When you undervolt a GPU, you adjust the amount of voltage it gets, which can improve performance and reduce temperatures. Traditional overclocking, where the hardware runs at higher than intended speeds, can use more power and create more heat. On the other hand, undervolting allows the GPU to run at lower voltages, using less power and producing less heat without significantly affecting performance. This approach is especially helpful for users who want to make their systems more efficient or extend the life of their components.
Undervolting a GPU involves making careful adjustments and testing to make sure everything stays stable. Tools like MSI Afterburner and Global Wattman are commonly used to check and change the voltage settings. By lowering the voltage and watching performance closely, you can achieve lower operating temperatures, which can lead to quieter and smoother gaming. It also helps reduce the strain on the graphics card, which is a bonus for systems that have trouble with cooling.
Tips for Success: How to Safely Undervolt Your GPU
Undervolting your GPU (graphics processing unit) is a way to make your computer run cooler, quieter, and use less power. It sounds complicated. But it doesn’t have to be. Here’s what you need to know.
Why would you undervolt?
There are a few good reasons to undervolt your GPU.
- Quieter Operation: Undervolting your GPU will also make your computer quieter. High-end GPUs have powerful fans that get loud under heavy load. Undervolting will lower the need for those fans, resulting in less noise.
- Extend the life of your GPU: Heat is the enemy of electronics. Reducing GPU temps can prolong its useful lifespan.
- Save money on your power bill: A GPU under heavy load can significantly increase power usage. Undervolting can lower your power bill.
Before you get started
It’s important to know that undervolting can cause your computer to become unstable. You won’t hurt your hardware by undervolting, but you might experience crashes. Start slow and be careful. We recommend checking the temperature of your GPU before and after undervolting to see how much improvement you achieve. If you aren’t happy with the results, you can always reset your GPU settings to their defaults.
Tools
Before you get started, you’ll need a couple of tools.
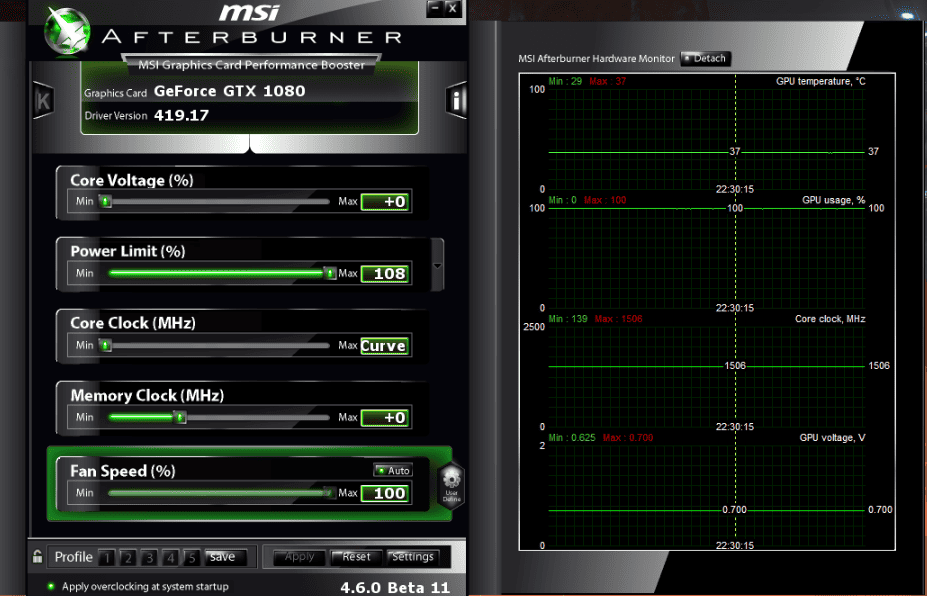
- MSI Afterburner: A free utility that allows you to adjust your GPU’s voltage and clock speed. You can download it from the MSI website.
- Benchmarking software: This is used to stress test your undervolt changes to make sure they are stable. Some popular options are 3DMark, Heaven Benchmark, or Superposition.
How to undervolt your GPU
Here’s a step-by-step guide on undervolting your GPU using MSI Afterburner.
- Check your current settings. Open MSI Afterburner and make a note of your GPU’s current voltage and clock speed.
- Open the curve editor. In MSI Afterburner, click on the Settings icon and go to the General tab. Click on the Unlock voltage control checkbox. Then open the curve editor by clicking on Ctrl+F.
- Lower the voltage. In the curve editor, find a point on the curve that corresponds to a lower voltage than your GPU’s current peak voltage. Select the point and then hold the Shift key and press Enter. Change the clock speed to match the original curve at that point. Then click on the Apply button.
- Test your undervolt. Run your chosen benchmark software to see if the undervolt is stable. If your system crashes, or if you notice any artifacts, raise the voltage slightly until you achieve stability.
- Rinse and repeat. Repeat steps 3 and 4 until you find the lowest stable voltage for your GPU. Keep tabs on the GPU’s temperature during your testing.
Undervolting Table
Here’s a table summarizing the key points about undervolting a GPU:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Benefits | Reduced heat, lower power usage, quieter computer, potentially longer lifespan for your GPU |
| Risks | Computer instability, crashes, and occasional visual glitches |
| Tools Needed | MSI Afterburner, benchmarking software |
Key Takeaways
- Undervolting reduces GPU power draw and heat.
- The process involves careful testing for stability.
- Lower temperatures can enhance system performance.
Understanding GPU Undervolting
Undervolting your graphics card can increase its efficiency by reducing power consumption and heat without compromising performance. This process involves adjusting the voltage settings for your GPU’s operation.
Basic Concepts of Undervolting
Undervolting refers to decreasing the default voltage of a GPU to a level that still allows the card to run stably at its designated frequencies. By supplying the GPU with lower voltage, the heat output and power draw decrease. This helps to maintain better temperatures and enhances the overall efficiency of the hardware. Silicon quality varies per chip, in what is known as the ‘silicon lottery’, affecting the undervolting potential of each graphics card.
Key points:
- Voltage: The amount of electrical power supplied to the GPU.
- Frequency: The speed at which the GPU operates; measured in MHz.
- Stability: The ability of the GPU to run without errors at set voltage and frequency.
Pros and Cons of GPU Undervolting
Pros:
- Lower Temperatures: Less voltage means less heat, contributing to cooler GPU operation.
- Reduced Power Consumption: A lower voltage reduces the amount of electricity the GPU uses, which can lower energy costs.
- Extended Lifespan: Operating at cooler temperatures can potentially lead to a longer hardware lifespan.
- Quieter Operation: Less heat generation often allows for slowed-down fans, resulting in quieter performance.
Cons:
- Time and Effort Required: Finding the ideal undervolt settings can take time and necessitates patient tweaking and testing.
- Potential for Instability: Incorrect undervolting can lead to crashes or hardware instability if the voltage is too low for the required frequency.
- Varying Results: Not all GPUs will undervolt equally well due to manufacturing differences; some might see negligible improvements.
By understanding the balance between voltage, frequency, and the thermal impact, enthusiasts can tailor their systems for a balance of performance and efficiency. However, considering the variances in individual GPUs, results can vary, and excessive undervolting can lead to system instability. Careful adjustments and testing are essential for achieving desired outcomes safely.
Executing The Undervolting Process
Undervolting a GPU involves adjusting the voltage and frequency to reduce heat and improve efficiency without compromising performance. Proper tools and a detailed guide help ensure safety and stability.
Tools and Software for Undervolting
Required software includes:
- MSI Afterburner or Radeon Wattman for tuning control.
- HWiNFO to monitor system details.
- FurMark or a similar benchmarking tool for stress testing.
Both MSI Afterburner and Radeon Wattman are free programs. They work with Nvidia and AMD graphics cards, respectively. HWiNFO helps you watch temperatures and other vital stats during the process. Run stress tests with tools like FurMark to check the GPU’s stability after changes.
Practical Guideline to GPU Undervolting
- Install the necessary software: Download and install MSI Afterburner or Radeon Wattman.
- Set a baseline: Before starting, run a benchmark to record default GPU performance.
- Begin tuning: Lower the voltage using the voltage-frequency curve in the software. Adjust in small MHz increments.
- Apply changes and test: After each adjustment, run a stress test to ensure stability.
- Find the balance: Look for the point where the GPU operates at lower temperatures with stable performance.
Always adjust settings gradually. Watch for instabilities like system shutdowns or graphical glitches.
Safety Measures and Testing
Follow these steps for a safe undervolting process:
- Save original settings: Create a profile with default settings in the undervolting software.
- Monitor closely: Keep an eye on temperatures and performance during testing.
- Test thoroughly: Use benchmarks and games to assess performance.
Start with mild adjustments and test for stability with each step. Look out for artifacts or fan noise changes. If issues appear, revert to the previous stable setting. Remember, stability is key. Avoid rushing the process.
Frequently Asked Questions
Undervolting a GPU involves careful adjustments to reduce power consumption and heat without harming performance. This section answers common questions on how to achieve these results safely and effectively.
What steps are involved in undervolting a GPU effectively?
To undervolt a GPU, one must first install software like MSI Afterburner. Then, access the voltage/frequency curve editor, decrease voltage settings gradually, and test stability and performance after each adjustment.
Can undervolting a GPU impact the overall system stability?
Undervolting reduces the power supply to the GPU, which can lead to system instability if not done correctly. Effective undervolting requires finding a balance where the GPU has enough power to operate reliably.
What are the potential risks associated with GPU undervolting?
If taken too far, undervolting can cause crashes, freezes, or even prevent the operating system from booting. It’s crucial to undervolt gradually and test for stability to avoid these risks.
How can one measure the temperature changes after undervolting a GPU?
To measure temperature changes post-undervolting, one can use hardware monitoring tools. These tools record the GPU’s temperature during idle and load conditions for a clear view of the impact.
Is it possible to undervolt a GPU using software tools like MSI Afterburner?
Yes, MSI Afterburner allows users to undervolt a GPU. It provides a user-friendly interface with a curve editor for adjusting the voltage to suitable levels.
How does GPU undervolting relate to power consumption and gaming performance?
Undervolting a GPU reduces power consumption, which can lower temperatures. This can lead to quieter operation and prolonged hardware life, without significantly impacting gaming performance when done correctly.