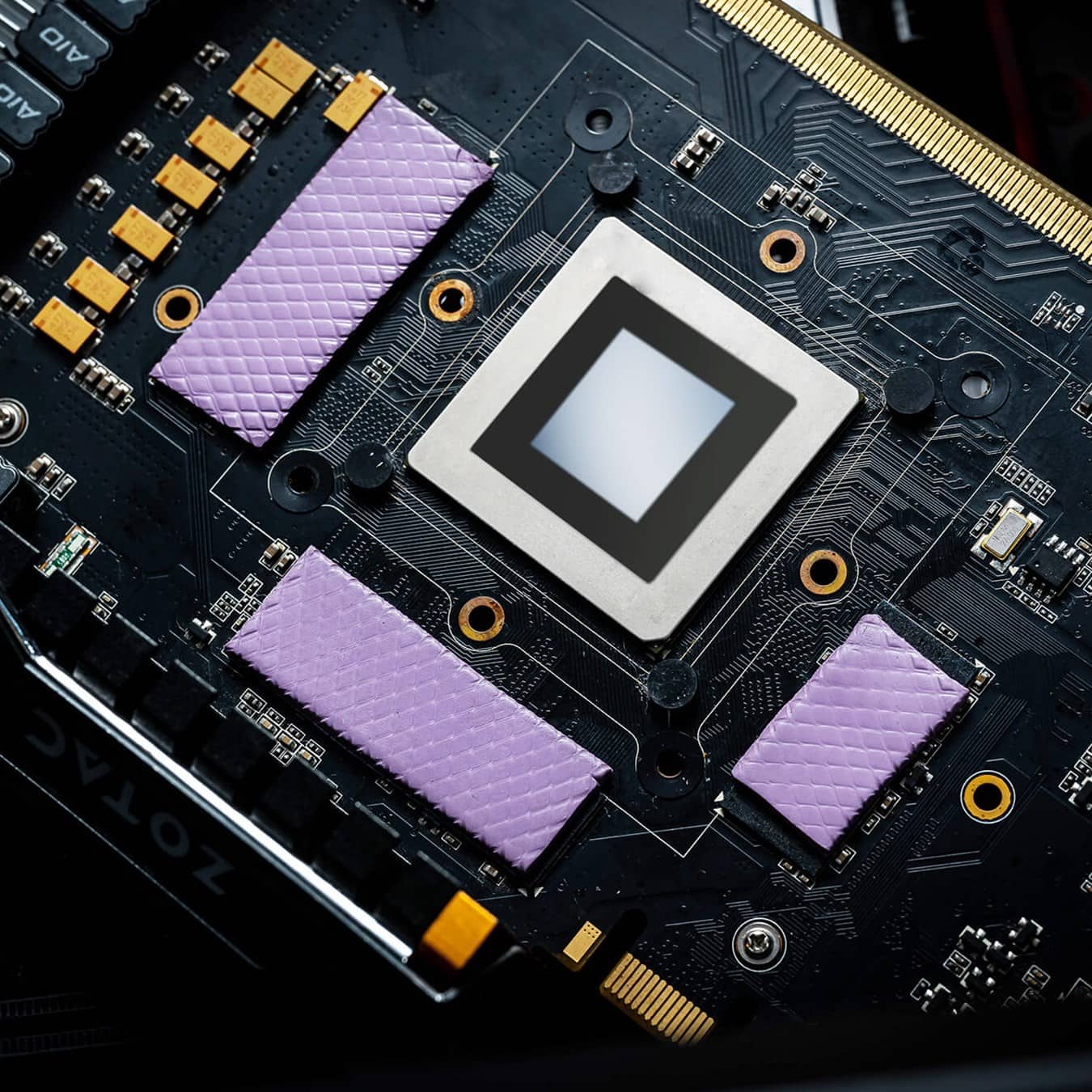
Thermal pads are important for managing the heat generated by GPUs (Graphics Processing Units). They help transfer heat from the GPU to the heat sink to maintain the right operating temperatures. The effectiveness of a thermal pad depends on its ability to transfer heat, which is called thermal conductivity. Choosing the right thermal pad is crucial for GPU performance. Factors such as thickness, material, and heat resistance affect a thermal pad’s ability to dissipate heat.
Silicone-based pads are common, and manufacturers usually specify thermal conductivity using a rating called watt-per-meter-Kelvin (W/mK). A higher number means the pad conducts heat better. When applying thermal pads to GPUs, it’s essential to cover the heat-generating components completely without overlapping. Pads that are too thick may not allow for sufficient contact between the heat sink and the GPU, while pads that are too thin might not fill the gap adequately, leading to overheating.
What Are Thermal Pads?
Thermal pads, also known as thermal interface pads or thermal gap pads, play a crucial role in the cooling system of your graphics card. These small, usually square or rectangular pads are made of a soft, compressible material that helps to fill the gap between the GPU die (the surface of the chip) and the heat sink or cooler.
How Thermal Pads Work
Thermal pads function as thermal interface materials (TIM) that facilitate efficient heat transfer between components. Here’s how they work:
- Gap Filling: They fill microscopic air gaps between surfaces that appear flat but have tiny imperfections
- Heat Conduction: They transfer heat from the hot component (GPU chip, VRAM, VRMs) to the cooler (heatsink)
- Conformability: They compress and conform to surface irregularities, maximizing contact area
- Thermal Bridge: They create a continuous thermal pathway for heat dissipation
Types of GPU Components That Use Thermal Pads
GPU Core/Die
While the main GPU chip typically uses thermal paste, some manufacturers use thermal pads for certain GPU configurations.
VRAM (Video Memory)
Memory modules generate considerable heat and often rely on thermal pads to transfer heat to heatsinks or backplates.
VRM Components (Voltage Regulator Modules)
Power delivery components like MOSFETs and capacitors use thermal pads to dissipate heat to heatsinks or the GPU’s metal backplate.
Other Components
- Power connectors
- Inductors
- Capacitors
- Various ICs on the PCB
Key Properties of Thermal Pads
Thermal Conductivity
Measured in watts per meter-kelvin (W/mK), this indicates how effectively the pad conducts heat. Higher values mean better heat transfer:
- Basic pads: 1-3 W/mK
- Good pads: 3-6 W/mK
- High-performance pads: 6-17 W/mK
Thickness
These small, seemingly insignificant pads play a significant role in transferring heat away from the GPU and ensuring proper cooling. Common thicknesses include:
- 0.5mm – 3.0mm for most GPU applications
- Thickness must match the gap precisely for optimal performance
Compressibility
The ability to compress under pressure while maintaining thermal conductivity.
Temperature Range
Operating temperature limits, typically from -40°C to 200°C for quality pads.
Common Thermal Pad Materials
Silicone-Based Pads
- Most common type
- Good balance of performance and cost
- Temperature stable
- Non-conductive (electrically safe)
Graphite Pads
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Ultra-thin profiles available
- Can be more expensive
- Naturally non-adhesive
Phase Change Materials
- Solid at room temperature, become fluid when heated
- Excellent gap filling
- Higher performance but more expensive
Ceramic-Filled Pads
- High thermal conductivity
- Excellent for high-temperature applications
- More rigid than silicone pads
When to Replace GPU Thermal Pads
Signs You Need Replacement
- Higher than normal GPU temperatures
- Thermal throttling during gaming or intensive tasks
- Age: Pads typically last 3-5 years
- Visible degradation: cracking, hardening, or oil separation
- After disassembling the GPU for cleaning or repairs
Performance Benefits of Replacement
Installation Considerations
Measuring Thickness
- Disassemble the GPU carefully
- Measure existing pad thickness with calipers
- Account for compression (new pads are typically 10-20% thicker than compressed originals)
Application Process
- Clean old thermal pad residue completely
- Cut new pads to proper size
- Remove protective film from both sides
- Apply with gentle, even pressure
- Reassemble carefully to avoid displacement
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using incorrect thickness (too thick prevents proper mounting pressure)
- Leaving air bubbles
- Using pads that are too small
- Mixing different thermal interface materials
Maintenance and Longevity
Lifespan Factors
- Operating temperatures
- Thermal cycling frequency
- Pad quality
- Environmental conditions
Monitoring Performance
- Use software like MSI Afterburner or GPU-Z to monitor temperatures
- Baseline temperatures after installation
- Watch for gradual temperature increases over time
Professional vs. DIY Replacement
DIY Considerations
- Requires technical skills
- Risk of damaging components
- Warranty implications
- Specialized tools needed
Professional Service
- Expertise and experience
- Proper tools and workspace
- Warranty protection
- Quality assurance
Cost Considerations
Budget Options
- Basic silicone pads: $10-20 for a full GPU set
- Adequate for most users
- Standard thermal conductivity
Premium Options
- High-conductivity pads: $30-60+ for a full set
- Custom-cut pads with precise thickness, high conductivity & clean application
- Maximum performance benefits
Conclusion
Thermal pads are essential but often overlooked components in GPU cooling systems. Understanding their function, properties, and maintenance requirements can help you maintain optimal graphics card performance and longevity. Whether you’re building a new system, troubleshooting cooling issues, or performing routine maintenance, proper thermal pad selection and installation is crucial for effective heat management.
Regular monitoring of GPU temperatures and proactive thermal pad replacement can prevent thermal throttling, extend component life, and ensure your graphics card delivers peak performance for years to come.
How to Select the Right Thermal Pad for Your GPU
Graphics cards are powerful components that generate significant heat during operation. To maintain optimal performance and prevent damage, GPUs rely on sophisticated cooling systems that include thermal pads—small but crucial components that play a vital role in heat management. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about thermal pads for GPUs.
What is Thermal Conductivity?
Thermal conductivity is a key factor when it comes to thermal pads. It’s measured in watts per meter-Kelvin (W/mK). Pads with higher thermal conductivity transfer heat more efficiently.
Understanding Thickness Matters
The thickness of a thermal pad is also critical. Choose a thermal pad thickness matching the gap between the GPU components and the heatsink. Too thin or too thick a pad will create problems with heat transfer. Many GPUs will list the ideal sizes for replacement thermal pads.
Hardness and Ease of Use
The hardness of thermal pads is measured on the Shore OO scale. Softer pads tend to be easier to work with. Harder pads provide better contact with components but require careful application.
Table of Considerations
Here’s a quick reference table summarising the key factors when choosing a GPU thermal pad:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Measured in W/mK, higher values mean better heat transfer. |
| Thickness | Choose a pad thickness to match the gap between components and heatsink. |
| Hardness | Softer pads are easier to apply, harder pads ensure better contact. |
Beyond the Essentials
Some thermal pads offer additional features like:
- Electrical conductivity: Some pads conduct electricity. Be careful if you choose one of these types.
- Reusable: While most thermal pads are single-use, some are designed to be reusable.
Choosing the right thermal pad can greatly enhance your GPU’s cooling performance and lifespan. Consider these factors carefully to make the best decision for your specific setup.
Key Takeaways
- Thermal pads facilitate heat transfer from GPUs to heat sinks
- Pad effectiveness is determined by thermal conductivity, material, and size
- Correct application is crucial for optimal heat dissipation
Essential Attributes of Thermal Pads
Thermal pads are crucial in managing heat in electronic devices, particularly GPUs. They maintain optimal temperatures, ensuring the GPU’s performance and longevity.
Materials and Thermal Conductivity
The materials used in thermal pads affect their performance. Pads often consist of silicone filled with heat-conductive materials such as ceramic or metal particles. A pad’s ability to conduct heat, measured in watts per meter-Kelvin (W/mK), varies. Higher thermal conductivity translates to better heat transfer. For instance, the Arctic Thermal Pad has a conductivity of about 6.0 W/mK, whereas high-end pads like Thermal Grizzly offer up to 8.0 W/mK.
Selecting the Right Size and Thickness
Size and thickness are vital for a proper fit. They must match the space between the GPU and its heatsink. Pads vary, typically from 0.5 to 3 mm in thickness. Too thin, and the pad won’t fill the gap; too thick, and it might put unnecessary strain on the components. Users need to measure their device’s gap carefully and opt for a pad that aligns with these dimensions.
Compatibility with GPUs and Other Components
Compatibility ensures effective heat transfer and prevents damage. Thermal pads suitable for GPUs might not be ideal for other components like VRAM or motherboards from AMD or Intel. Users should check compatibility with their specific device model. Brands like MSI and Asus often provide information on compatible thermal solutions for their products.
Price Ranges and Brands
Prices for thermal pads range from around $10 to $25 for basic models, climbing to $50 and above for premium options. Brand reputation plays a role in quality and price. Thermalright and Arctic offer valued thermal pads, with Thermal Grizzly presenting higher-end pads. Users balance cost against needs, such as the requirement for high thermal conductivity or a particular size.
Application and Performance
Thermal pads play a vital role in a GPU’s cooling system by ensuring effective heat transfer from the GPU to the heatsink. Proper application and consistent performance of thermal pads can significantly impact the GPU’s efficiency and longevity.
Installation Process
To install a thermal pad, one must first clean the surfaces of the GPU and heatsink. Isopropyl alcohol wipes work well for this task. Next, cut the pad to match the GPU chip and place it without stretching it. The pressure from the heatsink mount will secure the pad in place. Care should be taken to avoid air gaps as they hinder heat transfer.
Enhancing Cooling Efficiency
High-quality thermal pads enhance cooling by filling the gaps between the GPU and the heatsink more effectively than air. This ensures that heat spreads evenly and the cooler operates optimally. Using fans in conjunction with thermal pads can further improve the cooling efficiency by dispersing heat away from the heatsink.
Durability and Maintenance
Thermal pads usually last for several years, and top brands specify their lifespan. Manufacturers like Thermal Grizzly, Thermalright, and Arctic offer pads that maintain their performance without drying out. However, if a GPU’s temperatures begin to rise significantly over time, it may be time to replace the pad.
Evaluating Performance Post-Installation
Test the GPU for temperature and performance changes after installing thermal pads. Software tools can monitor these changes. Lower temperatures generally indicate a successful installation. In contrast, high temperatures might suggest the need for a readjustment or a different thickness of the thermal pad.
Key Brands and Manufacturers
Some reputable brands to consider for DIY cooling include:
- Thermal Grizzly: Known for high-quality thermal pads like the Minus Pad 8.
- Thermalright: Offers the ODYSSEY line with a broad range of sizes and thicknesses.
- Arctic: Their TP-3 pad is another well-known option in the market.
- Alphacool and EKWB: Also provide reliable cooling solutions for a variety of components.
It’s important to choose a thermal pad that suits the specific needs of one’s GPU, considering factors such as heat transfer capabilities and thickness.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we address the common queries regarding GPU thermal pads, focusing on their thickness, replacement indicators, material quality, and their impact on cooling efficiency.
What is the optimal thickness for thermal pads used in GPUs?
The optimal thickness for GPU thermal pads is often between 0.5mm to 2mm. It should closely match the gap it needs to fill between the GPU and the heatsink to ensure efficient heat transfer.
How frequently should thermal pads on a GPU be replaced?
Thermal pads should be replaced if they harden, crack, or no longer transfer heat effectively. This could be every few years or when the GPU is disassembled for cleaning or maintenance.
What are the signs that indicate a need to replace my GPU’s thermal pads?
Signs that GPU thermal pads need replacing include overheating, thermal throttling, and unexpected shutdowns. Users may also notice poor performance during high-load tasks.
How do thermal pads improve the cooling performance of a GPU?
Thermal pads enhance cooling by filling gaps between the GPU and heatsink. This ensures efficient heat transfer and prevents overheating, resulting in better performance and stability.
Can the quality of thermal pads affect GPU temperatures?
Yes, the thermal conductivity of pads can affect GPU temperatures. Higher quality pads often have better thermal conductivity, leading to more effective heat dissipation.
What factors should be considered when purchasing thermal pads for high-performance GPUs?
Consider thermal conductivity, thickness, and hardness when selecting thermal pads. Match these with the GPU’s specifications to ensure optimal cooling performance.