If you’ve ever looked into upgrading your smartphone’s memory and discovered that it’s impossible, you’re not alone. Unlike many desktop computers or some laptops, smartphones have soldered RAM — meaning the memory chip is permanently attached to the motherboard. But why do manufacturers do this, and what are the pros and cons? Let’s break it down.
What Does “Soldered RAM” Mean?
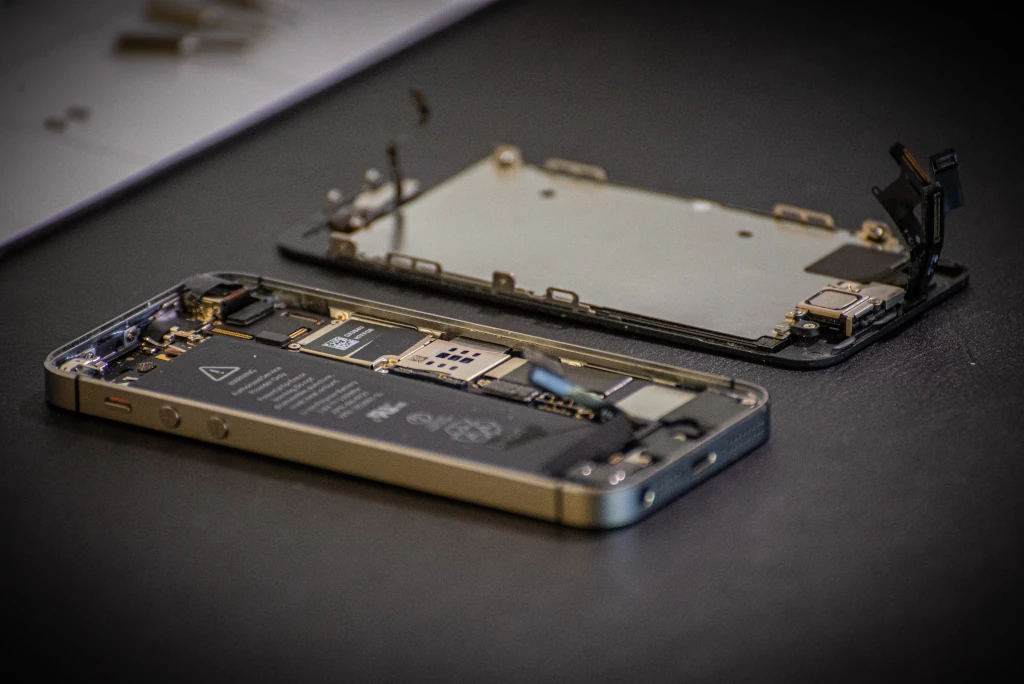
Soldered RAM refers to memory chips that are physically fused to the motherboard using solder — a conductive metal alloy that creates a permanent connection. This design means the RAM cannot be removed, replaced, or upgraded without highly specialized tools and expertise.
In smartphones, this approach has become universal. Whether you’re using an iPhone or an Android device, the RAM is soldered directly onto the logic board.
Why Manufacturers Solder Smartphone RAM
1. Space Efficiency
Smartphones have extremely limited internal space. Every millimeter counts when designing ultra-thin, lightweight devices.
By soldering RAM directly onto the motherboard, manufacturers save space that would otherwise be used for sockets or connectors. This allows for thinner designs and larger batteries.
2. Improved Performance
Soldered RAM provides faster data transfer speeds because it’s physically closer to the CPU.
This reduces latency and improves overall performance — a crucial factor for smartphones that need to multitask efficiently while maintaining low power consumption.
3. Power Efficiency
Since soldered RAM has a shorter electrical path to the processor, it consumes less power. This helps extend battery life, which is a major priority in mobile devices.
4. Structural Integrity
Smartphones undergo constant movement, drops, and vibration. Soldering makes the internal components more durable and resistant to physical stress.
Removable or socketed RAM could loosen or disconnect over time, leading to device instability.
5. Manufacturing Cost and Simplicity
Soldering RAM simplifies the assembly process and reduces the number of components.
For manufacturers, this means lower production costs and fewer potential points of failure — which contributes to better reliability and easier quality control.
Downsides of Soldered RAM
While soldered RAM has clear technical and design advantages, there are also significant drawbacks:
- No Upgradability: Once you buy a smartphone, the amount of RAM it has is permanent.
- Expensive Repairs: If the RAM fails, the entire motherboard often needs replacement.
- Environmental Impact: Non-upgradable components contribute to electronic waste, as users are more likely to replace devices rather than repair them.
Can You Add or Replace Smartphone RAM?
In theory, it’s possible to desolder and replace RAM chips using specialized equipment — but in practice, it’s nearly impossible for consumers. Even professional repair technicians rarely attempt it because of the high risk of damaging the CPU or logic board.
Some enthusiasts have tried “stacking” or “sandwiching” RAM chips (as discussed in Reddit threads), but these experiments are not practical or reliable for everyday use.
The Future of Smartphone Memory
As smartphone technology evolves, we’re seeing tighter integration between RAM and storage — such as LPDDR5X and UFS 4.0 technologies — to further boost performance and efficiency.
While this trend improves speed and power management, it also means that modular, upgradeable smartphones are becoming increasingly rare.
Final Thoughts
Smartphone RAM is soldered for good reasons: efficiency, performance, durability, and cost. However, this design choice sacrifices user flexibility and repairability.
When buying a new phone, it’s wise to choose a model with enough RAM to meet your long-term needs, because once it’s soldered in — it’s there for good.
Sources: