If you’re interested in drones, building your own can be a fun and rewarding project. You can create a drone that’s perfect for your needs by assembling a few essential parts like a frame, motors, and a flight controller. Many people use Arduino boards like the Uno or Nano to control their drones, and kits with detailed instructions make it easy for beginners to get started. If you’re looking for a more advanced project, adding features like an FPV (First-Person View) camera can make flying your drone even more exciting. This camera lets you see from the drone’s perspective while you control it, which can be great for both hobbyists and drone racing enthusiasts.
Building Your Dream Drone: DIY Projects for Enthusiasts
FPV Racing Drone
For thrill-seekers and tech enthusiasts, building an FPV (First Person View) racing drone is a rewarding project. These drones are built for speed and agility, requiring a lightweight frame, powerful motors, and a high-quality camera and transmitter for immersive flying. FPV racing drones can reach incredible speeds and perform acrobatic maneuvers, providing an adrenaline-pumping experience.
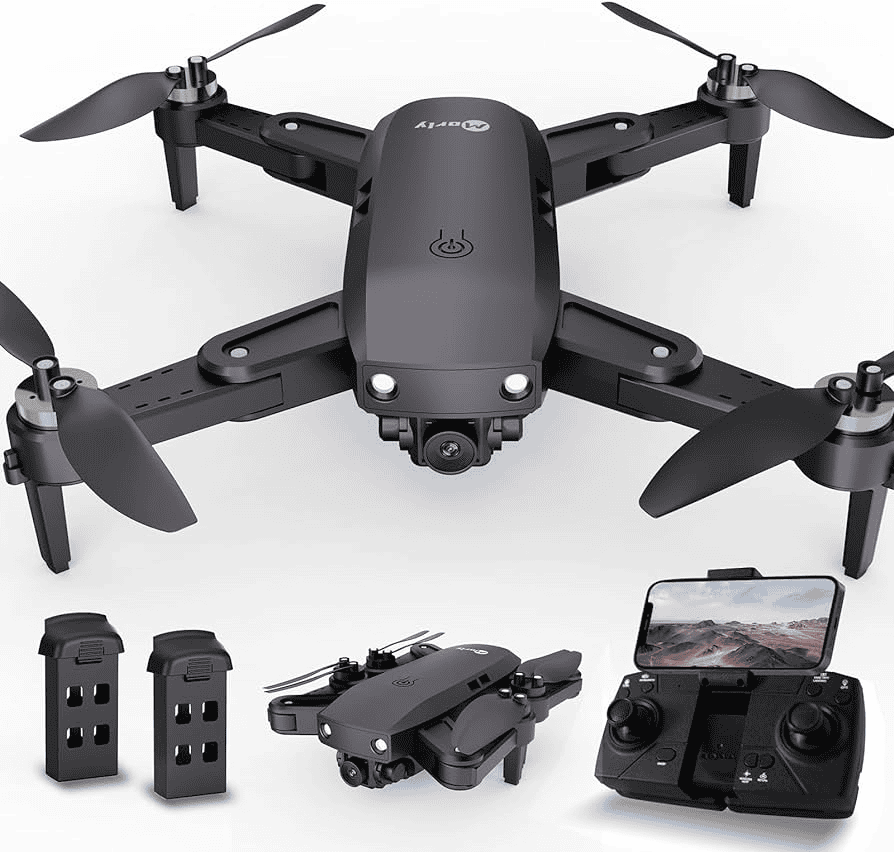

Autonomous Drone
Building an autonomous drone opens up a world of possibilities. These drones can be programmed to follow pre-determined flight paths, capture aerial footage, or perform specific tasks. Autonomous drones are increasingly used in various industries, including agriculture, construction, and inspection. Building one yourself allows you to experiment with cutting-edge technology and learn about programming and robotics.
Delivery Drone
The concept of drones delivering packages is becoming more and more realistic. By building a delivery drone, you can test out this innovative concept on a smaller scale. Your drone will need to be equipped with a payload mechanism to carry and release packages safely. It also needs a reliable GPS system for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
Photography/Videography Drone
For aerial photography and videography enthusiasts, building a customized drone allows you to capture stunning footage from unique perspectives. You can choose a drone frame that suits your camera equipment, optimize it for stability, and add features like gimbal mounts for smooth video recording. Building your own drone gives you complete control over the camera setup and flight capabilities.
DIY Drone Kit vs. Building from Scratch
There are two main approaches to building a DIY drone: using a pre-made kit or sourcing individual components and building it from scratch. Kits provide convenience and ease of assembly, but they limit customization options. Building from scratch offers more flexibility and control, but it requires a deeper understanding of drone technology and electronics.
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| DIY Drone Kit | Easy to assemble, suitable for beginners, usually includes all necessary parts | Limited customization options, less flexibility in component choices |
| Building from Scratch | Complete customization freedom, ability to choose specific components based on needs, potential for higher performance | Requires technical knowledge, more complex assembly, higher risk of errors |
Key Takeaways
- Essential parts for building a drone include a frame, motors, and a flight controller.
- Arduino can be used for controlling your DIY drone, and it’s beginner-friendly.
- Adding an FPV camera enhances the flying experience by providing a first-person view.
Essentials of Drone Building
Building a drone involves understanding its components and the necessary tools for assembling them. This guide outlines key parts and tools to help you get started on creating your custom drone.
Understanding Drone Components
Frame: The backbone of your drone. You can choose from materials like carbon fiber for strength and lightness.
Motors: These provide the necessary thrust. You may use coreless motors for smaller drones.
Propellers: Connected to the motors, they create lift.
Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs): These control the speed of the motors.
Power Distribution Board (PDB): Ensures efficient power delivery to each ESC.
Flight Controller: Serves as the brain of the drone. Popular options include *Arduino UNO, Mega, * and Nano.
Battery: A LiPo battery is commonly used for its high power-to-weight ratio.
Transmitter and Receiver: These allow remote control of the drone.
Sensors: GPS, accelerometer, and gyroscopes help stabilize and navigate the drone.
Camera: An FPV camera for first-person view flying.
Assembly and Tools Required
Soldering Iron: Essential for joining wires to components.
Heat Shrink: Insulate and protect soldered connections.
Standoffs: Used to mount the flight controller and other electronics securely.
Basic Tools: Screwdrivers, pliers, and wire cutters are needed.
Electrical Tape: Insulate wires and secure connections.
Circuit Diagrams: Helpful in wiring and connections.
Pin Headers: For connecting components like the Arduino.
Motor Driver Circuit: Allows the flight controller to manage motor speed and direction.
Battery Charger: Keeps the LiPo batteries ready for flight.
Combining these components and tools lets you build a functional drone. With the right knowledge and materials, you can create a drone tailored to your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section covers key questions about building and customizing DIY drones.
How can you integrate a camera into a DIY drone?
To add a camera, choose one designed for drones. Mount it securely, usually at the front of the drone. Connect the camera to the flight controller. Ensure the power source is stable. Use real-time video transmission systems for live feeds.
What are the essential components of a DIY drone kit?
A basic DIY drone kit includes a frame, motors, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), a flight controller, a battery, a transmitter, and a receiver. Propellers and a power distribution board (PDB) are also needed.
What are some innovative ideas for drone-based DIY projects?
Innovative projects include creating drones for aerial photography, building a drone with delivery capabilities, or designing a drone for environmental monitoring. Others may focus on automatic mapping or agricultural surveys.
What are the steps to build a drone for educational purposes?
First, start with a clear project plan. Gather all necessary parts. Assemble the frame and attach the motors and ESCs. Connect the flight controller and battery. Calibrate the system using software. Test flight in a safe area.
How can you construct a cost-effective DIY mini drone?
Select small, affordable components. Use lightweight materials for the frame. Choose low-cost motors and a compact flight controller. Opt for a simple, minimal design. Make sure to practice careful budgeting and sourcing.
What are the financial considerations of building vs. buying a drone?
Building may save money and offer customization, but it requires time and skills. Buying a drone is quicker and provides warranties but can be more expensive. Consider costs of tools and replacement parts when building.