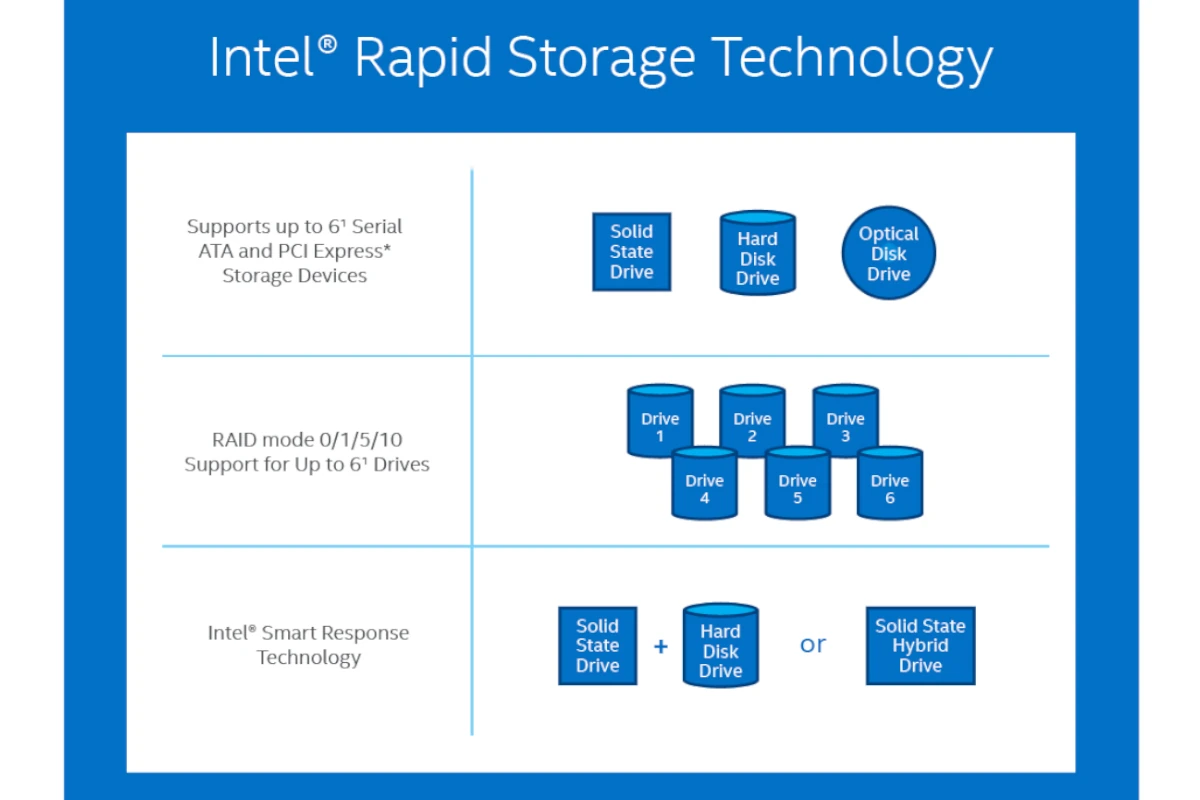
Intel Rapid Storage Technology, often referred to as RST, is a solution created by Intel to make computer systems with SATA drives faster and more reliable. It is software and a driver that speeds up and improves how data is transferred between high-speed solid-state drives (SSDs) and traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). RST combines multiple drives to improve the speed of reading and writing to the storage devices. It is beneficial for users who want faster boot times, quicker data access, and an overall more responsive system.
RST supports RAID setups that provide data protection and increased performance. It also allows users to customize their storage system for specific needs, such as emphasizing redundancy, speed, or a mix of both. Additionally, with Intel’s Smart Response Technology, users can combine a smaller SSD as a cache with an HDD to create a cost-efficient, high-performance storage solution that combines the speed of an SSD with the capacity of an HDD.
What is Intel Rapid Storage Technology?
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a Windows-based software and firmware solution that improves the performance and reliability of computers equipped with SATA-based storage (hard drives and SSDs). |
| Features | RST offers several key features: * RAID: Enables RAID configurations (RAID 0, 1, 5, 10) for improved data redundancy, protection, or performance. * AHCI: Provides the AHCI interface, a standard allowing faster communication between the SATA controller and storage devices. * Intel Smart Response Technology: Uses a small, fast SSD as a cache for a larger, slower hard drive, boosting system responsiveness. |
| System Requirements | * Intel Chipset: RST usually requires specific Intel chipsets. Check the compatibility list for your motherboard. * SATA Drives: Works with SATA hard drives and SSDs. * Windows OS: Designed for Windows operating systems. |
| Benefits | * Improved Performance: Can boost storage performance, especially in RAID configurations or when using Intel Smart Response Technology. * Data Protection: RAID levels like RAID 1, 5, and 10 offer redundancy and protection against data loss due to disk failure. |
Important Notes:
- Need for RST: Modern operating systems and SATA controllers do a good job managing storage. RST might not be strictly necessary for everyone.
- Intel Optane: RST also manages Intel Optane Memory, which acts as a cache-like acceleration drive.
Key Takeaways
- Intel RST optimizes SATA drive performance and reliability.
- It supports RAID configurations for a customizable storage experience.
- Smart Response Technology enables a blend of speed and storage capacity.
Understanding Intel Rapid Storage Technology
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (Intel RST) is a powerful tool designed to boost storage performance and reliability for systems equipped with SATA drives. It uses various methods to improve the computing experience across desktop and mobile platforms, as well as Intel chipsets.
Core Technologies and Benefits
Intel RST incorporates features such as RAID and Rapid Recover Technology to enhance the capability of SATA disks and solid-state drives. The software offers several core benefits:
- Storage Performance: By enabling configurations like RAID 0, it enhances speed and the speed of data access.
- Reliability and Data Protection: Features such as RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10 provide data redundancy and fault tolerance, helping to protect against disk failure and data loss.
Supporting technologies like AHCI and NCQ are integral to Intel RST, improving the efficiency of storage operations. Intel’s Smart Response Technology enhances the responsiveness of PCs by allowing an SSD to act as a cache for frequently accessed data.
Supported Hardware and Systems
The Intel RST driver and firmware work with a broad range of Intel chipsets and processors, such as Core i9, Alder Lake, and Ice Lake. The compatibility extends to various operating systems and hardware configurations. Here’s an overview:
- Chipsets: Intel RST supports a variety of Intel chipsets.
- Drives: It facilitates RAID configurations with SATA disks, solid-state drives, and PCIe NVMe storage.
- Systems: Desktop and mobile systems using supported Intel chipsets can utilize Intel RST.
Before using Intel RST, it’s crucial to check in the BIOS menu if the system supports VMD (Volume Management Device) and ensure the relevant settings are configured.
Configuring RAID Levels for Various Needs
Setting up RAID levels correctly can lead to vastly different outcomes depending on the user’s needs, be it speed, data protection, or a balance of both. Here’s how they differ:
- RAID 0 (Striping): Offers increased speed by spreading data across multiple drives but offers no fault tolerance.
- RAID 1 (Mirroring): Provides data redundancy by duplicating data across two drives for protection against failure.
- RAID 5 and RAID 10: These offer a combination of speed and data protection, utilizing multiple drives for data redundancy and performance improvements.
- Matrix RAID: Allows for different RAID levels on separate partitions of the same drive for tailored user needs.
Configuring these RAID levels can be done through the Intel RST BIOS menu or within the operating system using the Intel RST application. Depending on the system’s requirements, Intel RST provides a range of options to optimize storage for a better computing experience.
Intel RST Technology in Action
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (Intel RST) is a software application designed to improve the performance and reliability of systems with SATA drives. Using an array of features, it allows for advanced management of storage units, ensuring efficient operation for users.
Optimizing System Performance
Intel RST can significantly accelerate system performance, particularly in RAID 0 configurations. RAID 0 splits data across storage drives, allowing faster data access and improved response times. When paired with Intel Optane memory, the technology further enhances system speed, reducing load times for applications and files. This boost is especially beneficial in resource-intensive tasks like video editing.
- CPU Load Reduction: By offloading storage operations from the CPU, Intel RST allows the CPU to focus on more crucial tasks.
- Caching: Utilizes fast memory to store frequently accessed data, speeding up read/write processes.
- Link Power Management: Saves energy by putting SATA links into a sleep state when not in use.
- Dynamic Storage Accelerator: Adapts system power policies to increase storage performance dynamically.
Management and Recovery Features
Intel’s technology equips users with tools for seamless storage management. The software includes Rapid Recover Technology, which creates recovery points to safeguard data, and supports Intel Rapid RAID, which aids in configuring RAID levels for better data protection.
- Rapid Recover Technology: Helps users quickly recover a system if a drive failure occurs.
- Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI): Enables features like hot-plugging and native command queuing.
Installation and Driver Updates
To ensure Intel RST operates smoothly, it’s important to regularly update the software and drivers. Updates often include bug fixes, support for new operating systems, and improvements to existing features.
- Installation:
- Check if your system supports Intel RST.
- Download the drivers from the official Intel website or through the Microsoft Store.
- Run the installer and follow the prompts to install the software.
- Driver Updates:
- Visit the Intel website to locate the latest Intel RST drivers.
- Compare your current driver version to the latest release notes or readme files.
- Download and install the latest driver if an update is available.
Consider checking for known issues listed by Intel before updating to ensure compatibility with your system’s configuration. Users running Windows 10 or Windows 11 should look for driver support specific to their operating system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a system that improves both performance and reliability for your computer’s storage devices. It is particularly useful when you’re working with Serial ATA (SATA) drives and chipsets from Intel. Here are some common questions people ask about Intel RST.
How does Intel Rapid Storage Technology enhance system performance?
Intel RST uses various methods to speed up data transfer and access times for storage drives. It does this by optimizing the way data is read from and written to the disk, resulting in faster system responsiveness and improved load times.
Is it recommended to enable Intel Rapid Storage Technology in the BIOS settings?
Yes, enabling Intel RST in the BIOS is generally recommended as it allows the technology to interact directly with the storage hardware at a low level, leading to the performance enhancements it is designed to provide.
What benefits does Intel Rapid Storage Technology offer for gaming?
For gaming, Intel RST reduces game load times and may improve in-game performance by ensuring data is quickly accessible. This is especially noticeable in games that frequently load new textures and environments.
What is the purpose of Intel Rapid Storage Technology on laptops?
On laptops, Intel RST aims to improve battery life and data protection. It manages how the storage drives operate, reducing power usage when full speed isn’t needed and providing options to protect data in case a drive fails.
Can Intel Rapid Storage Technology be safely disabled or turned off?
Intel RST can be turned off without harming the system. However, doing so might result in slower disk performance and reduced energy efficiency. It’s safe to disable it if you don’t need the benefits it offers.
What are the implications of using Intel Rapid Storage Technology with solid-state drives (SSDs)?
Using Intel RST with SSDs can lead to improvements in the drive’s performance and lifespan. This technology can optimize the way data is stored on the SSD, potentially speeding up the overall system performance.