When dealing with OS corruption, there are several tools that you can use. The two most important might be SFC (System File Checker) and DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management). Each tool serves a different purpose, and when used together you can usually recover from most minor corruption problems. DISM is the command designed to repair the Windows image.
The primary DISM command you will be interested in is:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
To run this command make sure you are in an elevated command prompt (CMD.exe, Run As Administrator)
How To Use DISM: Step By Step
Here’s a table outlining the steps to fix Windows corruption with DISM:
| Step | Description | Command |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Open an elevated command prompt. | Right-click on the Start button and select “Command Prompt (Admin)”. | |
| 2. Check for corruption (optional). | Assesses the integrity of the Windows image files. | DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth |
| 3. Scan for corruption (optional). | Provides more details about any detected corruptions. | DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth |
| 4. Repair corrupted files. | Attempts to repair corrupted or missing files using Windows Update resources. | DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth |
| 5. Provide a repair source (if required). | If the previous step fails, specify a local Windows image file (WIM) or installation media as a repair source. | DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:C:\RepairSource\Windows |
| 6. Verify the repair. | (Optional) Checks if the repair was successful. | DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth |
| 7. Run SFC scan. | Scans and repairs protected system files using the repaired image as a reference. | sfc /scannow |
Additional notes:
- Elevated command prompt: This is necessary to run DISM with administrative privileges.
- Internet connection: The
/RestoreHealthcommand usually requires an internet connection to download necessary files. - Repair source: If you don’t have an internet connection or the online repair fails, you can use a local installation media or a mounted WIM file as a repair source.
- Time: The repair process can take several minutes or longer, depending on the extent of corruption and your internet speed.
- Persistence: If DISM fails to repair corruption, you may need to consider reinstalling Windows.
Step 1: Run DISM
Load Command Prompt As Administrator and execute: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
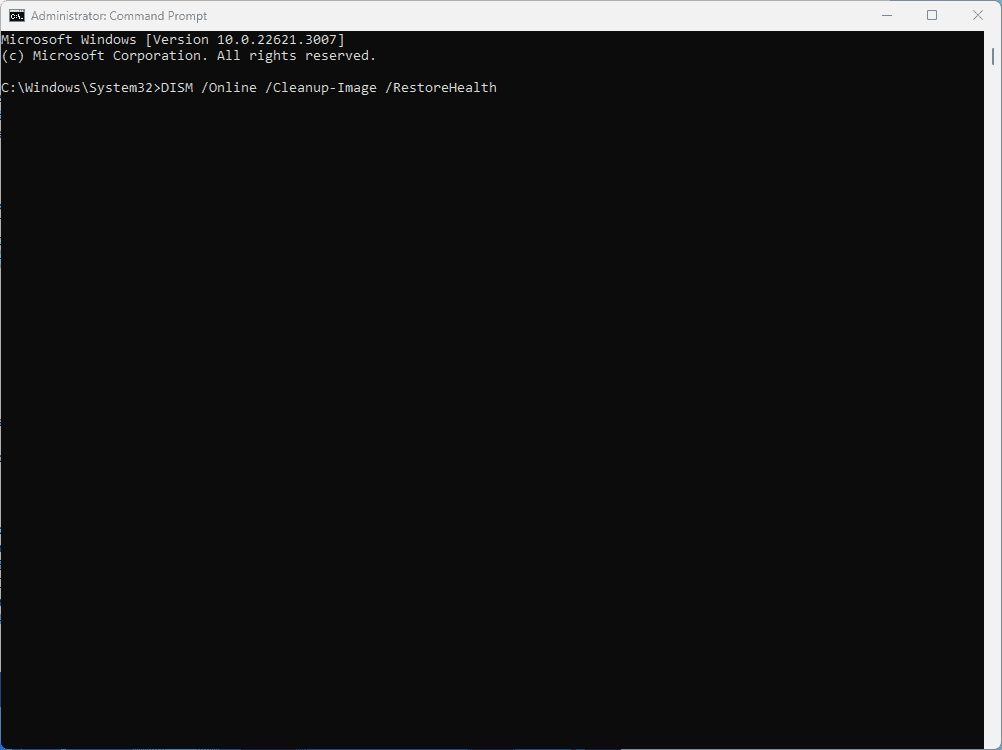
Step 2: Let DISM Run
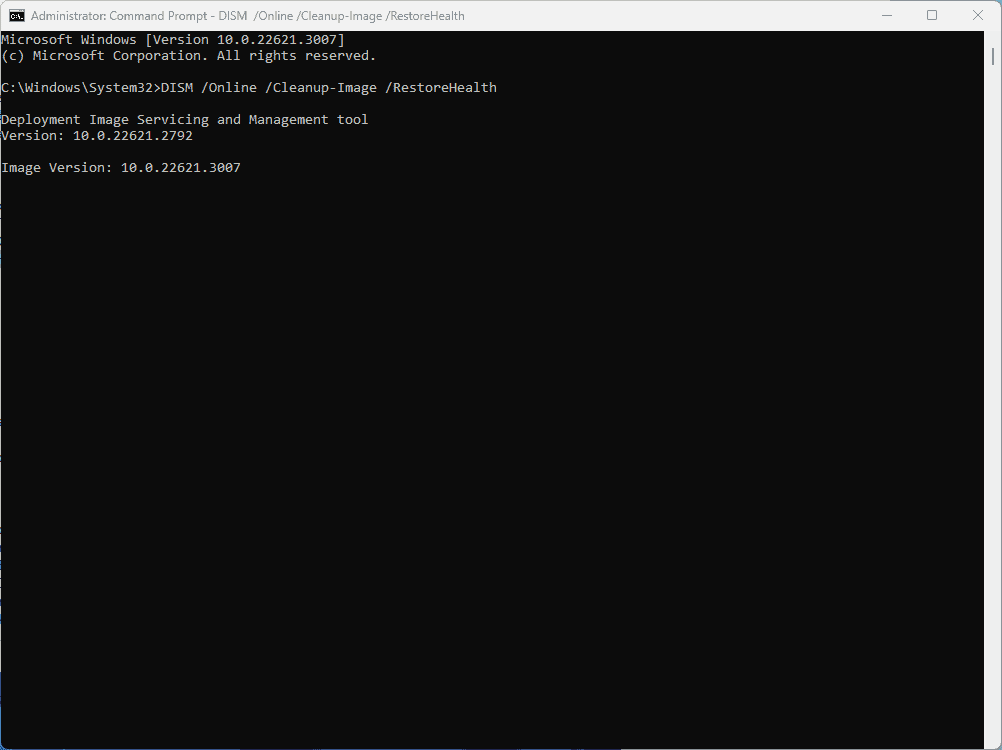
Step 3: Look For Messages As DISM Completes
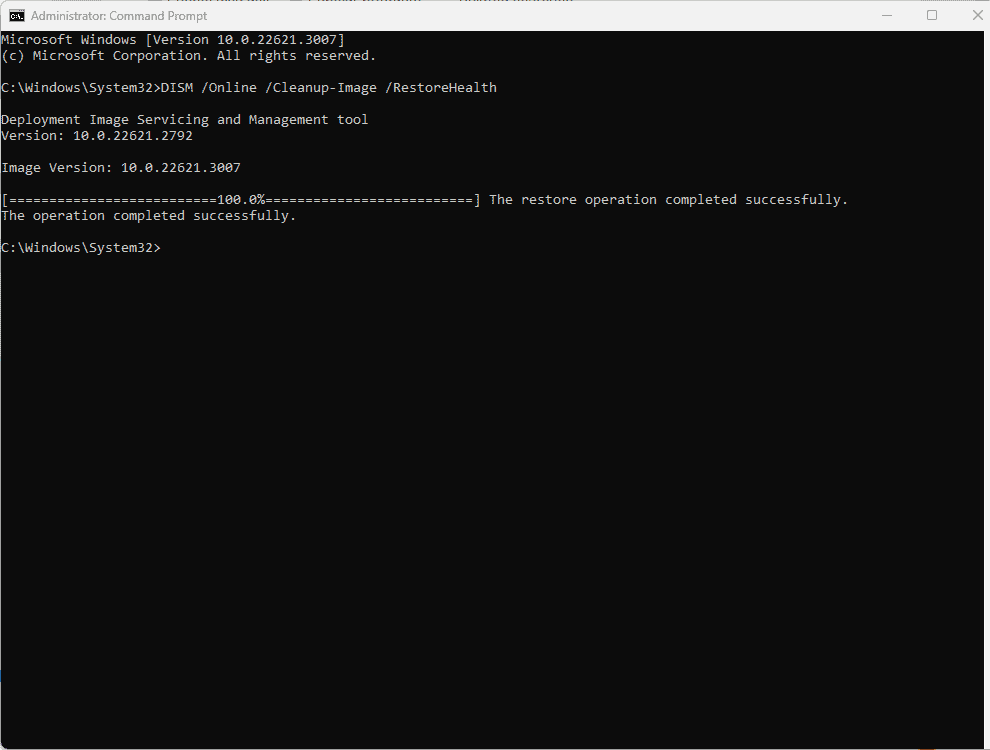
DISM will give you a progress bar as it runs. Look for any error messages that pop up. If everything goes smoothly you will get a notification that says “The restore operation completed successfully.”
Windows Image: What Is It and Why Fix It?
Windows Image is like a blueprint of your computer’s operating system. It contains everything needed for Windows to work correctly. Think of it as a detailed map of a city – if the map gets damaged or outdated, navigating becomes difficult. Similarly, if the Windows Image gets corrupted, your computer might start having problems.
Common issues that lead to Windows Image corruption include:
- Malware or virus attacks
- Incomplete or failed updates
- System crashes
Repairing the Windows Image is like fixing the map, so your computer knows how to navigate and operate smoothly again.
Core Functions of DISM
DISM comes with several commands, but three of them are particularly important:
- CheckHealth: This is like a quick health check-up for your computer. It scans the system to see if there are any problems.
- ScanHealth: Think of this as a more thorough health examination. It takes a deeper look into your system to find any issues.
- RestoreHealth: If problems are found, RestoreHealth is like the medicine that helps fix them.
Each command has its specific role, and knowing when to use them is key to maintaining a healthy computer system.
Comparing DISM and SFC
There’s another tool called SFC (System File Checker). While DISM repairs the Windows Image, SFC focuses on repairing individual system files. It’s like using a small brush to clean a specific spot, while DISM is like using a large mop to clean the whole floor.
In scenarios where there are broader system issues, DISM is often the better choice compared to SFC.
How DISM Works
DISM can sound complicated, but it’s not too hard to understand. When you run a DISM command, it checks your system against a fresh and correct version of Windows Image. If it finds differences, it tries to fix them by replacing the damaged parts with the good ones.
For a more detailed explanation, you can check out Microsoft’s Official DISM Documentation.
Preparing Your System for DISM
Before using DISM, it’s important to make sure your computer is ready. Here are some steps to follow:
- Make sure your computer is plugged in and has a stable power source.
- Close all open programs and files.
- It’s a good idea to back up your important data, just in case.
The Most Important Commands For Windows Problems
Here’s a listing of the most important “first-step” commands to run to fix most Windows OS related issues:
- Run CMD as Administrator
- sfc /scannow
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
By running that command sequence you will automatically fix a lot of errors that arise and can avoid a lot of wasted time trying to troubleshoot using a different method.
/Restorehealth: The Repair Function
The /Restorehealth command option is what is really doing all the work. As can be seen from the description:
/Cleanup-Image {/CheckHealth | /ScanHealth | /RestoreHealth} Use /CheckHealth to check whether the image has been flagged as corrupted by a failed process and whether the corruption can be repaired. Use /ScanHealth to scan the image for component store corruption. Use /RestoreHealth to scan the image for component store corruption, and then perform repair operations automatically.
/RestoreHealth is what scans for the corruption and repairs it automatically.
Using DISM with Installation Media
Sometimes, your Windows might have trouble starting up. In these cases, you can use DISM with installation media, like a USB drive or DVD with Windows setup. Here’s how to do it:
- First, insert your installation media and boot your computer from it.
- Choose your language and other preferences, then select ‘Repair your computer.’
- In the ‘Advanced options’, select ‘Command Prompt.’
Now, you’re ready to use DISM commands to repair your system, just like if Windows was running normally.
Advanced DISM Techniques
For those who like to dive deeper, DISM has some advanced tricks up its sleeve. Let’s explore a couple:
- Removing Specific Updates: Sometimes, a Windows update might cause issues. You can use DISM to remove these problematic updates.
- Converting Image Types: If you’re a pro, you might need to convert between different types of system images. DISM can do this too, changing a standard image to a bootable one, for example.
Remember, these are advanced operations. It’s best to have a bit of technical know-how before trying these out.
Integrating DISM into Regular Maintenance
Just like you regularly clean your room, your computer also needs regular maintenance. Integrating DISM into your routine can help keep your PC healthy. Here’s what you can do:
- Schedule Regular Scans: Set a reminder to run DISM commands every few months. It’s like a regular check-up for your computer.
- After Major Changes: If you’ve just done a big update or installed new software, running a quick DISM scan can ensure everything is still in good shape.
Real-World Applications
Understanding how DISM works in real-world scenarios can be super helpful. Imagine your computer starts acting up after a big update. Instead of panicking, you can run a DISM scan to see if the update caused any issues and even roll it back if necessary. Or, if your computer refuses to start one fine morning, using DISM through installation media could be your ticket to getting things back to normal.
User Experiences and Tips
- “After a major Windows update, my computer started crashing randomly. I used DISM to remove the recent updates, and it was back to normal!” – A user’s experience.
- Tip: Always ensure your computer is connected to a stable power source when running DISM commands. Interruptions can cause more issues.
- Tip: DISM /Online /Cleanup-image /RestoreHealth /Source:<knowngood>
is extremely helpful for OS corruption issues, specifically related to Windows Updates. I have to hit at least 10 servers a month in a population of about 2500 total systems. Works 75% of the time.
FAQ
What Exactly is DISM?
DISM, or Deployment Image Servicing and Management, is a command-line tool in Windows that helps repair and prepare Windows images, including the Windows Recovery Environment, Windows Setup, and Windows PE (Preinstallation Environment). It’s essential for diagnosing and fixing system issues.
Should I run SFC or DISM first?
In most scenarios, it’s advisable to run the SFC (System File Checker) command before using DISM. SFC attempts to repair individual system files that may be corrupted. If SFC is unable to fix these files because the system image is damaged, that’s when DISM becomes crucial. DISM can repair the system image, thereby providing SFC with the correct files to solve the problem.
Does DISM fix corrupt files?
Yes, DISM can fix corrupt files, but specifically those that are part of the Windows system image. If the system image becomes corrupt or damaged, DISM has the capability to restore it, effectively resolving issues related to corrupted system files. However, DISM does not directly fix individual non-system files.
What are the three DISM commands?
The three primary DISM commands used for system repair are:
- CheckHealth: This command quickly checks for any corruption within the system image but does not perform any repairs.
- ScanHealth: This is a more thorough scan that checks for any issues within the system image, providing a detailed report of any detected corruption.
- RestoreHealth: This command actually repairs any detected
corruption within the system image. It can take a bit longer to run but is effective in restoring system integrity.
How long does DISM online cleanup take?
The duration of a DISM online cleanup (using the command DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth) can vary depending on the extent of the corruption and your computer’s performance capabilities. Typically, it can take anywhere from 20 minutes to a couple of hours. It’s important to be patient and not interrupt the process once it starts, as doing so can lead to further system issues.
When Should I Use DISM?
You should consider using DISM when your computer encounters system-related issues, especially after problematic updates or in cases where the system files are corrupted. It’s also a valuable tool for regular maintenance to ensure system integrity.
Is DISM Hard to Use?
While DISM is a command-line tool, which might seem daunting at first, it’s quite user-friendly once you get familiar with its basic commands. It requires following specific instructions, but it doesn’t demand extensive technical knowledge.
Can DISM Fix All My Computer Problems?
DISM is powerful, but it’s not a catch-all solution. It’s specifically designed to address issues related to the Windows system image. For other types of computer problems, such as hardware issues or non-system related software errors, other solutions would be more appropriate.
Do I Need to Be an Expert to Use DISM?
Being an expert is not a prerequisite for using DISM. Basic knowledge and understanding of command-line interfaces can be sufficient for running simple DISM commands. However, for more complex operations, a higher level of technical expertise may be beneficial.
How Often Should I Run DISM Checks?
Running DISM checks periodically, especially after significant system updates or installations, is a good practice. It helps in early detection and resolution of any system image corruption, ensuring smoother system performance.
What’s the Difference Between DISM and SFC?
DISM and SFC (System File Checker) both serve to repair Windows systems, but they operate differently. DISM primarily repairs the Windows image and handles more global system issues, while SFC focuses on scanning and repairing individual corrupted system files.