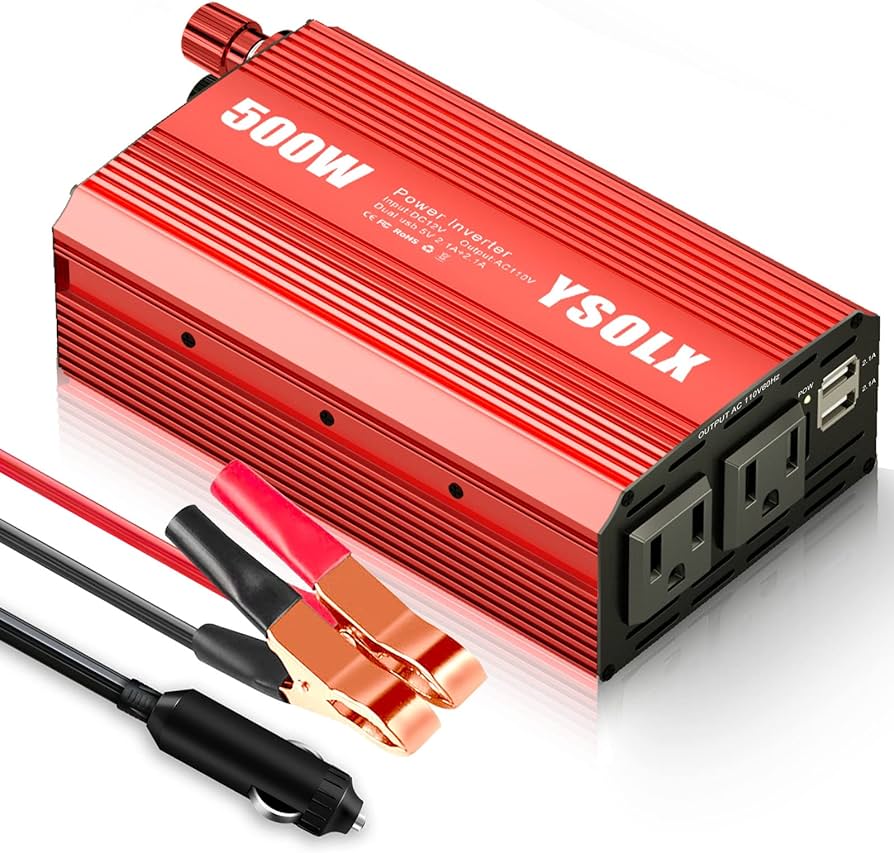
A power inverter is a device that changes direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This allows devices and appliances to run on a power source like a battery that only provides DC power. Many household items and gadgets need AC power to operate, making inverters essential for a wide range of applications, from emergency backup to camping trips. For example, when using renewable energy sources like solar panels, which generate DC electricity, a power inverter is crucial to convert this power into usable AC electricity for your home.
Power inverters help ensure that you have a reliable power source for your essential devices, no matter the situation. Understanding how they work and where they can be used can help you make the most of this technology in your daily life. Power inverters are indispensable tools for anyone needing AC power in situations where only DC power is available. By understanding how they work and choosing the right one for your needs, you can enjoy the convenience and versatility of portable power.
Power on the Go: Understanding Inverters
How Power Inverters Work
Power inverters transform direct current (DC) power, like from a car battery or solar panel, into alternating current (AC) power. This AC power is what most household appliances and electronics use. This conversion makes it possible to run devices that normally plug into a wall outlet using a DC power source.
Types of Power Inverters
There are two main types of power inverters:
- Modified Sine Wave Inverters: These are more affordable but produce a rougher form of AC power. They work well for simple devices like lights and power tools, but may not be suitable for sensitive electronics.
- Pure Sine Wave Inverters: These provide cleaner, smoother AC power that’s similar to what you get from a wall outlet. They are ideal for sensitive electronics, appliances with motors, and medical equipment.
Uses for Power Inverters
Power inverters are incredibly versatile and can be used in various scenarios:
- In vehicles: Charge phones, laptops, or power small appliances while on the road.
- Camping and RVing: Run TVs, refrigerators, and other essentials in remote areas.
- Emergency backup power: Keep critical devices running during power outages.
- Off-grid living: Provide AC power in locations without access to the electrical grid.
Choosing the Right Power Inverter
When selecting a power inverter, consider the following factors:
- Power requirements: Determine the wattage of the devices you need to power. The inverter’s wattage should be higher than the total wattage of your devices.
- Type of inverter: Choose a modified sine wave inverter for basic devices or a pure sine wave inverter for sensitive electronics.
- Additional features: Some inverters offer extra features like USB ports, multiple outlets, or remote control.
Safety Precautions
When using a power inverter, it’s crucial to follow safety guidelines:
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Proper grounding: Connect the inverter to a properly grounded power source.
- Overload protection: Don’t exceed the inverter’s wattage rating.
- Read the manual: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe use.
Power Inverter Comparison
| Feature | Modified Sine Wave | Pure Sine Wave |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Power quality | Rough | Smooth |
| Suitable devices | Basic electronics, power tools | Sensitive electronics, appliances with motors |
| Applications | Cars, camping, basic power needs | RVs, off-grid living, medical equipment |
Key Takeaways
- A power inverter converts DC to AC power.
- Inverters allow household items to run on DC sources like batteries.
- They are useful in emergencies, camping, and homes with solar panels.
Understanding Power Inverters
Power inverters convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). They are vital in many applications where AC power is needed.
Fundamentals of Power Inversion
A power inverter changes DC to AC. It achieves this by using electronic components like transistors and semiconductors. This conversion process allows devices that run on AC power to operate using a DC source, such as a battery.
Inverters generate a specific output frequency and voltage. The conversion involves oscillators that create a waveform. Common types include sine wave, square wave, and modified sine wave inverters. The choice of inverter can affect the efficiency and performance of the connected devices.
Types of Inverters
Pure Sine Wave Inverter: Provides clean, smooth AC power. Suitable for sensitive electronics.
Modified Sine Wave Inverter: Generates a less smooth waveform. Less expensive but may cause noise in some devices.
Square Wave Inverter: Simplest design, produces a rough waveform. Typically used for simpler electronics.
Single-Phase Inverter: Commonly used in residential settings. Converts DC to single-phase AC.
Three-Phase Inverter: Used in industrial applications. Converts DC to three-phase AC.
Key Components
Transistors (IGBT, MOSFET): Switches that control the flow of electricity in the inverter.
Oscillators: Create the waveform needed for AC output.
Semiconductors: Materials that help in the conduction and switching processes.
Rectifiers: Convert AC to DC within the inverter for specific functions.
Terminals and Switches: Connect the inverter to other components and control its operation.
Voltage Regulators: Ensure stable output voltage to protect connected devices.
Each component plays a crucial role. The efficiency of these parts determines the performance and reliability of the inverter. Proper design and quality materials are essential to avoid issues like harmonic distortion and ensure a stable output.
By focusing on these aspects, one can understand the functionality and importance of power inverters in various applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common questions about power inverters, covering their uses in homes and vehicles, how they work, and practical steps to use them effectively.
How can a power inverter be used at home?
A power inverter can convert DC electricity from batteries or solar panels into AC power for household appliances. This allows people to use renewable energy to run home devices like lamps, televisions, and refrigerators.
In what ways does a power inverter operate within a vehicle?
Within a vehicle, a power inverter converts the DC power from the car’s battery into AC power. This makes it possible to use household items like laptops, chargers, and small appliances while on the road.
What are the steps for utilizing a power inverter with a vehicle’s battery?
First, ensure the vehicle’s battery is in good condition. Connect the inverter to the battery terminals using proper cables. Turn on the inverter. Plug in your AC device to the inverter. Always follow safety guidelines to prevent damage or injury.
What are the fundamental functions of a power inverter generator?
A power inverter generator combines a traditional generator with an inverter to provide stable AC power. It is portable and efficient, making it ideal for sensitive electronics. It adjusts the engine speed according to the power demand, which saves fuel.
What are the applications of a power inverter while camping?
While camping, a power inverter can be used to power lights, cooking devices, and electronic gadgets. It is especially useful in remote areas where there is no access to conventional power sources.
What are the reasons to consider using an inverter?
Using an inverter allows access to AC power from DC sources, enabling the use of standard appliances during power outages or in off-grid areas. It can enhance the convenience and functionality of various devices without needing a direct AC supply.