A CPU cooler is an essential component of any PC, designed to manage the heat generated by the processor. Without effective cooling, the CPU can overheat, leading to reduced performance and potential damage. CPU coolers come in various types, each offering unique benefits and fitting different use cases.
There are three primary categories of CPU coolers: air coolers, All-in-One (AIO) liquid coolers, and custom or open-loop cooling systems. Air coolers use fans and heat sinks to dissipate heat, making them a cost-effective and straightforward option. In contrast, AIO coolers integrate liquid cooling within a sealed unit, often offering quieter and more efficient cooling.
Selecting the right CPU cooler depends on factors such as compatibility with your processor and case, cooling performance, noise levels, and budget. Careful consideration of these aspects ensures that your PC remains efficient, cool, and quiet, enhancing both performance and longevity.

Cooling Down the Brain of Your Computer
A CPU cooler is a device designed to draw heat away from the CPU (Central Processing Unit) and other components inside your computer case. The CPU is the “brain” of your computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. As it works, it generates a lot of heat, and if that heat isn’t managed properly, it can cause performance issues or even damage the CPU.
Why Does Your CPU Need a Cooler?
Your CPU is like a tiny furnace, constantly generating heat as it processes data. Overheating can lead to:
- Reduced performance: Your computer may slow down or become unresponsive as the CPU throttles its speed to prevent damage.
- System instability: Overheating can cause crashes, freezes, and other unexpected errors.
- Component damage: In extreme cases, prolonged overheating can permanently damage the CPU and other components.
How Does a CPU Cooler Work?
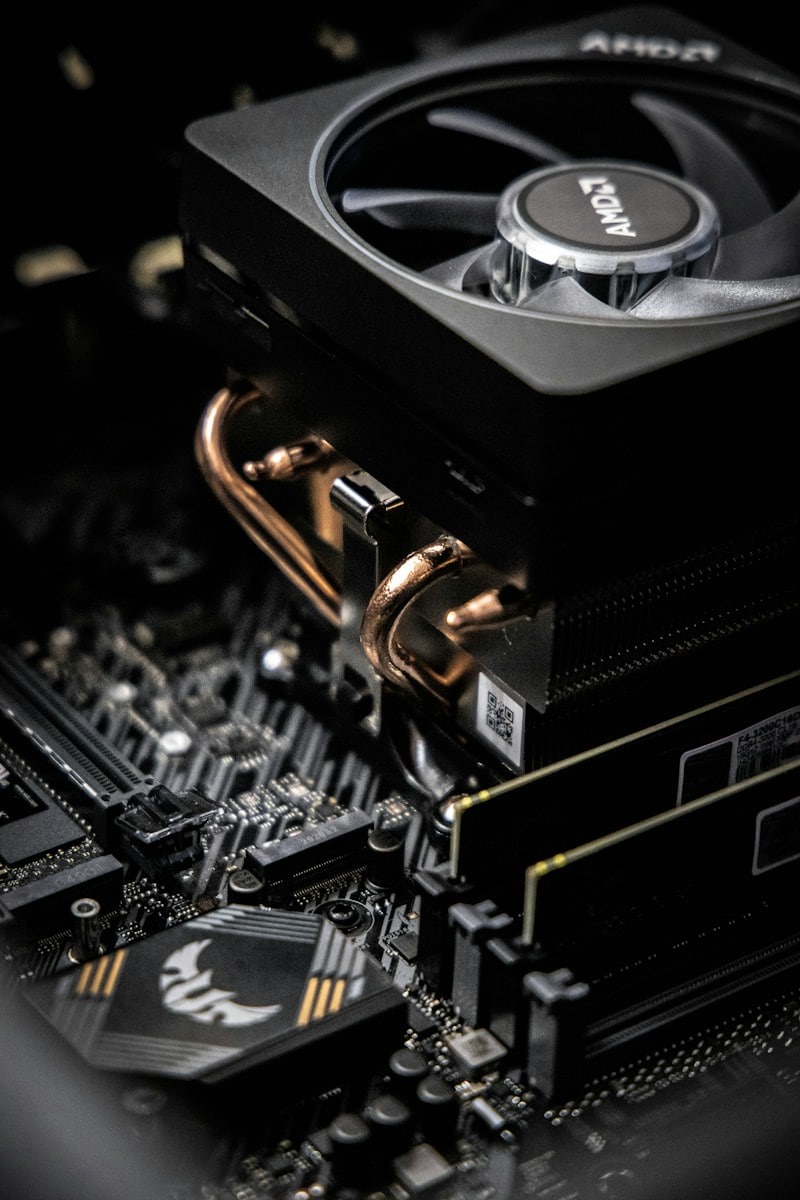
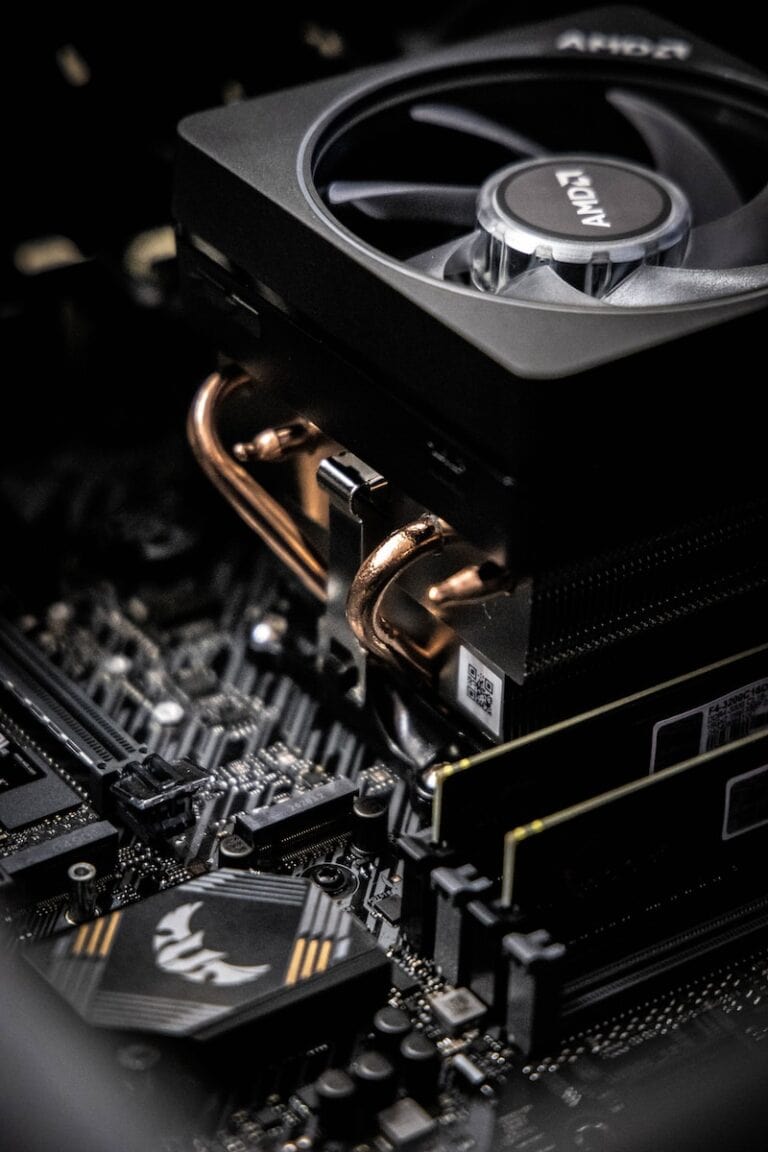
A CPU cooler typically consists of two main components: a heatsink and a fan.
- Heatsink: The heatsink is a metal block with fins that increase its surface area. It absorbs heat from the CPU and dissipates it into the surrounding air.
- Fan: The fan blows air over the heatsink, accelerating the heat dissipation process.
Together, the heatsink and fan work to keep your CPU cool and operating at optimal temperatures.
Types of CPU Coolers
There are two main types of CPU coolers: air coolers and liquid coolers.
Air Coolers
Air coolers are the most common type of CPU cooler. They are relatively inexpensive, easy to install, and effective at cooling most CPUs under normal operating conditions. Air coolers use a combination of heat pipes, a heatsink, and a fan to dissipate heat.
Liquid Coolers
Liquid coolers are more complex and expensive than air coolers, but they offer superior cooling performance, especially for high-end CPUs and overclocking scenarios. They use a closed-loop system with a pump, radiator, and water block to transfer heat away from the CPU.
Choosing the Right CPU Cooler
The right CPU cooler for you depends on several factors, including:
- CPU: The type and model of your CPU will determine its heat output and the type of cooler it requires.
- Usage: If you use your computer for demanding tasks like gaming or video editing, you’ll need a more powerful cooler than someone who primarily uses it for web browsing and email.
- Budget: CPU coolers range in price from affordable to high-end. Consider your budget when choosing a cooler.
- Case size: Make sure the cooler you choose is compatible with your computer case.
Comparison Table: Air Coolers vs. Liquid Coolers
| Feature | Air Cooler | Liquid Cooler |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Performance | Good | Excellent |
| Noise Level | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Price | Affordable | Expensive |
| Installation | Easy | Moderate to Difficult |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate |
Maintaining Your CPU Cooler
To ensure your CPU cooler functions properly, it’s important to perform regular maintenance. This includes:
- Cleaning: Dust and debris can accumulate on the heatsink and fan, reducing their efficiency. Clean them regularly with compressed air or a soft brush.
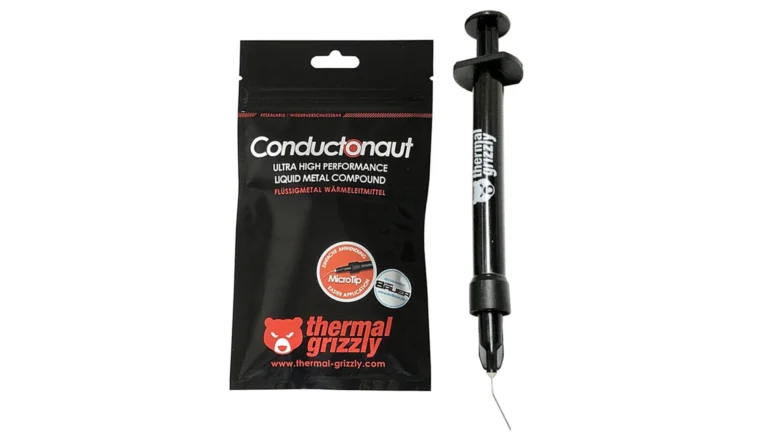
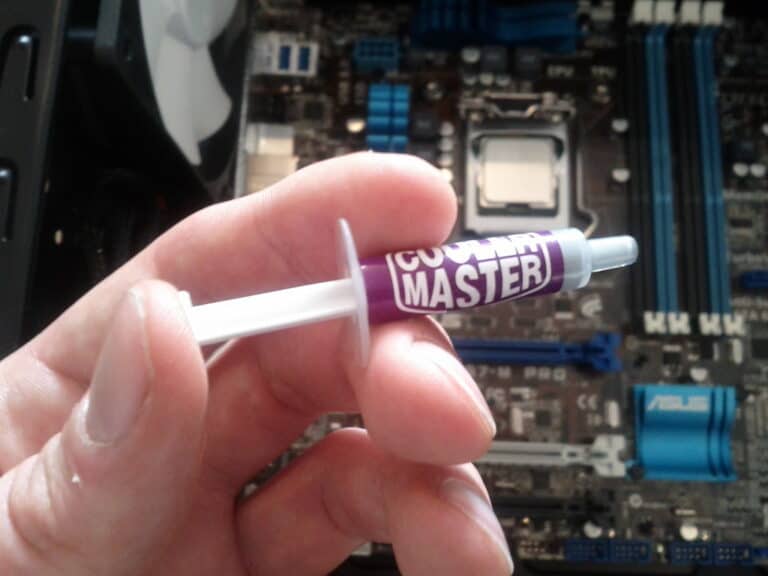
- Thermal paste: The thermal paste between the CPU and heatsink helps to transfer heat. Reapply thermal paste if it dries out or becomes ineffective.
By following these tips, you can keep your CPU cool, ensure optimal performance, and extend the lifespan of your computer components.
Key Takeaways
- CPU coolers prevent overheating and protect the processor.
- Air and liquid coolers are the main types available.
- Choose based on compatibility, performance, noise, and budget.
Types of CPU Coolers
Choosing the right CPU cooler is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of your computer. There are three main types of CPU coolers: air coolers, liquid coolers, and All-In-One (AIO) coolers.
Air Cooling
Air coolers use air to dissipate heat away from the CPU. These consist of a heatsink and at least one fan. The heatsink, typically made of copper or aluminum, absorbs heat from the CPU. The fan then blows air over the heatsink’s fins, transferring the heat away.
Pros:
- Usually more affordable.
- Easier to install.
- Low maintenance.
Cons:
- Can be bulky.
- May not be as effective for overclocking.
Key Points:
- Heatsink material matters: copper offers better thermal conductivity.
- Fan size and speed can impact cooling efficiency.
Liquid Cooling
Liquid coolers use a liquid (usually a mixture of water and coolant) to transfer heat away from the CPU. The system includes a pump, a radiator, and tubes to circulate the liquid. Heat is transferred from the CPU to the liquid, which is then cooled by the radiator’s fans.
Pros:
- Superior cooling performance.
- Quieter operation.
- More efficient for high-performance or overclocked systems.
Cons:
- More complex to install.
- Higher cost.
- Risk of leakage.
Key Points:
- Radiator placement and size can affect performance.
- Maintenance may require periodic coolant top-ups.
- Custom loops offer flexibility but are more complex.
All-In-One (AIO) Coolers
AIO coolers are a compromise between air coolers and custom liquid cooling systems. These self-contained units include a pump, tubes, and a radiator pre-filled with coolant. AIO coolers provide the benefits of liquid cooling without the complexity.
Pros:
- Easier installation compared to custom loops.
- Effective cooling performance.
- Reduced risk of leaks due to sealed design.
Cons:
- More expensive than air coolers.
- Potential for pump noise over time.
- Smaller radiators can limit cooling efficiency.
Key Points:
- Compatibility with different case sizes varies.
- Vendor reliability and warranty are crucial factors.
- Regularly check for dust accumulation on the radiator.
Key Considerations for CPU Coolers
When choosing a CPU cooler, focus on performance, compatibility, and noise levels to ensure optimal system operation and reliability.
Cooling Performance
Cooling performance is crucial. It determines how well the cooler maintains the CPU temperature within safe limits. Look for coolers with high Thermal Design Power (TDP) ratings, as they dissipate more heat. Benchmark tests are useful for comparing real-world performance. Consider liquid coolers for enhanced cooling efficiency, especially for overclocking. All-in-one (AIO) liquid coolers can offer better heat distribution compared to traditional air coolers, which rely on heat sinks and fans.
Compatibility and Installation
Compatibility with your motherboard and CPU socket is essential. Coolers need to match the specific socket type, such as LGA 1700 for Intel 12th Gen CPUs or AM4 for AMD Ryzen. Check if the cooler includes the necessary mounting brackets. Installation can vary; while some coolers require complex setups, others are more user-friendly. Ensure there is enough space around the CPU area for the cooler. This often involves checking the cooler’s clearance with other motherboard components like RAM.
Size and Form Factor
Size and form factor are important to consider, especially if space is limited. Low-profile coolers are suited for smaller cases but may offer less cooling power. Large tower coolers provide excellent performance but require ample space within the PC case. Measure available space inside the case to avoid clearance issues with the cooler. The height, width, and depth of the cooler should be checked against the dimensions of the PC case and other installed components.
Noise and Aesthetics
Noise level is a key consideration, especially for users seeking a quiet system. Air coolers with larger fans tend to operate at lower RPMs, reducing noise. Liquid coolers often feature pumps that can also produce sound, but many high-quality models operate quietly. Aesthetics can enhance the overall look of a build. Consider coolers with RGB lighting if visual appeal matters. Many modern coolers offer customizable RGB options to match the system’s color scheme.
Frequently Asked Questions
A CPU cooler plays a vital role in maintaining the performance and longevity of a processor. Different types of coolers are better suited for varied uses such as gaming, while liquid and air cooling have their own advantages and disadvantages.
What is the purpose of a CPU cooler in a computer system?
A CPU cooler dissipates the heat produced by the processor, preventing overheating. It ensures the CPU runs efficiently and avoids thermal throttling, which can degrade performance. By maintaining lower temperatures, CPU coolers contribute to a longer lifespan for the processor.
How do CPU coolers differ for gaming applications?
Gaming often places a high demand on the CPU, generating significant heat. High-performance CPU coolers, particularly those with better heat dissipation capabilities, are essential for gaming systems. They typically have larger heat sinks, more powerful fans, or employ liquid cooling solutions to keep temperatures stable during intense operation.
What are the pros and cons of liquid cooling compared to air cooling?
Liquid cooling provides superior thermal performance and quieter operation due to the efficient transfer of heat away from the CPU. However, it is more expensive and complex to install. Air cooling is generally more cost-effective and easier to install but may be noisier and less efficient at high-performance demands.
What criteria determine the quality of a CPU cooler?
Key criteria include thermal performance, compatibility with the CPU and motherboard, noise levels, and build quality. A high-quality cooler should efficiently dissipate heat, fit well with the system components, operate quietly, and be robustly constructed.
Can a CPU cooler be used interchangeably with a case fan?
No, a CPU cooler cannot be used interchangeably with a case fan. CPU coolers are specifically designed to handle the concentrated heat output of the CPU, whereas case fans aid in general airflow within the PC case. Each component has a distinct role and design suited to its specific cooling task.
What are the distinctions between AIO and traditional air CPU coolers?
AIO (All-in-One) coolers integrate a pump, radiator, and coolant into a closed-loop system and typically offer better cooling performance and quieter operation than traditional air coolers. Traditional air coolers rely on a heatsink and fan mechanism, which is simpler and more affordable but may be less effective at high thermal loads.