A sound card, also called an audio card or sound board, is a piece of computer hardware that handles audio input and output. It converts digital audio from the computer into analog signals for speakers or headphones, and it can also capture analog sound from devices like microphones. Without it, a computer cannot play or record sound through traditional audio devices.
Most modern computers have sound card functions built into the motherboard, but dedicated sound cards still exist for better audio quality or advanced features. These can support multiple channels for surround sound, connect to professional audio equipment, and process sound with less strain on the computer’s main processor.
Understanding how a sound card works helps explain why it matters for music, games, video calls, and any task that uses audio. It is the link between the computer’s digital data and the physical sound people hear.
What Is a Sound Card?
Here’s a clear and complete guide on What Is a Sound Card — including types, functions, and why they matter today.
1. Definition
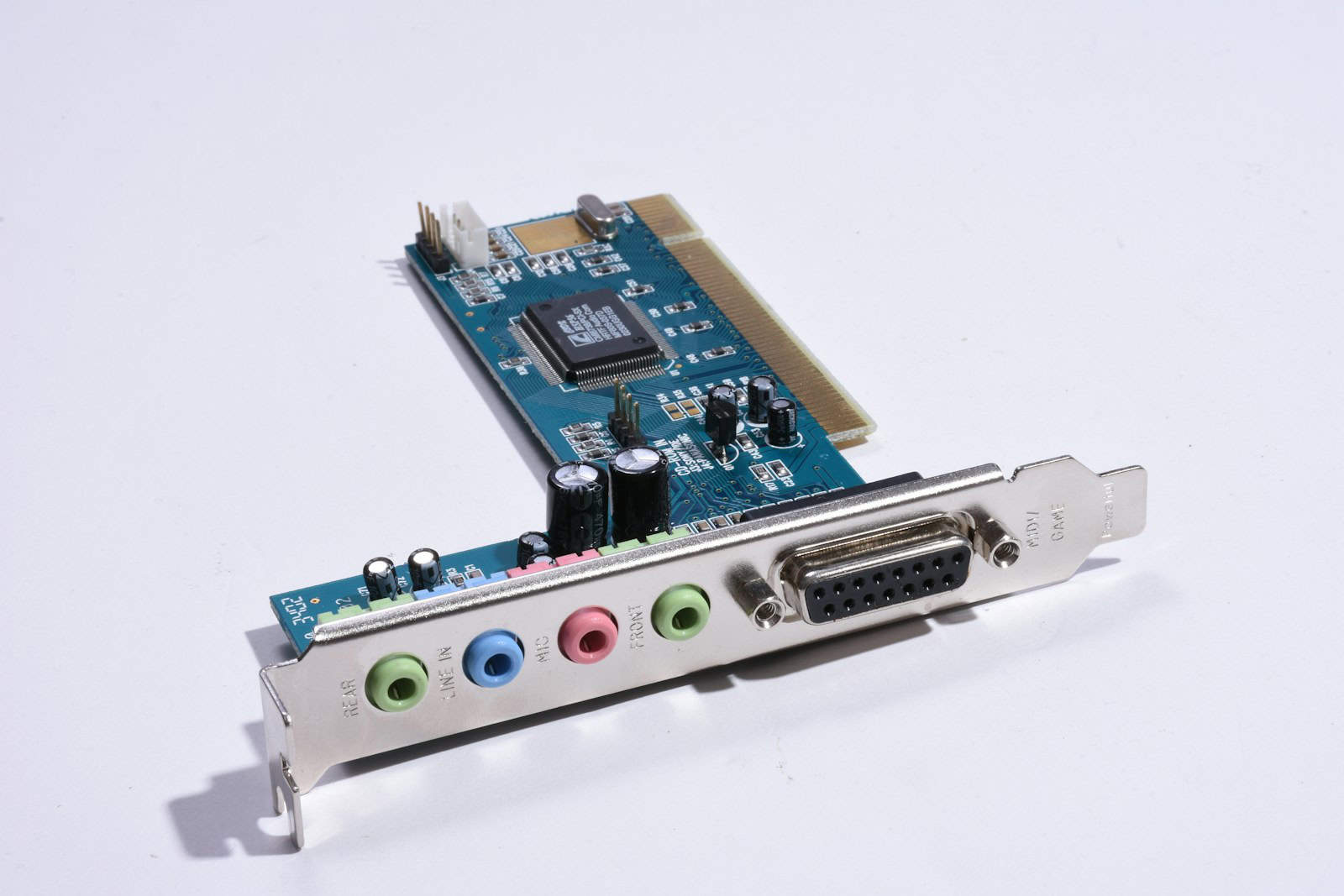
A sound card (also called an audio card or audio interface) is a hardware component that processes audio data for a computer.
Its main job is to convert digital audio signals into analog signals (for speakers/headphones) and analog signals into digital (for recording via microphone).
2. How It Works
- Digital-to-Analog Conversion (DAC): Turns computer data into sound you can hear.
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC): Captures external audio (like your voice) and turns it into data for the computer.
- Signal Processing: Enhances audio with effects, surround sound, or noise reduction.
3. Types of Sound Cards
- Integrated Sound Cards
- Built into the motherboard.
- Sufficient for everyday use (music, video calls, casual gaming).
- Lower cost, but less powerful than dedicated cards.
- Dedicated/Internal Sound Cards
- Installed in a PCIe slot inside the PC.
- Offer higher audio quality, better DAC/ADC performance, and more ports.
- Popular with gamers, musicians, and audio engineers.
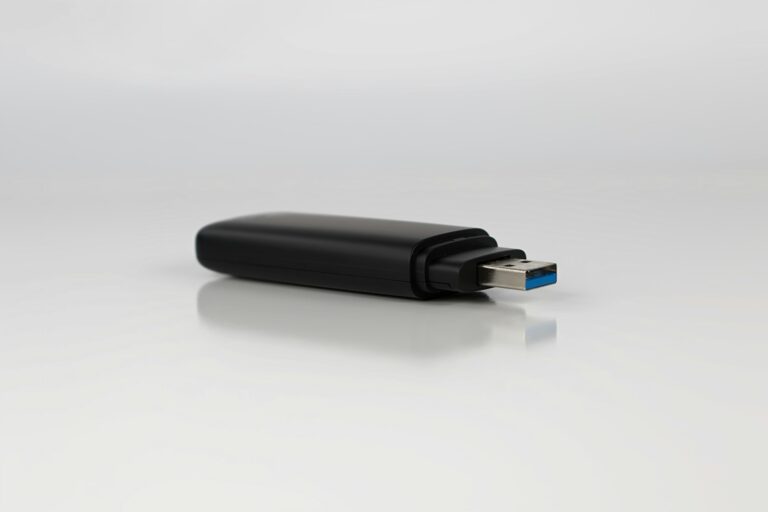
- External Sound Cards / Audio Interfaces
- Connect via USB, Thunderbolt, or FireWire.
- Portable and ideal for laptops or professional recording setups.
- Often used in music production and podcasting.
4. Key Functions
- Playback: Send audio to speakers, headphones, or home theater systems.
- Recording: Capture sound from microphones or instruments.
- Audio Enhancement: Support for surround sound, 3D audio, and high-resolution formats.
- Multiple Channel Support: Stereo (2-channel), 5.1, 7.1, or more.
5. Why They Matter
While many modern devices have good built-in audio, a dedicated or external sound card can:
- Improve sound clarity and detail.
- Reduce background noise.
- Provide more input/output options for professional work.
- Support high-impedance headphones and advanced audio formats.
6. Common Uses
- Gaming: For immersive surround sound and positional audio.
- Music Production: For accurate sound monitoring and multi-track recording.
- Video Editing: To ensure precise audio sync and clarity.
- Home Theater: For high-quality playback and multi-channel setups.
💡 Tip: If you’re unsure whether you need a dedicated sound card, start with your PC’s built-in audio. Upgrade only if you need better quality, more ports, or professional-level recording.
Key Takeaways
- A sound card processes audio signals for playback and recording.
- It can be built into the motherboard or installed as a separate component.
- It enables connection to speakers, headphones, and microphones.
Frequently Asked Questions
A sound card processes audio signals so a computer can send sound to speakers or headphones and receive sound from microphones or other inputs. It can be built into the motherboard or installed as a separate internal or external device.
How does a sound card function in a computer?
A sound card converts digital audio data from the computer into analog signals for speakers or headphones.
It also converts analog input from a microphone or other source into digital data the computer can process.
It uses dedicated audio processors and digital-to-analog converters (DACs) to handle these tasks.
What are the primary uses of a sound card?
A sound card enables playback of music, videos, and games through speakers or headphones.
It also supports recording from microphones and other audio sources.
Some models provide features like multi-channel surround sound or extra input and output ports.
What are the different types of sound cards available?
Internal sound cards connect to the motherboard through PCI or PCIe slots.
External sound cards connect through USB, Thunderbolt, or similar ports.
Some are simple stereo devices, while others support professional multi-channel audio.
Can you use a sound card for professional recording?
Yes, high-quality sound cards or audio interfaces can be used for recording music, podcasts, or voice-overs.
Professional models often include balanced inputs, multiple channels, and low-latency monitoring.
They can connect to studio microphones and instruments directly.
Does a sound card serve as an input, output, or both?
A sound card handles both input and output.
It outputs audio to speakers or headphones and inputs sound from microphones or line-in devices.
Many models process both functions at the same time.
What are some common examples of sound cards, including USB versions?
Examples include internal PCIe cards from brands like Creative and ASUS.
USB sound cards range from compact adapters with a headphone jack to full-sized audio interfaces from makers like Focusrite and Behringer.
These devices vary in features, from basic stereo output to multi-channel recording and playback.