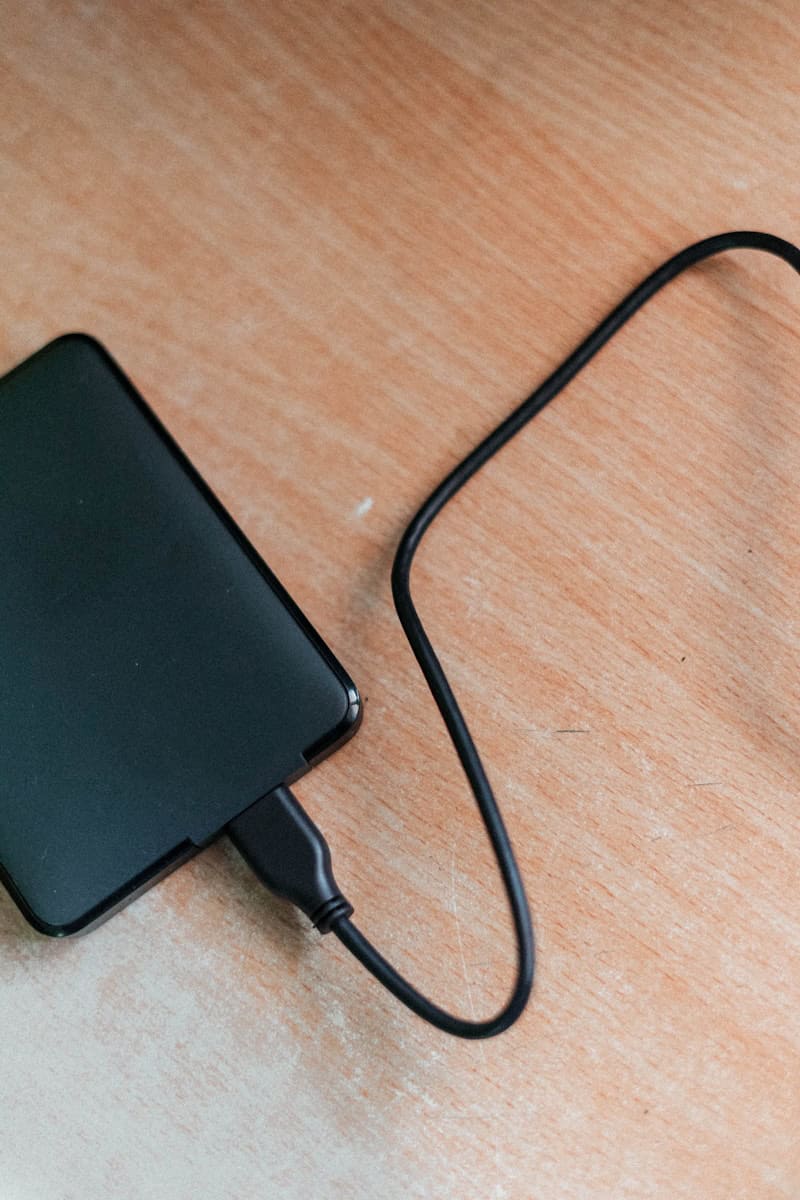
An external hard drive offers additional storage space and serves as a portable storage solution for files, documents, and media. Like a hardcover book with pages, an external hard drive can store a large number of files that are easy to access. It is essential for individuals and businesses seeking a reliable backup to prevent data loss from computer issues or accidents.
External hard drives are also useful for transferring data between computers and are available in various storage sizes. They are not just for file storage – creative professionals use them to edit digital content due to their high storage capacity, and gamers appreciate the extra space for their game collections. People and companies depend on external hard drives to share large files and create backups, ensuring that their digital assets are duplicated and safe.

What is an External Hard Drive?
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Storage device |
| Function | Provides additional storage space for your computer |
| Connection | Connects to your computer via USB, Firewire, or Thunderbolt cable |
| Benefits | * Back up important files * Store large files (videos, music, games) that don’t fit on your internal drive * Increase storage capacity without opening your computer |
| Drawbacks | * Slower than internal storage * More fragile and susceptible to damage |
| Form Factor | Available in various sizes: 2.5-inch (portable) and 3.5-inch (desktop) |
Key Takeaways
- External hard drives provide additional storage and are portable.
- They are crucial for backing up important data to prevent loss.
- Usage ranges from data transfer to expanded storage for tasks like digital editing and gaming.
Understanding External Hard Drives
External hard drives serve as an extension of a computer’s storage. They provide additional space for backups, files, and applications, and can be connected via various interfaces.
Different Types and Interfaces
SSDs (Solid State Drives) and HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) are the two main types of external hard drives. SSDs have no moving parts and are faster, while HDDs are more affordable and offer larger storage capacities. Key interfaces for connecting these drives to a PC or Mac include USB (2.0, 3.0, 3.1, 3.2), Thunderbolt 3, and eSATA. The choice of interface impacts the drive’s compatibility and transfer speeds.
Storage Capacities and Physical Size
Capacities of external drives vary widely, starting from a few hundred gigabytes to several terabytes. Common sizes include portable 2.5-inch drives, which are compact and typically powered through a USB cable, and larger 3.5-inch drives, which might require an external power source. The physical size correlates with the drive’s capacity; as capacity increases, the drive may become larger.
Data Transfer and Speed
Data transfer speed is a crucial aspect of external hard drives. It’s affected by the drive’s technology (SSD or HDD) and the interface used. For instance, USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 can transfer data much faster than USB 2.0. Also, Thunderbolt 3 supports even higher speeds which is ideal for transferring large files quickly. Drives must be formatted with the correct file system to work with different operating systems, and some might require specific drivers to function properly.
Practical Uses of External Hard Drives
External hard drives offer several practical benefits to users looking to expand their digital capabilities. From backing up important documents to entertainment purposes, these devices enhance the functionality of electronic systems.
Efficient Data Backups and Transfer
External hard drives provide a reliable method for backing up files. They help protect against data loss due to drive failure. With backup software, users can set up automatic backups to copy files regularly. This option is simpler than using online cloud storage due to direct access through file explorers.
Additional Storage for Various Devices
The need for additional storage is common as users work across multiple devices. By connecting an external hard drive to a smartphone, tablet, or computer, one can easily move or store apps, photos, and document files. This solution often comes at a lower cost compared to upgrading internal memory or subscribing to a cloud service.
Media and Entertainment
For entertainment, external hard drives are perfect for storing large files like music, videos, and images. Gamers, too, use these drives to keep their extensive game libraries without burdening the console’s internal storage. Transferring media between devices becomes more convenient with these portable drives.
Security and Portable Work
External hard drives with hardware encryption offer security for sensitive information. Rugged options are available for those on adventure, as some drives are waterproof and built to withstand harsh conditions. Such features add to the drive’s durability and reliability, making them suitable for taking work on the go.
Frequently Asked Questions
When exploring the use of external hard drives, several common queries arise.
Why would you use an external hard drive?
Individuals opt for external hard drives to expand their storage space beyond the limitations of their computer’s internal drive. This choice is practical for backing up important files and transferring data from one computer to another.
What can you store on an external hard drive?
You can store virtually any digital content on an external hard drive, including documents, photos, music, videos, and applications. Its purpose spans from file backup to serving as a library for large media collections.
What are the advantages of using an external hard drive?
External hard drives offer portability, rendering them convenient for transporting data. They also provide additional storage capacity and a simple method for creating system backups.
Can an external hard drive be used to run a computer?
An external hard drive cannot replace the internal drive to run a computer’s operating system as its primary role. However, technicians sometimes use them to troubleshoot issues, perform diagnostics, or run alternative operating systems without internal drive installation.
What should you not do with an external hard drive?
It is essential not to expose an external hard drive to harsh conditions, such as extreme heat, moisture, or physical shocks. Avoid disconnecting the drive while transferring data to prevent data loss or corruption.
How does an external hard drive differ from a flash drive?
While both are portable storage devices, external hard drives generally offer more storage capacity than flash drives. Flash drives are smaller, have no moving parts, which makes them more durable, but are typically slower in data transfer speed compared to external hard drives that use traditional spinning disks or SSD technology.