature | LED Screens | OLED Screens |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Lifespan | 30,000 – 100,000 hours (at half brightness) | 20,000 – 100,000 hours (at half brightness) |
| Degradation Pattern | Gradual and uniform brightness reduction | Potential for uneven degradation, color shift (especially blue), and burn-in |
| Burn-in Risk | Very low | Moderate to high, especially with static images |
| Factors Affecting Lifespan | Overall usage time, brightness settings, display content | Overall usage time, brightness settings, display content (static images pose the highest risk ) |
| Strengths | Generally longer lifespan, less susceptible to burn-in | Potential for superior image quality with deeper blacks and vibrant colors |
The LED Advantage: Durability Through the Years
- Long-lasting Champions: LED screens boast lifespans ranging from 30,000 to 100,000 hours, according to industry reports. That translates to roughly 10 to 30 years of use, assuming moderate viewing times.
- Fading with Grace: As LEDs age, they tend to lose brightness uniformly, preserving image quality for a longer duration.
The OLED Conundrum: A Trade-off for Beauty
- Shorter Lifespan: While offering exceptional visuals, OLEDs generally have lifespans of 20,000 to 100,000 hours. This range depends heavily on usage patterns and OLED type.
- The Burn-in Issue: A significant concern with OLEDs is burn-in, a phenomenon where static images become permanently etched on the screen with prolonged exposure. This can significantly reduce the usable lifespan of an OLED display.
- Color Degradation Over Time: The organic materials in OLEDs are susceptible to degradation, especially blue pixels. This can lead to color imbalances over time.
Beyond Lifespan: A Look at User Reviews
“I’ve had my LED TV for over 8 years, and the picture quality is still excellent,” says David Chen, a satisfied LED user. “While OLEDs look amazing, the burn-in risk makes me hesitant.”
“For my gaming PC, an OLED monitor was a game-changer,” shares Sarah Miller, an avid gamer. “The deep blacks and vibrant colors create an immersive experience. I just have to be mindful of static elements on the screen.”
The Verdict: It’s All About Your Needs
Both LED and OLED excel in different aspects. While LEDs boast superior lifespans, OLEDs offer unparalleled image quality. Here’s a quick cheat sheet to guide your decision:
Choose LED if:
- Lifespan is a top priority.
- You plan to use the screen for extended periods.
- You’re concerned about burn-in.
Choose OLED if:
- Image quality and vibrant colors are paramount.
- You’re willing to take some precautions to avoid burn-in.
- Your budget allows for a premium display experience.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your individual preferences and viewing habits!
FAQs
Can OLED burn-in be fixed?
While minor burn-in might improve with varied content display and pixel refreshing features, severe burn-in is permanent.
How to extend my screen’s lifespan?
Using moderate brightness levels, turning off the screen when not in use, and avoiding static images for long durations can significantly improve your screen’s lifespan, regardless of technology.
Is QLED the same as OLED?
No, QLED is a type of LED display that uses quantum dots to enhance color and brightness. OLEDs, on the other hand, rely on organic light-emitting diodes for illumination.
Which screen offers better color accuracy?
OLED screens are generally known for superior color accuracy and deeper blacks due to individual pixel lighting control.
Are LED screens immune to burn-in?
LEDs are far less susceptible to burn-in compared to OLEDs. However, prolonged exposure to static images can still cause image retention or minor burn-in on LED screens in extreme cases.