Upgrading a processor in a laptop can be harder than upgrading desktop hardware, and in most cases, impossible. Most modern laptops have processors that are attached to the motherboard, making them difficult to replace. However, depending on the laptop’s design and construction, it may be possible to upgrade the processor. It’s important for laptop owners to understand their system’s specifications and the type of processor it has before considering an upgrade.
Before attempting to change a laptop’s processor, you should check your user manual or the manufacturer’s guidelines. These resources typically show whether the processor is soldered to the motherboard or if it can be removed. If an upgrade is possible, you must then check if the new processor is compatible with the existing motherboard. Additionally, it’s important to consider the cost and the potential risks associated with modifying the hardware.
Is a Laptop CPU Upgrade Possible?
In most modern laptops, you cannot replace the processor.
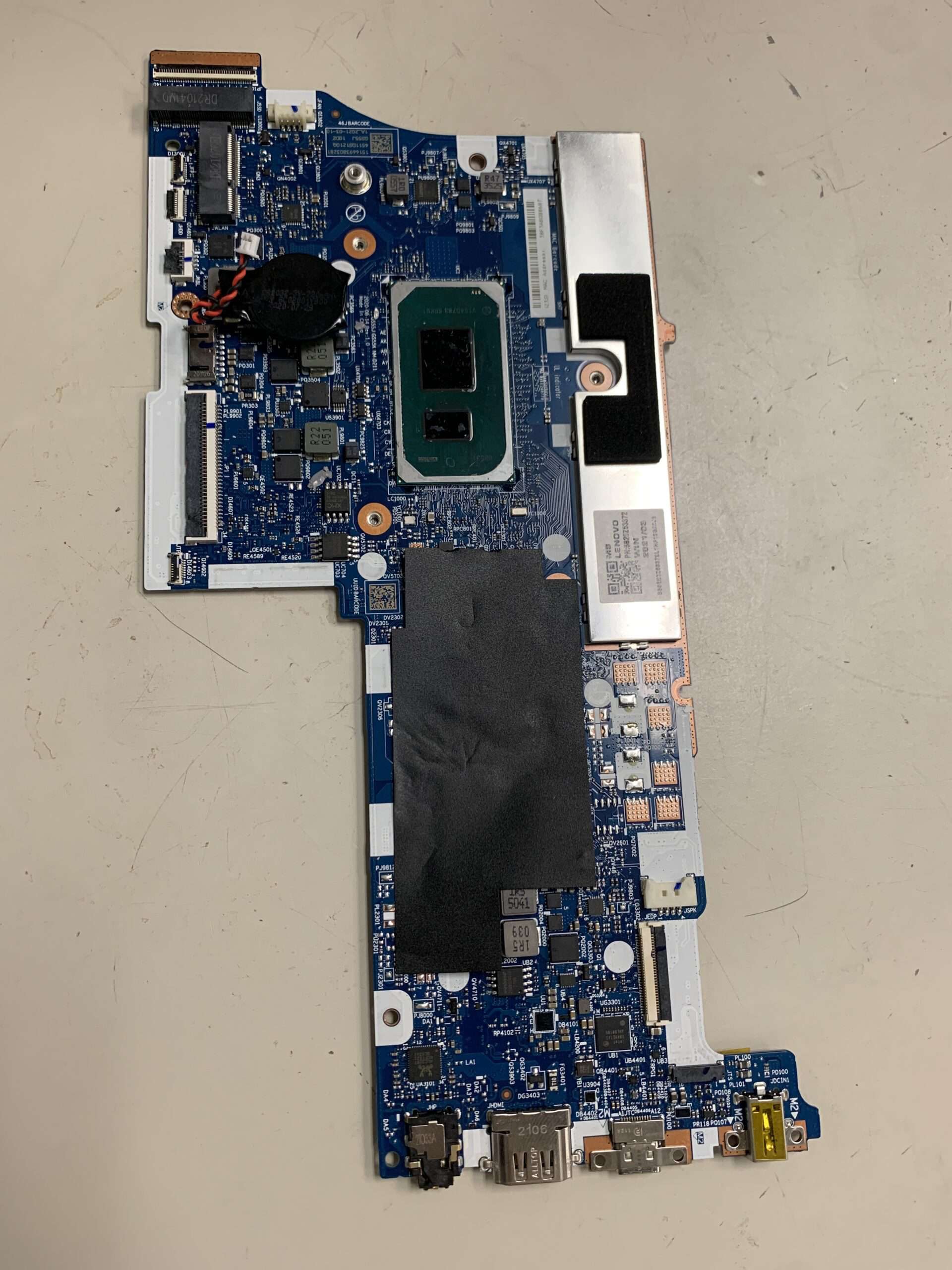
That’s because the CPU is soldered directly to the motherboard using a BGA (Ball Grid Array) socket — meaning it’s permanently attached and not designed for removal or upgrades (source: Tom’s Hardware).
However, there are a few exceptions — mainly in older or high-end gaming/workstation laptops — where the CPU is installed in a PGA (Pin Grid Array) or LGA (Land Grid Array) socket, which can be replaced.
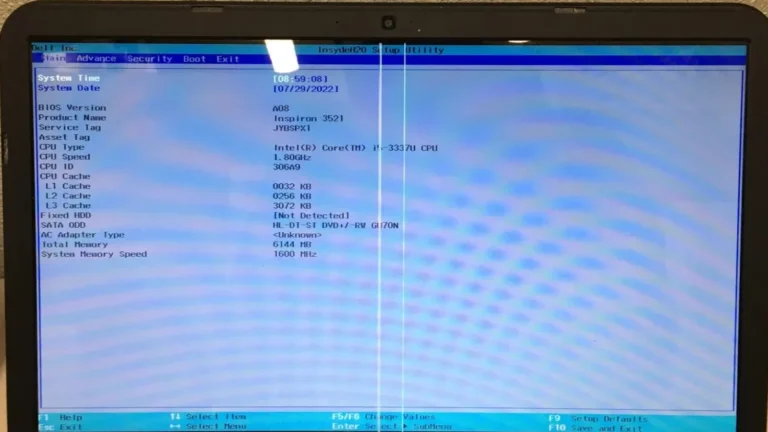
⚙️ Step 1: Identify Your Laptop’s CPU Type
Before considering any upgrade, check if your CPU is soldered (BGA) or socketed (PGA/LGA).
🔍 How to Check:
- Find your CPU model:
- On Windows: Press
Win + R, typemsinfo32, and look under Processor. - On macOS: Click the Apple menu → About This Mac.
- On Windows: Press
- Search your CPU model online (e.g., “Intel Core i7-9750H socket type”).
- Check the socket type:
- BGA = Soldered → Not replaceable
- PGA/LGA = Socketed → Potentially replaceable
You can verify socket types on Intel’s official site (Intel CPU Sockets by Generation).
🧩 Step 2: Check Compatibility
If your laptop has a socketed CPU, you still need to ensure compatibility with:
- Motherboard chipset
- BIOS support
- Power (TDP) limits
- Cooling system capacity
Even if the new CPU fits the socket, it won’t work if your BIOS doesn’t support it (source: HP Support Community).
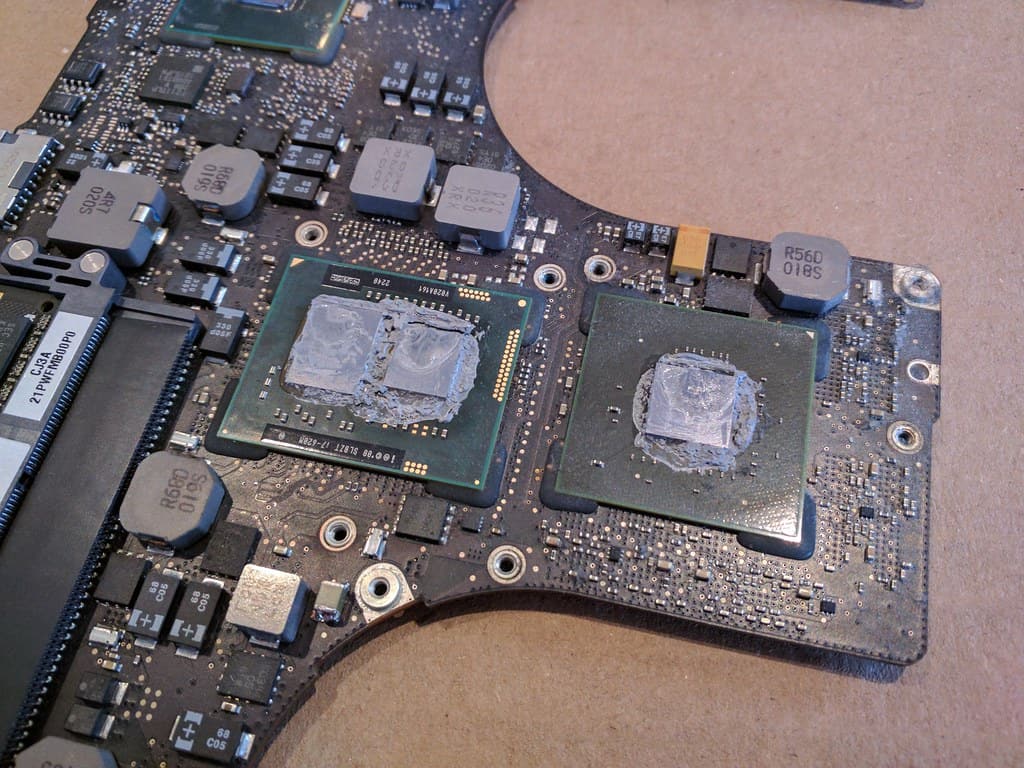
🔧 Step 3: Understand What’s Involved in a Replacement
If your CPU is replaceable, the process involves:
- Disassembling the laptop (removing keyboard, cooling system, and motherboard).
- Removing the old CPU from its socket.
- Installing the new CPU and reapplying thermal paste.
- Reassembling and testing the system.
⚠️ Warning: This is an advanced procedure.
Even experienced technicians risk damaging the motherboard or voiding the warranty. For soldered CPUs, it requires desoldering and reballing equipment, which is not practical for most users (source: CPU Forever).
💡 Step 4: Alternatives to CPU Replacement
If your goal is better performance, consider these safer upgrades:
- Add more RAM – improves multitasking and speed.
- Upgrade to an SSD – drastically improves boot and load times.
- Clean and repaste your CPU – helps maintain performance by reducing thermal throttling.
- Undervolt or optimize software – improves efficiency and stability.
🧱 Step 5: When It Is Possible
You might be able to replace the CPU if:
- You have an older laptop (pre-2015) with a socketed CPU (e.g., Intel Core i5/i7 2nd–4th Gen).
- You own a high-end gaming or workstation laptop with modular components (e.g., some Clevo, Alienware, or MSI models).
- The TDP and chipset match the new processor.
Example:
A laptop with an Intel Core i5-4200M (socket G3, PGA946) can sometimes be upgraded to an i7-4700MQ — same socket and chipset (source: YouTube guide).
🧩 Step 6: Contact the Manufacturer
Before attempting any upgrade, always check with your laptop’s manufacturer.
Intel itself recommends contacting your system or motherboard manufacturer before upgrading, as most laptops are not designed for CPU replacement (source: Intel Support).
✅ Summary
| Situation | Can You Replace CPU? | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Modern ultrabooks (post-2016) | ❌ No | CPU is soldered (BGA) |
| Older gaming/workstation laptops | ✅ Possibly | Check socket type and BIOS |
| Thin & light laptops | ❌ No | Not designed for upgrades |
| Custom-built (Clevo, Alienware) | ✅ Yes | Some models support CPU swaps |
🧭 Bottom Line
In most cases, you cannot replace a laptop processor, especially in modern models.
If your laptop uses a socketed CPU, it may be upgradeable — but only if the motherboard, BIOS, and cooling system support it.
For most users, upgrading RAM or storage is the safer and more cost-effective way to boost performance.
Why Laptop CPU Upgrades Are Rare
- Soldered CPUs: The majority of laptops have the CPU directly soldered to the motherboard. It’s physically impossible to remove and replace them without specialized equipment and skills.
- Compatibility: Even if you find a laptop with a socketed CPU, finding a compatible replacement processor can be a challenge due to BIOS restrictions and different power requirements.
- Cost-effectiveness: The process of replacing a laptop CPU is technically intricate. The cost of labor and a replacement chip often negates the value of upgrading.
When It Might Be Possible
Here are limited scenarios when a laptop CPU upgrade might be a viable option:
- High-end Workstations: Some specialized, high-end laptops and gaming models offer socketed CPUs, allowing for upgrades – but this is the exception, not the rule.
- Older Laptops: Laptops from earlier eras may have had socketed CPUs, offering a small chance of finding a compatible, more powerful CPU to upgrade with.

Alternatives to CPU Upgrades
If your laptop’s performance slows down, here are alternatives to a costly CPU replacement:
| Upgrade Option | What It Helps With |
|---|---|
| Increase RAM | Handles multitasking and larger application workloads |
| Upgrade to an SSD | Improves system responsiveness and loading times |
| Clean unused files | Helps free up storage space for better performance |
| Consider a new laptop | Provides a comprehensive performance upgrade |
It’s usually more practical and cost-effective to focus on these upgrades first, or start thinking about purchasing a new laptop if your current model is holding you back significantly.
Key Takeaways
- Laptops often have fixed processors, making upgrades difficult.
- Consultation with manufacturer guidelines is essential before upgrading.
- Compatibility and cost are key considerations for potential upgrades.
Understanding the Laptop’s Processor
Knowing how a laptop’s processor works helps you decide if an upgrade is right for you. This section talks about the basic parts of a processor, how it fits into a laptop, and how it compares to a desktop CPU.
Processor Fundamentals
The central processing unit or CPU is the brain of a laptop. It carries out instructions and handles operations. Cores in a CPU work on tasks. More cores can mean better multitasking. Thermal design power (TDP) is important too. It shows how much heat a CPU makes and how much power it needs.
Compatibility and Laptop Architecture
Not all CPUs will work with every laptop. Each processor needs the right socket on the motherboard. A laptop’s design also affects what CPU it can hold. The generation of a CPU tells us about its age and tech level. When you look for an upgrade, you’ll see names like Intel or AMD. These companies make CPUs.
Comparing Laptop and Desktop Processors
Laptop processors differ from desktop CPUs. They often run slower than desktop CPUs. This helps them use less power and make less heat. This is key because laptops have less space to get rid of heat. A CPU upgrade can make your laptop run faster. But it’s a bigger task than changing RAM or a hard drive.
Replacement Process and Considerations
Upgrading a laptop’s processor involves several key steps and considerations. This section outlines what you need to know before attempting such an upgrade.
Assessing Upgradeability
The first step is to find out if your laptop’s CPU can be replaced. Check the service manual or contact the laptop manufacturer to see if the processor is soldered to the motherboard. Some laptops have a CPU that one can remove, while others do not. If the CPU is soldered, the laptop’s processor is not user-upgradeable.
Choosing the Right Processor
If the CPU is replaceable, identify the correct type. It must match the laptop’s socket type on the mainboard and fit within the same thermal design power (TDP) specifications. You can consult the manufacturer’s specifications or a knowledgeable retailer to select the appropriate processor model that is compatible with your laptop chassis and framework.
Step-by-Step Replacement Guide
To replace the processor, one should follow these steps carefully:
- Power Down: Shut down the laptop and disconnect all power sources.
- Disassemble: Carefully open the laptop chassis according to the service manual instructions.
- Remove Old CPU: Take off the cooling system and gently unlatch and remove the existing processor.
- Install New CPU: Place the new processor in the socket and lock it in place, then reattach the cooling system.
- Reassemble: Put the laptop back together, ensuring all connections are secure.
This process requires precision, so proceed with caution or let a professional handle it.
Potential Risks and Warranty Implications
Replacing a laptop CPU can void the warranty. Always check the warranty status and understand the implications before starting any upgrade. There is also a risk of damaging the motherboard or other components if the replacement is done incorrectly. If unsure, it is best to seek service from a professional with experience in laptop upgrades.
Frequently Asked Questions
The section below answers common questions about upgrading a laptop’s CPU.
Is it possible to upgrade a laptop CPU from an i3 to an i7?
Upgrading from an i3 to an i7 can offer a significant performance boost. It depends on the laptop’s motherboard and chipset compatibility.
What are the costs associated with replacing a laptop processor?
Costs can vary widely based on the processor model and whether a specialist is involved. Prices often range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars.
How can I determine if my laptop’s CPU is upgradeable?
Check the laptop’s manual or manufacturer’s website. They provide details on upgrade options and compatible processors.
What steps are involved in upgrading a laptop processor?
Upgrading typically involves opening the laptop, removing the existing CPU, and inserting the new one. It requires technical skill and the right tools.
Can a laptop’s CPU be upgraded from a Celeron to an i3?
This upgrade is possible on some laptops. They must have compatible sockets and the laptop’s cooling system must be adequate for the new CPU.
Are there tools available to check if a laptop CPU can be upgraded?
Yes, software tools can assess a system’s specs. They suggest potential upgrades while online forums and official user manuals also offer guidance.