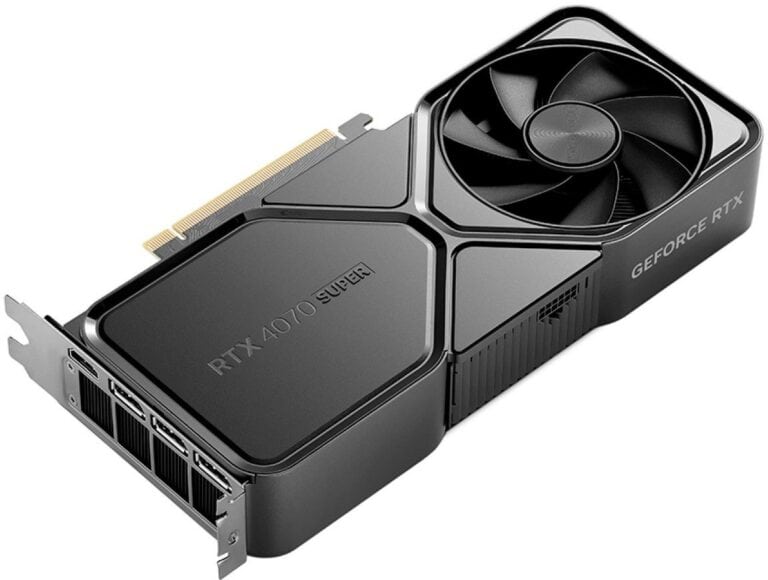
Modern GPUs rely heavily on VRAM (Video RAM) for rendering graphics, gaming, and professional workloads. Many users wonder if you can add more VRAM to extend the life of an older graphics card or boost performance.
Upgrading your GPU’s memory might seem like it would be a straightforward way to boost your computer’s performance, especially for graphics-intensive tasks. After all, upgrading your system RAM memory can be easily done.
Unfortunately, for graphics cards, it’s not quite as simple. Let’s dive into the complexities and realities of enhancing your GPU’s memory.
Understanding GPU Memory (VRAM)
- VRAM is high-speed memory (like GDDR6, GDDR6X, or HBM) soldered directly onto the GPU’s PCB (printed circuit board).
- It works in tandem with the GPU core and is tightly integrated with the memory controller.
- Unlike system RAM, VRAM isn’t modular—you can’t just plug in more like you do with DDR RAM sticks.
Can You Physically Add More VRAM?
Short answer: No, not in a practical way.
Here’s why:
- Soldered Chips – VRAM chips are soldered onto the GPU board, not slotted.
- Memory Controller Limits – The GPU’s architecture defines how much memory it can address. For example, a GPU designed for 8 GB may not support 16 GB even if you add chips.
- Firmware/BIOS Restrictions – Even if you somehow soldered new chips, the GPU BIOS would need modification to recognize them.
- High Risk of Damage – Attempting to desolder and replace VRAM requires advanced tools, micro-soldering skills, and knowledge of memory mapping.
Some hardware modders have successfully upgraded GPU VRAM (example: upgrading an 8 GB card to 16 GB), but these are rare, experimental projects—not something feasible for everyday users (source: Hackaday, Reddit).
✅ Practical Alternatives to “Adding” VRAM
Since physical upgrades aren’t realistic, here are better options:
- Upgrade to a New GPU – The most effective solution for more VRAM.
- Optimize In-Game Settings – Lower texture resolution, shadows, or ray tracing to reduce VRAM usage.
- Use Upscaling Tech – NVIDIA DLSS, AMD FSR, or Intel XeSS reduce VRAM load while maintaining quality.
- Leverage System RAM (Shared Memory) – Some integrated GPUs allow allocating more system RAM as VRAM in BIOS/UEFI.
- Cloud Gaming or Remote Rendering – Offload heavy workloads to services like GeForce NOW or Azure.
🛠️ Bottom Line
- Physically adding VRAM to a GPU is not practical for 99.9% of users.
- It requires micro-soldering, BIOS modding, and deep hardware knowledge—and success isn’t guaranteed.
- The best solution is to upgrade your GPU or optimize your software settings.
Adding Memory To A GPU
Here’s a table addressing the possibility of physically adding memory to a GPU:
| Reason | Answer |
|---|---|
| GPUs are soldered onto the motherboard: | No, physical addition of memory is impossible. |
| Limited space on laptops and mobile devices: | No, GPUs are often integrated into the device, leaving no room for expansion. |
| Cost considerations: | Manufacturers often design GPUs with specific memory configurations for cost-effectiveness. Adding memory would require a new GPU design. |
Key Points:
- Physical limitations: GPU memory is usually soldered directly onto the graphics card’s circuit board, making it extremely difficult to replace or upgrade.
- Integrated GPUs: In laptops and many mobile devices, the GPU is often integrated into the main processor, further limiting upgrade options.
- Design and cost factors: Manufacturers carefully consider memory requirements and costs during GPU design. Adding memory would involve significant engineering and cost implications.
Alternative Solutions:
- Upgrade to a GPU with more memory: If you need more memory for demanding tasks, consider purchasing a new GPU with a higher memory capacity.
- Optimize graphics settings: Adjust in-game settings or software configurations to reduce memory usage and improve performance within the available memory constraints.
- Explore cloud-based solutions: For certain tasks, consider using cloud-based services that can offload GPU-intensive workloads to remote servers with more powerful hardware.
Key Takeaways:
- GPU memory, or VRAM, plays a crucial role in graphics performance.
- Upgrading GPU memory is not as straightforward as it seems due to technical and hardware limitations.
- Alternative methods exist to optimize GPU performance without physical modifications.
Understanding GPU and Its Memory
What is GPU Memory?
The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is the heart of rendering images and videos on your computer. Its memory, known as Video RAM (VRAM), is crucial for storing graphical data like textures and rendering them efficiently. Unlike regular system RAM, VRAM is specifically designed to handle the high demands of graphics processing.
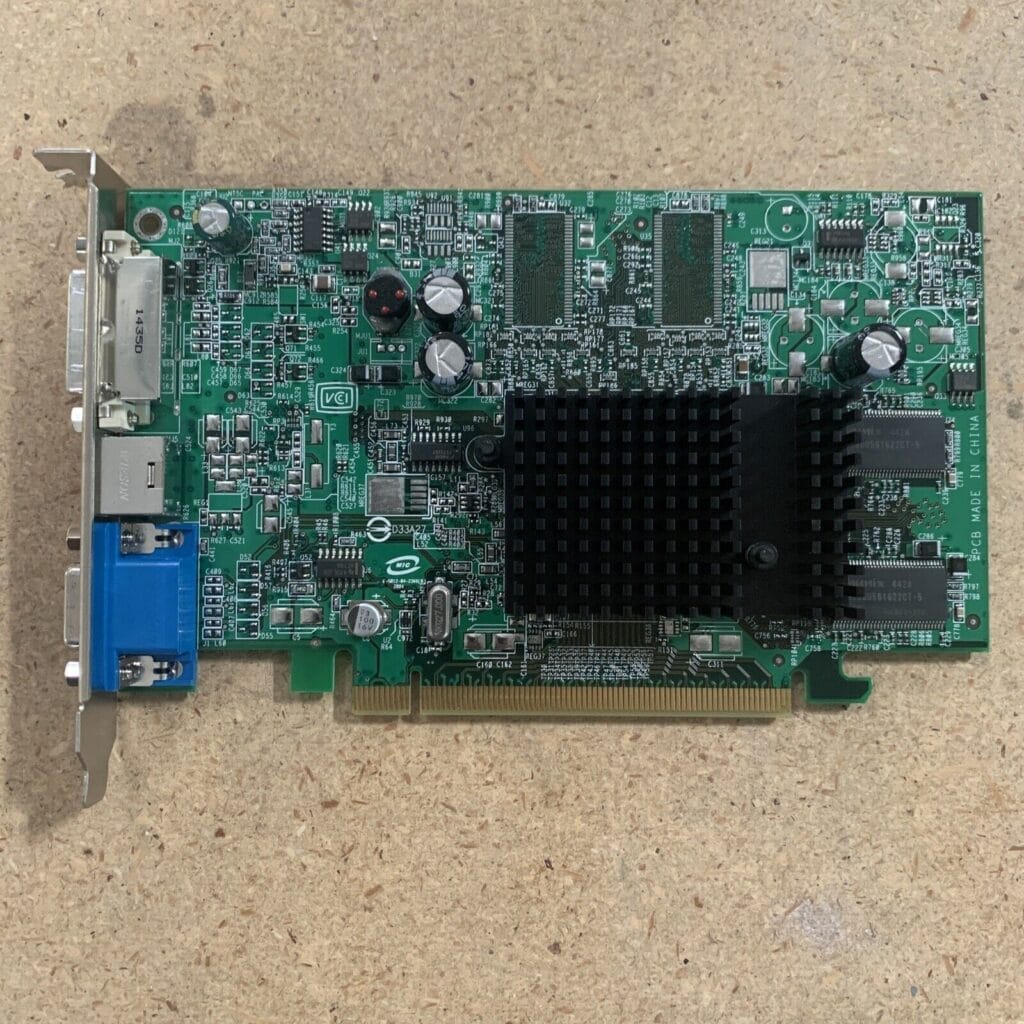

The Role of VRAM in Performance
VRAM is pivotal in determining how well your GPU can handle high-resolution textures and complex 3D models. More VRAM generally means better performance in graphics-intensive applications like video games and 3D rendering software.
Myths and Realities of GPU Memory Upgrades
Common Misconceptions
Many believe that simply adding more memory to their GPU will result in a significant performance boost. However, this overlooks the complexities of GPU architecture and compatibility issues.
Technical Limitations
The reality is that most GPUs have VRAM soldered onto the board, making it nearly impossible for the average user to upgrade. Even if you manage to add more memory, compatibility with the GPU’s BIOS and drivers is not guaranteed.
User Experiences and Anecdotes
Insights from Reddit Discussions
Discussions on platforms like Reddit reveal a mix of success and failure stories. Some users have attempted to solder additional memory onto their GPUs, often with mixed results.
Real-World Attempts and Outcomes
These real-world experiments highlight the technical challenges and risks involved in manually upgrading GPU memory. Success stories are rare and often require advanced technical skills.
Technical Challenges in Adding Memory to GPUs
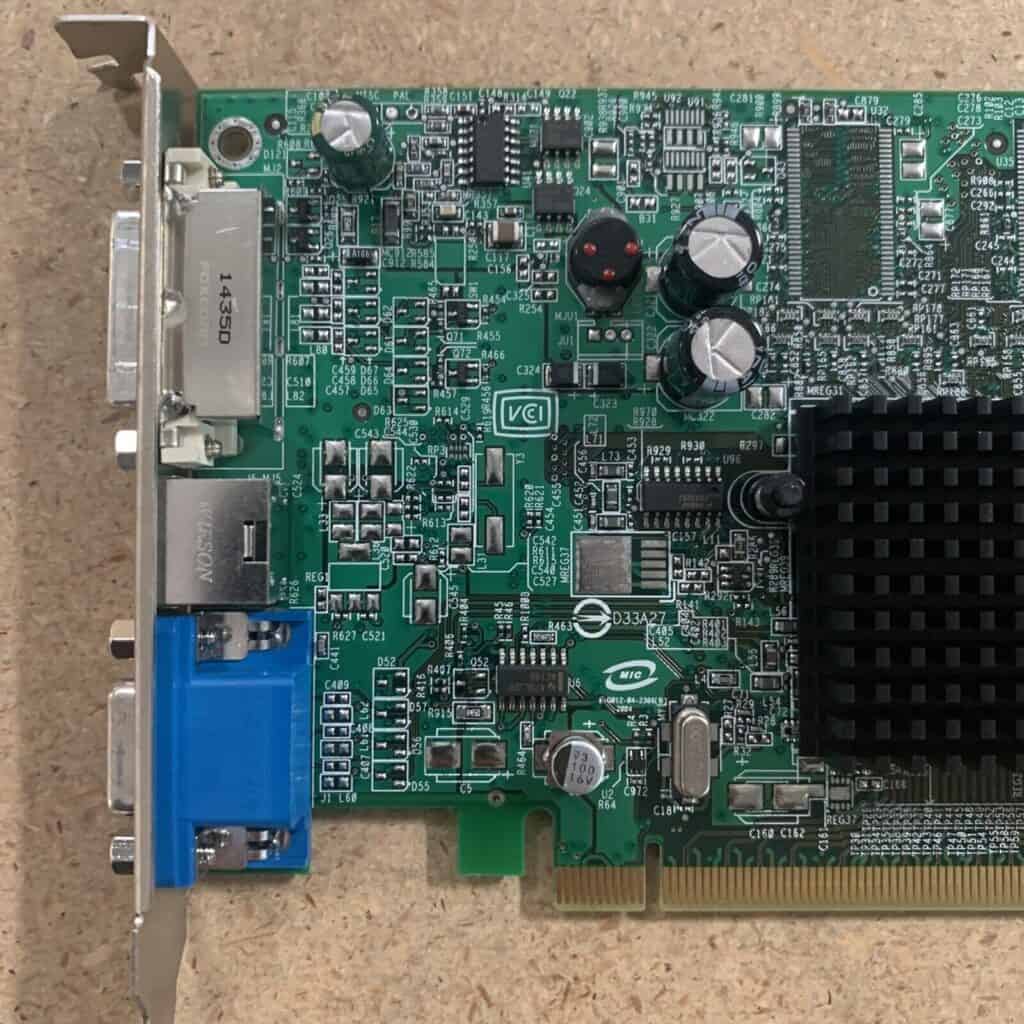

Soldering Challenges and Risks
Soldering additional memory onto a GPU is a delicate process, requiring precision and expertise. There’s a high risk of damaging the GPU beyond repair.
BIOS and Firmware Limitations
Even if you successfully add more memory, the GPU’s BIOS may not recognize it. Modifying the BIOS is risky and can lead to irreversible damage.
Compatibility Issues with Memory Chips
Finding memory chips that are compatible with your GPU’s architecture is another hurdle. Mismatched memory can lead to instability and poor performance.
Alternative Solutions to Enhance GPU Performance
Upgrading to a New GPU
For most users, the best way to improve graphics performance is to upgrade to a newer GPU model. This ensures compatibility and optimal performance without the risks of manual modification.
Optimizing Existing GPU Settings
Adjusting your GPU’s settings can also enhance performance. Tweaking the resolution, texture settings, and other graphics options can provide a noticeable boost without hardware changes.
Software Solutions and Tweaks
Software updates and optimizations can also improve GPU performance. Keeping your drivers up-to-date and using software tools to optimize settings can make a significant difference.
Practical Advice for Enthusiasts and Gamers
When to Consider Upgrading Your GPU
If you’re facing performance issues in the latest games or software, it might be time to consider a GPU upgrade. Assess your current GPU’s capabilities against the requirements of the software you’re using.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of GPU Memory Enhancement
Weigh the costs of a new GPU against the potential risks and limited benefits of manually upgrading memory. In most cases, purchasing a new GPU is more cost-effective.
Recommendations for Non-Technical Users
For those without technical expertise, it’s advisable to avoid manual GPU modifications. Instead, focus on software optimizations and consider hardware upgrades when necessary.
Upgrading to a New GPU: A Safer Bet
When it comes to enhancing your GPU’s capabilities, upgrading to a newer model is often the most straightforward and effective approach. This not only ensures compatibility but also offers a significant boost in performance, especially with the latest advancements in GPU technology.
Factors to Consider When Upgrading:
- Compatibility with your system: Ensure the new GPU is compatible with your motherboard and power supply.
- Performance requirements: Match the GPU’s capabilities with your specific needs, whether it’s gaming, video editing, or 3D rendering.
- Budget: Balance the cost against the performance benefits.
Optimizing Existing GPU Settings
Before considering hardware upgrades, tweaking your current GPU’s settings can yield noticeable improvements. Adjusting resolution, texture details, and other graphics settings can enhance performance without any additional cost.
Tips for GPU Optimization:
- Update drivers: Keep your GPU drivers up-to-date for optimal performance and compatibility.
- Adjust in-game settings: Lowering graphics settings can improve frame rates in games.
- Use optimization software: Tools like NVIDIA GeForce Experience or AMD Radeon Software can automatically optimize settings for your games.
Software Solutions and Tweaks
Software updates and optimizations can also play a significant role in enhancing GPU performance. Regularly updating your GPU drivers and using software tools for optimization can make a substantial difference.
Effective Software Solutions:
- Driver updates: Regularly updating your GPU drivers can resolve compatibility issues and improve performance.
- Game mode settings: Many operating systems now include a ‘Game Mode’ that optimizes system resources for gaming.
- Third-party tools: Software like MSI Afterburner allows for fine-tuning of GPU settings for advanced users.
Practical Advice for Enthusiasts and Gamers
When to Consider a GPU Upgrade
If you’re consistently facing performance issues in the latest games or software, it might be time to consider upgrading your GPU. Assess your current GPU’s capabilities against the requirements of the software you’re using.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Weigh the costs of a new GPU against the potential risks and limited benefits of manually upgrading memory. In most cases, purchasing a new GPU is more cost-effective and less risky.
For those without technical expertise, it’s advisable to avoid manual GPU modifications. Instead, focus on software optimizations and consider hardware upgrades when necessary.
Conclusion: Balancing Risk and Reward in GPU Upgrades
It might sound like upgrading the physical memory on your GPU is a good idea, but in reality it’s a difficult – nearly impossible task. For most users, the smarter choice is either to change & optimize settings on the current card or to upgrade to a new GPU.
These approaches offer a balance of improved performance, cost-effectiveness, and minimal risk, making them suitable for both casual users and enthusiasts alike.
FAQs on GPU Memory and Performance
- Can I add more memory to my existing GPU?
- In most cases, no. GPU memory is typically soldered onto the card and not designed to be upgraded by the end user.
- Will upgrading my GPU’s memory improve gaming performance?
- Upgrading GPU memory can improve performance, but it’s often not possible for the average user. Upgrading the entire GPU is usually a more effective solution.
- What is the role of VRAM in a GPU?
- VRAM (Video RAM) is dedicated memory used by the GPU to store graphical data like textures, aiding in efficient rendering of images and videos.
- How can I optimize my current GPU’s performance?
- Update your GPU drivers, adjust in-game graphics settings, and use optimization software to enhance performance.
- Is it worth upgrading to a new GPU for better performance?
- Yes, if your current GPU is not meeting your performance needs, upgrading to a newer model is often the best solution.
- Can software updates improve GPU performance?
- Yes, keeping your GPU drivers up-to-date can improve performance and compatibility with new games and software.
- What risks are involved in manually upgrading GPU memory?
- Manually upgrading GPU memory can lead to compatibility issues, potential damage to the GPU, and voiding of warranties. It’s generally not recommended for most users.