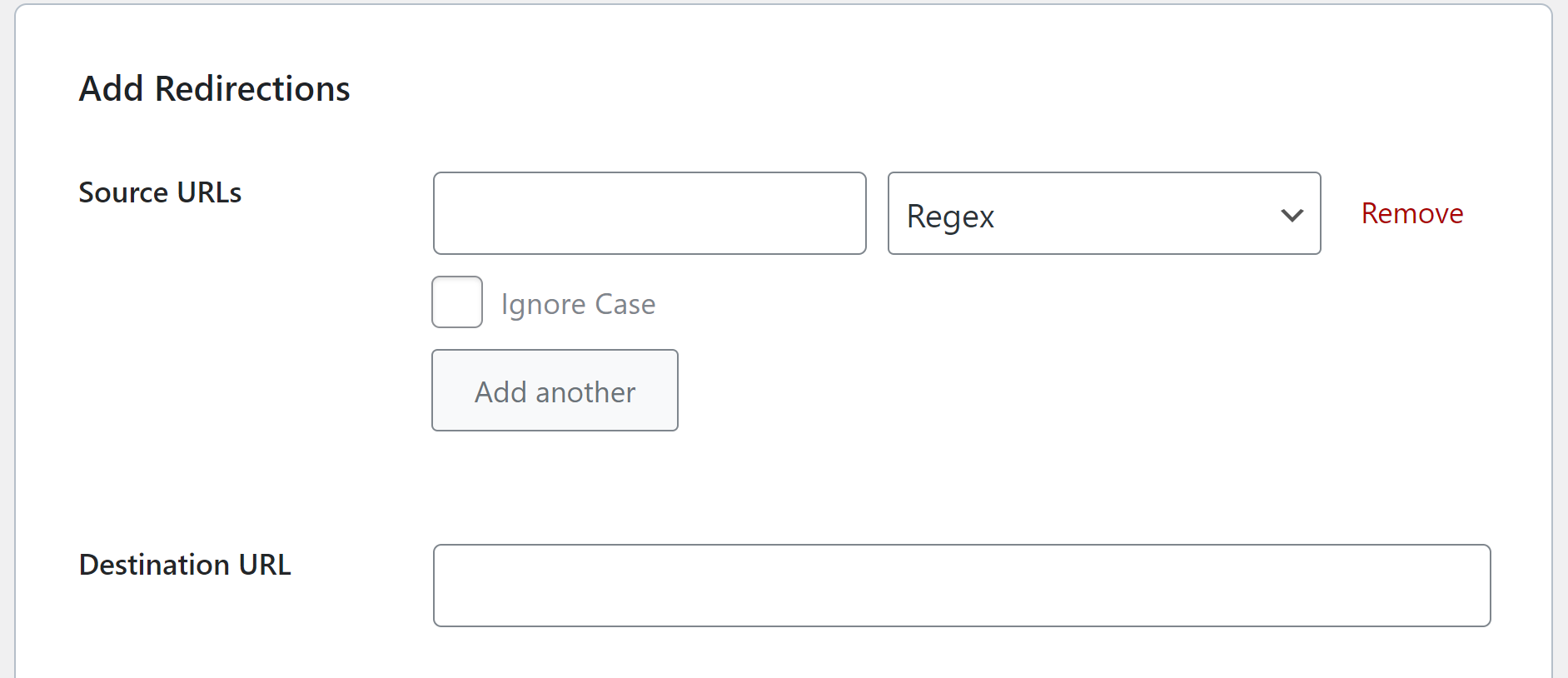
A regex redirect is a tool used on websites to manage the flow of traffic between URLs. Regular expressions, or regex, are patterns that identify a sequence of characters in a string. When applied to redirects, these patterns allow webmasters to create rules that efficiently handle multiple URL redirection scenarios with a single instruction. This method is essential when a website undergoes restructuring, changing many URLs simultaneously. By using regex redirects, the manual task of creating individual redirection rules for each URL is eliminated, which saves time and reduces the chance of errors.
Understanding how regex redirects work can seem challenging at first. However, once grasped, they become a powerful asset in a webmaster’s toolkit. They enable precise and pattern-based redirection, covering a broad range of URL variations without creating a specific rule for each possibility. For example, if a website’s product pages are moved from one directory to another, a regex redirect can reroute all traffic to the new pages without needing to redirect each product individually.
Guide: What is a Regex Redirect (and Understanding Regex)
🧠 What Is Regex?
Regex (short for Regular Expression) is a sequence of characters that defines a search pattern. It’s commonly used in programming, web development, and SEO for finding, matching, or replacing text that follows a certain structure.
In simpler terms, Regex helps you match multiple similar patterns of text or URLs without writing separate rules for each one.
For example:
- The pattern
^/blog/.*matches any URL that starts with/blog/, such as/blog/post1,/blog/category/seo, etc.
This makes Regex incredibly powerful for redirects, validation, and automation.
🚦 What Is a Regex Redirect?
A Regex Redirect is a type of redirect that uses regular expressions to match multiple URLs based on a pattern, and redirect them all to a single destination or to a dynamically generated destination.
🔍 Example
Let’s say you moved all your product pages from /shop/ to /store/.
Instead of creating dozens of individual redirects like:
/shop/product1 → /store/product1
/shop/product2 → /store/product2
You can use one Regex redirect rule:
| Source (Regex Pattern) | Destination |
|---|---|
^/shop/(.*) | /store/$1 |
Explanation:
^means “start of the URL”(.*)captures everything after/shop/$1reuses the captured part in the new destination
So /shop/product1 automatically redirects to /store/product1.
⚙️ Why Use Regex Redirects?
Regex redirects are especially useful when:
- You’ve changed a URL structure (like
/old-category/→/new-category/) - You need to redirect multiple pages with similar patterns
- You want to avoid hundreds of manual redirects
- You’re managing redirects in WordPress, Apache (.htaccess), NGINX, or SEO plugins (like Yoast, Rank Math, or Redirection)
🧩 Common Regex Symbols and What They Mean
| Symbol | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
^ | Start of string | ^/blog matches URLs starting with /blog |
$ | End of string | /blog$ matches URLs ending with /blog |
. | Any single character | /b.g/ matches /bag/, /bug/ |
* | Zero or more of the previous character | /blog.* matches /blog, /blog-post, /blog/category/ |
( ) | Capturing group | (.*) captures everything matched |
| ` | ` | OR operator |
? | Optional character | /blog/? matches /blog and /blog/ |
\ | Escape character | /v1\.0/ matches /v1.0/ literally |
🧱 How Regex Redirects Work in Practice
🔸 In WordPress (via Redirection or Rank Math)
- Enable Regex when creating a redirect rule.
- Enter the pattern in the source field.
- Use backreferences (
$1,$2, etc.) in the destination to reuse captured groups.
Example (Rank Math / Redirection plugin):
Source URL: ^/old-blog/(.*)
Target URL: /new-blog/$1
🔸 In Apache (.htaccess)
RedirectMatch 301 ^/shop/(.*)$ /store/$1
🔸 In NGINX
rewrite ^/shop/(.*)$ /store/$1 permanent;
⚠️ Best Practices for Regex Redirects
- Test before deploying.
Use tools like regex101.com to test your patterns. - Be specific.
Overly broad patterns can accidentally redirect unintended URLs. - Use anchors (
^and$).
They ensure your pattern only matches where intended. - Backup your redirect rules.
A single typo in Regex can break multiple redirects. - Avoid chaining redirects.
Keep your redirect paths clean and direct for SEO efficiency.
📚 Additional Resources
- Yoast: What are Regex Redirects?
- Rank Math: How to Use Regex Redirects
- Redirection Plugin: Regex Support
- Wikipedia: Regular Expression
✅ Summary
| Feature | Normal Redirect | Regex Redirect |
|---|---|---|
| Matches one URL | ✅ | ❌ |
| Matches multiple URLs | ❌ | ✅ |
| Uses patterns | ❌ | ✅ |
| Requires coding knowledge | Low | Moderate |
| Best for | Simple redirects | Complex or bulk redirects |
Using Regex for Flexible Redirects
Understanding Regex Redirects
Regex, or regular expressions, are patterns used to match and manipulate text. In the context of redirects, regex allows you to match multiple URLs based on a specific pattern and forward them to a new destination. This is incredibly useful when dealing with a large website or complex URL structures.
Common Use Cases for Regex Redirects
- Changing Site Structure: If you’ve revamped your website’s structure, regex redirects can seamlessly guide users from old URLs to their new counterparts.
- Consolidating Content: Merging multiple pages or categories? Regex can redirect all relevant URLs to a single destination.
- Fixing Broken Links: Use regex to catch any broken links and automatically redirect users to the correct page, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- Redirecting with Parameters: Regex can handle URLs with dynamic parameters, forwarding them to new pages while preserving the parameter values.
- Matching Specific Patterns: Target URLs containing specific words, numbers, or characters using regex patterns.
Regex Syntax Basics
Regex uses special characters and syntax to define patterns. Here are some common elements:
- .` (period): Matches any single character.
*(asterisk): Matches zero or more of the preceding character.+(plus): Matches one or more of the preceding character.?(question mark): Matches zero or one of the preceding character.^(caret): Matches the start of a string.$(dollar sign): Matches the end of a string.[ ](square brackets): Matches any single character within the brackets.()(parentheses): Creates a capturing group, allowing you to extract parts of the matched URL.
Implementing Regex Redirects
The implementation method depends on your platform or server. Many web servers and content management systems (like WordPress) support regex redirects through plugins or configuration files. For example, in WordPress, the Redirection plugin provides a user-friendly interface to create regex redirects.
Example Regex Redirect
| Original URL Pattern | Redirect To | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
/blog/(.+)/ | /news/$1/ | Redirects all blog posts to the news section, preserving the post name. |
/product/?(.+) | /shop/$1 | Redirects product pages to the shop section, keeping any query parameters. |
^/old-page/$ | /new-page/ | Redirects the exact URL “/old-page/” to “/new-page/”. |
/category/(.+)/page/([0-9]+)/ | /category/$1/?page=$2 | Redirects paginated category pages, preserving the category and page number. |
Key Takeaways
- Regex redirects use patterns to direct website traffic from one URL to another.
- They simplify the management of large-scale URL changes.
- Understanding regex rules is crucial for effective website maintenance.
Understanding Regex Redirects
Regex redirects provide a powerful way to guide users from multiple source URLs to a specific destination URL. They use patterns to match a broad set of URLs, streamlining the redirection process.
Concepts and Terminology
Regex or regular expression is a sequence of characters forming a search pattern. When you use regex for URL redirection, you apply these search patterns to identify a range of URLs for redirection.
Characters and String: Basic building blocks of regex are characters and strings. Characters can be literal text or special symbols that signify broader sets of characters.
Pattern Match: The heart of a regex is to match patterns within strings. Using regex, you can define a pattern that captures all the URLs within a directory or with a common base URL.
Capture Groups: These are parts of the pattern that can extract certain portions of the matched URLs. They help in reusing elements from the source URL in the destination URL.
Character Set: This is a set of characters that a regex can match. It can be as broad as any digit or as specific as a list of characters.
Flags: Regex uses flags to modify the search pattern’s behavior, like case-insensitivity (i) or multi-line matches (m).
Implementing Regex Redirects
To implement regex redirects, one needs a clear understanding of the source and destination URL patterns. Redirects are configured within web servers or using plugins on platforms like WordPress.
Redirect Rules: These are specific directives you place in your web server configuration or WordPress redirect manager. They tell the server how to handle URL requests that match the regex pattern.
Test: Before saving a redirect, always test to ensure it works as intended. Testing helps catch errors that might send users to the wrong page or break the site.
SSL: Secure connections use SSL, and regex redirects should be tested to work with both http and https URLs to ensure a secure user experience.
Troubleshooting: If a redirect isn’t working, check the pattern, test strings, and server configuration for errors. Common issues include syntax errors or incorrect flags in the regex pattern.
By understanding the syntax and structure of regex, webmasters can efficiently redirect users from outdated URLs to new pages, improving site navigation and UX. With careful implementation and testing, regex redirects enhance the functionality of your website while preserving user experience and search engine visibility.
Practical Applications and Examples
When you set up a website, ensuring that visitors can find content smoothly is key. This often involves redirecting old or broken URLs to updated ones. Regex redirects are an effective tool for managing such tasks. They can transform a time-consuming chore into an efficient process.
Common Use Cases
Regex redirects serve many purposes in website management. Here are a few specific examples:
Handling 404 errors: When a page is not found, instead of showing a 404 error, you can redirect users to a relevant page.
URL structure changes: For sites that reorganize content, regex can automatically redirect old category paths to new ones.
Tracking and marketing: Using patterns in the source URL, you can add tracking codes or change URLs for marketing campaigns.
Simplifying multiple redirects: Instead of creating individual rules for each redirect, a single regex pattern can cover a range of similar URL variations.
Tools and Tutorials
To implement regex redirects, you can use various tools:
- WordPress users have plugins like the Yoast SEO Premium redirect manager, which offers a user-friendly interface for setting up regex redirects.
- Online platforms like regexr and regex101.com let you test your patterns to ensure they work before going live.
For those looking to learn, plenty of resources exist. Tutorials on JavaScript regex can be found on educational websites. The WordPress community also provides guides for their specific redirect plugins.
Using these tools ensures that visitors always end up where they are supposed to, which is great for the user experience (UX). It streamlines redirecting URLs and helps keep your site’s structure clean and updated.
Frequently Asked Questions
Regular expression redirects streamline the process of sending visitors from one URL to another. They’re key for site maintenance and SEO.
How can one create a 301 redirect using regular expressions?
One creates a 301 redirect using regex by crafting a pattern that matches the old URL structure. They then apply this pattern in the web server’s configuration to point to the new location.
Can you provide an example illustrating the use of regex in URL redirection?
For example, to redirect all pages under a directory to a new one, the regex ^/old-directory/(.*)$ could be used. This would match any content after the /old-directory/ and redirect it.
What tools are available for testing regular expression redirects?
Tools like regex testers and redirection plugins in content management systems let users test their regex patterns before going live. They ensure the redirects work as intended.
How can you use regular expressions to redirect URL parameters?
Using regular expressions to redirect URL parameters involves matching the parameter structure in the URL with a regex pattern and rewriting it to the desired structure.
What are the implications of having a wildcard regex redirect on a domain?
A wildcard redirect can lead to unintended redirects, affecting user experience and SEO. One must use them with care to avoid such issues.
Are there automated tools to generate redirection rules using regular expressions?
Yes, there are automated tools. They help generate precise regex rules for various web servers and content management systems, simplifying the process.