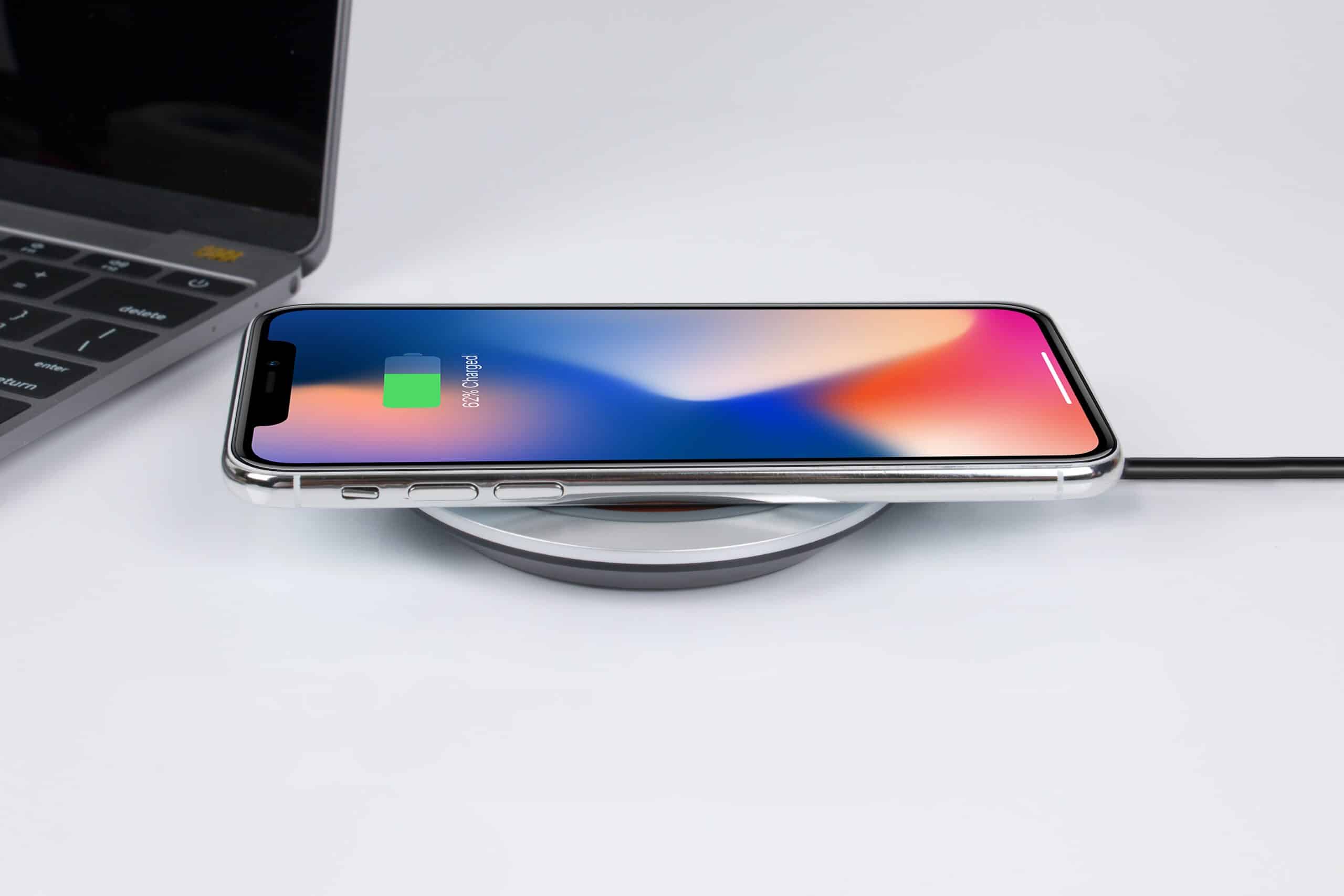
Wireless charging offers a convenient way to power up smartphones without the clutter of cables. It allows users to simply place their device on a charging pad, making it a popular choice for home and office setups. However, many wonder about the impact of wireless charging on battery health. While it is an efficient method, it does generate a small amount of extra heat compared to traditional wired chargers. This heat could potentially affect the battery’s longevity over time.
Smartphones today are designed with advanced battery management systems. These systems help to regulate charging speed and ensure safety. Many wireless chargers also come with built-in features to manage heat. Even so, it is still important for users to understand how wireless charging influences the overall life span of their device’s battery.
Understanding the right balance between convenience and optimal battery maintenance is key. This can help maximize both the life of the battery and the usefulness of wireless charging technology. It is essential to consider device specifications and manufacturer recommendations when choosing a charging method to maintain the health of the battery.
How Wireless Charging Works
Wireless charging uses inductive charging. A charging pad creates an electromagnetic field, and your phone’s coil converts that energy into electricity to recharge the battery.
This process is less efficient than wired charging, which means some energy is lost as heat—a key factor in battery wear.
The Main Concerns
- Heat Generation
- Wireless charging produces more heat than wired charging.
- Excessive heat can accelerate lithium-ion battery aging.
- Charging Efficiency
- Wireless charging is slower and less efficient, meaning your phone may stay on the charger longer.
- Longer charging times can keep the battery at higher temperatures.
- Battery Cycles
- Every full charge/discharge cycle reduces battery capacity slightly, regardless of charging method.
What the Experts Say
- Minimal impact with safeguards: Modern phones include thermal management and optimized charging to minimize damage (source: SimplyMac).
- Heat is the real enemy: The main risk comes from excess heat, not the wireless charging itself (source: How-To Geek).
- Apple’s stance: Apple acknowledges that every charge cycle slightly reduces battery health, whether wired or wireless, but recommends using genuine chargers for safety (source: Apple Community).
Best Practices for Preserving Battery Health
If you prefer wireless charging, you can still protect your battery by following these tips:
- Use high-quality chargers: Stick to certified MagSafe or Qi chargers.
- Avoid overheating: Don’t charge on soft surfaces like beds or couches that trap heat.
- Don’t charge overnight: Prolonged charging at 100% generates unnecessary heat.
- Enable optimized charging: On iPhones and some Androids, this feature helps reduce wear.
- Remove thick cases: Some cases trap heat and make wireless charging less efficient.
Verdict: Is Wireless Charging Bad?
Wireless charging is not inherently bad for your battery. While it does generate slightly more heat than wired charging, modern devices are designed with safeguards to minimize damage. The real key to battery longevity is temperature management—whether you charge wirelessly or with a cable.
If convenience is important to you, wireless charging is safe to use daily. For maximum battery health, mix in wired charging, avoid heat buildup, and use certified accessories.
✅ Bottom Line: Wireless charging won’t ruin your battery, but keeping your phone cool and avoiding constant overnight charging will help it last longer.
Does Wireless Charging Harm Your Phone’s Battery?
Let’s bust the myth of wireless charging destroying phone batteries. While it’s a common concern, this fear is mostly unfounded. Here’s why:
Heat – The Main Concern
Wireless charging relies on magnetic induction, which generates heat. Excessive heat can degrade battery health over time. However, modern wireless chargers have safety features to address this:
- Temperature control: They regulate charging speed or stop charging if temperatures exceed safe limits.
- Design: Many chargers use fans or strategic material choices for heat dissipation.

Wired vs. Wireless Charging
Both charging methods generate heat, and both can slightly impact battery health in the long run. The difference in their effect on the battery is usually minimal.
Maximizing Battery Lifespan
Here’s how to ensure your battery lasts, regardless of your preferred charging method:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Avoid extremes | Keep battery levels between 20% and 80% for most of the time. |
| Minimize heat exposure | Avoid placing your phone in direct sunlight or hot environments, whether charging or not. |
| Optimized charging | Many modern phones have built-in features to optimize charging patterns, which can help with battery health. |
The Bottom Line
The convenience of wireless charging doesn’t come with a major compromise to battery health. If you’re concerned, choose quality wireless chargers with safety features, and follow general battery health practices.
Key Takeaways
- Wireless charging is convenient but can produce extra heat, which may affect battery health.
- Modern smartphones include systems to mitigate heat during wireless charging.
- Balancing convenience and battery care is crucial when using wireless charging.
Understanding Wireless Charging and Battery Health
Wireless charging offers a convenient way to power up devices, but its impact on battery health is a topic of interest. We will explore how this technology works and its effects on the longevity of batteries.
Principles of Wireless Charging Technology
Wireless chargers use electromagnetic fields to transfer energy from the charger to the battery. The charger has coils that create a magnetic field. The device has a receiver coil that picks up the energy from this field and converts it back into electrical energy to charge the battery. Compatibility is key; for instance, Qi wireless charging is a widely adopted standard that allows different devices to use the same charging mat.
Impact on Smartphone Battery Longevity
Batteries have a lifespan that’s measured in charge cycles. One cycle accounts for a full 0 to 100 percent charge. Regular use of wireless charging can potentially increase the number of cycles the battery goes through. This can lead to a shortening of the overall battery life as compared to using the battery less frequently.
Wireless vs Wired Charging Efficiency
Wireless charging often has lower energy efficiency than wired charging due to energy loss during the transfer. This means that more electrical energy is required to charge a battery wirelessly than it would for a wired charger. Additionally, wireless chargers may charge a device more slowly than wired chargers, especially when comparing to fast chargers.
Heat Generation and Battery Degradation
Heat is an enemy of battery health. Wireless charging can generate more heat than wired charging because of the distance between the charging coils and inefficiencies in energy transfer. If the temperature gets too high, it can lead to overheating. Many smartphones have built-in mechanisms to slow or stop charging to prevent damage from excess heat. Devices and chargers should be used according to manufacturer guidelines to minimize risk.
Practical Considerations and Optimal Usage
Wireless charging offers a convenient way to power up smartphones without cables. It is essential to use wireless charging correctly to maintain battery health and ensure safety.
Choosing the Right Wireless Charger
Select a wireless charger that matches the manufacturer’s recommendations for your smartphone. For instance, iPhone 8 or later should use a charger that supports the Qi2 standard like MagSafe, while Samsung devices benefit from chargers that align with their power needs. A high-quality wireless charger delivers the correct power output without causing wear and tear associated with plugging in cables. It should provide a steady current and have built-in measures to prevent overcharging.
Maintaining Optimum Battery Health
To keep your smartphone battery in good condition, avoid extreme temperatures and direct sunlight during charging. Use slow charging options overnight to reduce heat generation, which can lead to battery degradation. Be mindful of the depth of discharge; it’s better for battery longevity to charge your phone before it drops too low. Software in phones from Apple, Samsung, and other manufacturers often includes optimizations to reduce battery wear during charging.
Safety and Precautions in Wireless Charging
Always place the phone correctly on the charging pad to prevent misalignment, which can lead to inefficient charging and excess heat. Remove thick phone cases that may hinder the transfer process or cause overheating. Ensure the charging area is clear of clutter to reduce the risk of fire. Look for chargers with safety certifications and built-in fans to dissipate heat if you prefer fast charging options.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we address some common queries about the impact of wireless charging on smartphone batteries.
Does wireless charging affect the lifespan of smartphone batteries?
Wireless charging does not inherently shorten the lifespan of smartphone batteries. Most modern smartphones are designed to handle wireless charging without significant wear to the battery.
Are there any negative effects of wireless charging on battery health for iPhones?
For iPhone models that support wireless charging, using this feature correctly should not harm the battery’s health. The iPhone’s design includes measures to protect the battery during wireless charging.
Can using a wireless charger damage the battery of Samsung devices?
As long as the wireless charger is compatible and used as directed, it is unlikely to cause damage to the battery of Samsung devices. The company ensures that its devices have safeguards to prevent overheating during wireless charging.
Is there a difference in battery degradation between wireless and wired charging methods?
Battery degradation over time is normal with both wireless and wired charging methods. However, wireless charging may generate more heat, which can contribute to battery wear if not managed properly by the device.
Are there specific models of iPhone that are impacted more by wireless charging?
All iPhone models that support wireless charging are designed to minimize battery impact. There is no evidence to suggest that certain models are more affected than others by wireless charging.
What are the potential risks to battery life when frequently using wireless chargers?
The main risk to battery life with frequent wireless charger use is heat build-up. Devices typically regulate heat, but a poor-quality charger or a protective case that traps heat could potentially increase wear and tear on the battery.